好的,我现在需要帮用户总结一篇文章,控制在100字以内。首先,我得仔细阅读文章内容,抓住主要信息。 文章讲的是一个持续了11年的GNU InetUtils telnetd服务器的严重漏洞,编号是CVE-2026-24061。这个漏洞允许攻击者绕过身份验证,获取root权限。漏洞的原因是telnetd传递未经过滤的环境变量到login程序。受影响的版本从2015年的1.9.3到2.7,已在2.8版本修复。 此外,文章提到虽然Telnet现在不常用,但仍在工业系统中广泛使用,尤其是在嵌入式设备中。研究人员发现有实际的攻击活动利用这个漏洞,尽管目前影响有限,但建议用户升级或采取缓解措施。 接下来,我需要将这些信息浓缩到100字以内。重点包括:漏洞名称、影响范围、攻击方式、受影响系统类型、修复版本以及当前的攻击情况。 可能的结构:漏洞名称+影响+攻击方式+受影响系统+修复建议+当前威胁。 最后检查字数是否符合要求,并确保信息准确无误。 </think> 一个持续11年的严重漏洞(CVE-2026-24061)被发现存在于GNU InetUtils telnetd服务器中,允许攻击者绕过身份验证并获取root权限。该漏洞因未过滤环境变量导致,并影响多个版本的telnetd组件。尽管Telnet已逐渐被SSH取代,但在工业和嵌入式设备中仍广泛使用。研究人员已检测到针对该漏洞的实际攻击活动。建议受影响用户升级至安全版本或采取缓解措施以应对潜在威胁。 2026-1-23 16:30:19 Author: www.bleepingcomputer.com(查看原文) 阅读量:4 收藏
A coordinated campaign has been observed targeting a recently disclosed critical-severity vulnerability that has been present in the GNU InetUtils telnetd server for 11 years.
The security issue is tracked as CVE-2026-24061 and was reported on January 20. It is trivial to leverage and multiple exploit examples are publicly available.
Bug persisted since 2015
Open-source contributor Simon Josefsson explains that the telnetd component of GNU InetUtils contains a remote-authentication bypass vulnerability caused by unsanitized environment variable handling when spawning ‘/usr/bin/login.’
The flaw occurs because telnetd passes the user-controlled USER environment variable directly to login(1) without sanitization. By setting USER to -f root and connecting with the telnet -a command, an attacker can skip authentication and obtain root access.
The issue affects GNU InetUtils versions 1.9.3 (released in 2015) through 2.7, and was patched in version 2.8. For those who cannot upgrade to the safe release, mitigation strategies include disabling the telnetd service or blocking TCP port 23 on all firewalls.
GNU InetUtils is a collection of classic network client and server tools (telnet/telnetd, ftp/ftpd, rsh/rshd, ping, traceroute) maintained by the GNU Project, and used across multiple Linux distributions.
Although Telnet is an insecure, legacy component largely replaced by SSH, many Linux and Unix systems still include it for compatibility or specialized usage needs. It is particularly prevalent in the industrial sector because of its simplicity and low overhead.
On legacy and embedded devices, it can run without updates for more than a decade, explaining its presence in IoT devices, cameras, industrial sensors, and Operational Technology (OT) networks.
Cristian Cornea of Zerotak, a penetration testing and cybersecurity services company, told BleepingComputer that critical systems are difficult to replace in OT/ICS environments.
The researcher said that this is sometimes impossible because upgrades are accompanied by reboot operations. "As a result, we still encounter systems running Telnet servers, and even if you tried to replace them with more secure protocols such as SSH, this is not feasible due to legacy systems that remain in operation."
More technical users still rely on telnet for some projects:
Another user confirmed the use of telnet "to connect to older Cisco devices that are way past “End of Life.” Same SSH issue."
However, devices exposed on the public internet that still have telnet active are scarce, prompting many researchers to describe the CVE-2026-24061 vulnerability as less critical.
Threat monitoring firm GreyNoise reports that it has detected real-world exploitation activity leveraging CVE-2026-24061 against a small number of vulnerable endpoints.
The activity, logged between January 21 and 22, originated from 18 unique attacker IPs across 60 Telnet sessions, all deemed 100% malicious, sending 1,525 packets totaling 101.6 KB.
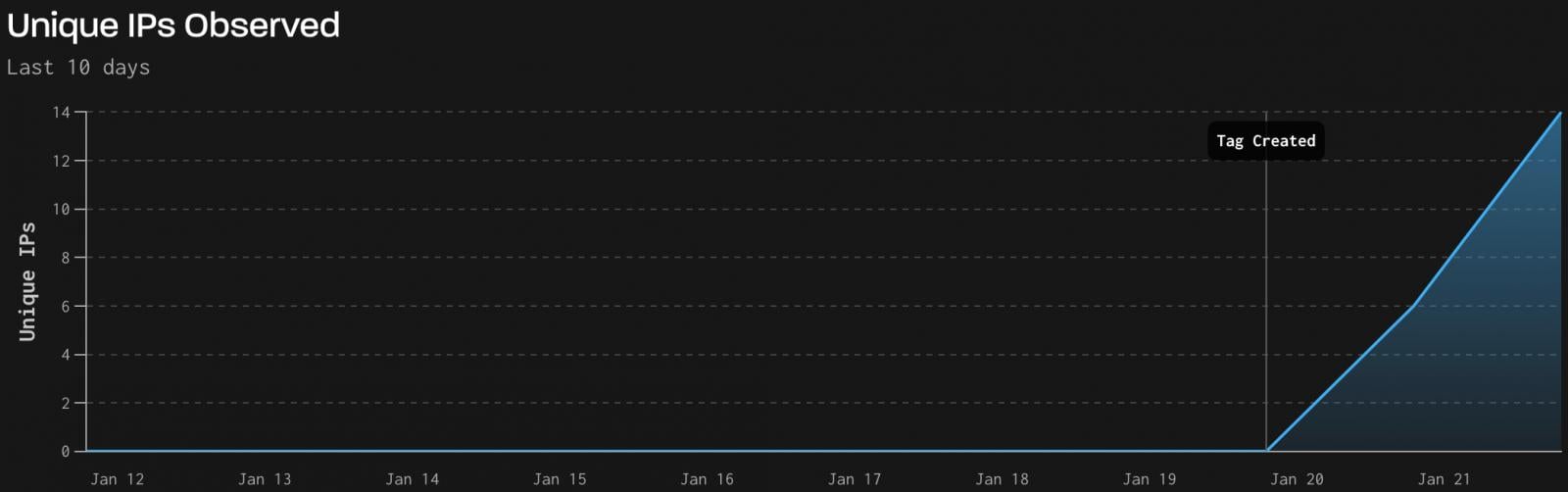
Source: GreyNoise
The attacks abuse the Telnet IAC option negotiation to inject ‘USER=-f <user>’ and grant shell access without authentication. GreyNoise says most of the activity appears automated, although it noted a few “human-at-keyboard” cases.
The attacks varied in terminal speed, type, and X11 DISPLAY values, but in 83.3% of the cases, they targeted the ‘root’ user.
In the post-exploitation phase, the attackers conducted automated reconnaissance and attempted to persist SSH keys and deploy Python malware. GreyNoise reports that these attempts failed on the observed systems due to missing binaries or directories.
While the exploitation activity appears limited in scope and success, potentially impacted systems should be patched or hardened as per the recommendations before the attackers optimize their attack chains.
The 2026 CISO Budget Benchmark
It's budget season! Over 300 CISOs and security leaders have shared how they're planning, spending, and prioritizing for the year ahead. This report compiles their insights, allowing readers to benchmark strategies, identify emerging trends, and compare their priorities as they head into 2026.
Learn how top leaders are turning investment into measurable impact.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh