好的,我现在需要帮用户总结一篇文章的内容,控制在100个字以内。首先,我得仔细阅读文章,抓住关键点。 文章讲的是一个名为SharkStealer的恶意软件,用Golang编写,利用区块链技术建立隐蔽的命令控制通道。它使用BNB智能链测试网作为死信存储器,这种方法让传统的检测机制难以发现。 接下来,文章提到SharkStealer使用了EtherHiding技术,将感染链的关键部分存储在公共区块链上,而不是传统的服务器。这样区块链网络变成了抗审查的基础设施,防御者很难破坏或监控。 然后,攻击向量利用了区块链的透明和可用性,并通过加密来保持操作安全。恶意软件通过发送Ethereum RPC请求到特定的智能合约节点来获取加密数据。合约返回包含初始化向量和加密负载的数据包,恶意软件使用内置的AES-CFB密钥进行解密,得到实际的C2服务器地址。 技术分析部分详细描述了感染机制的过程:连接到BSC测试网的RPC端点,构造JSON-RPC请求,查询特定合约地址并执行函数获取加密数据。解密过程结合了硬编码密钥和动态获取的IV。 最后,分析样本显示C2服务器仍然活跃,证明了该技术的有效性。 总结的时候要突出几个关键点:恶意软件名称、使用的技术(Golang、区块链)、C2机制的特点(抗审查、利用智能合约)、以及其带来的威胁。控制在100字以内,直接描述内容。 </think> 一种基于Golang的信息窃取恶意软件SharkStealer利用区块链技术建立隐蔽的命令控制通道。该恶意软件采用BNB智能链测试网作为抗审查基础设施,并通过智能合约存储加密数据以规避传统检测机制。其创新技术EtherHiding将关键组件存储于公共区块链中,并结合AES-CFB加密实现C2通信。 2025-10-24 06:57:49 Author: cybersecuritynews.com(查看原文) 阅读量:0 收藏
A sophisticated information-stealing malware written in Golang has emerged, leveraging blockchain technology to establish covert command-and-control channels.
SharkStealer represents a significant evolution in malware design, utilizing the BNB Smart Chain Testnet as a resilient dead-drop resolver for its C2 infrastructure.
This novel approach demonstrates how threat actors exploit Web3 technologies to evade traditional detection mechanisms and maintain persistent communication channels.
The malware employs an innovative technique known as EtherHiding, where critical infection chain components are stored on public blockchains rather than conventional web servers.
This method transforms immutable blockchain networks into censorship-resistant infrastructure that defenders struggle to disrupt or monitor effectively.
By embedding C2 addresses within smart contract responses, SharkStealer creates a distributed communication layer that remains operational even when traditional domains or IP addresses are blocked.
SharkStealer’s attack vector centers on leveraging the transparency and availability of public blockchain networks while maintaining operational security through encryption.
VMRay analysts identified that the malware issues Ethereum RPC eth_call requests to specific smart contracts deployed on the BSC Testnet nodes.
These contracts serve as encrypted data repositories, returning tuples containing an initialization vector (IV) and encrypted payload when queried.
The malware then decrypts this data using a hardcoded AES-CFB key embedded within the binary, ultimately extracting the actual C2 server addresses.
Technical Analysis of C2 Resolution
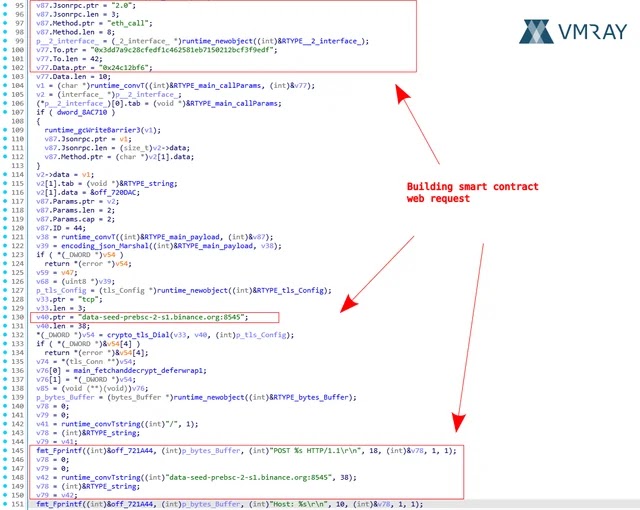
The infection mechanism operates through a multi-stage process that begins with establishing a secure connection to data-seed-prebsc-2-s1.binance.org:8545, the BSC Testnet RPC endpoint.
The code snippet below illustrates how SharkStealer constructs the JSON-RPC request:-
v87.Jsonrpc.ptr = "2.0";
v87.Method.ptr = "eth_call";
v77.To.ptr = "0x3dd7a9c28cfedf1c462581eb7150212bcf3f9edf";
v77.Data.ptr = "0x24c12bf6";.webp)
The malware’s C2 resolution mechanism demonstrates sophisticated engineering combining blockchain interaction with traditional cryptographic techniques.
Once the eth_call request reaches target smart contract addresses—specifically 0xc2c25784E78AeE4C2Cb16d40358632Ed27eeaF8E and 0x3dd7a9c28cfedf1c462581eb7150212bcf3f9edf—the contracts execute function 0x24c12bf6, returning encrypted C2 data.
The decryption process utilizes AES-CFB mode, combining the hardcoded key with the dynamically retrieved IV to decrypt the payload.
Analysis of sample SHA-256 hash 3d54cbbab911d09ecaec19acb292e476b0073d14e227d79919740511109d9274 revealed active C2 servers at 84.54.44.48 and securemetricsapi.live, demonstrating the technique’s operational effectiveness.
Follow us on Google News, LinkedIn, and X to Get More Instant Updates, Set CSN as a Preferred Source in Google.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
