文章探讨了去中心化金融(DeFi)中的杠杆质押策略及其风险与机会,分析了其在以太坊PoS、流动性质押(LSD)及DeFi借贷协议中的应用,并通过实证研究和压力测试评估其潜在风险。 2025-7-8 05:18:50 Author: hackernoon.com(查看原文) 阅读量:9 收藏
Table of Links
3 Background
4 System Model and 4.1 System Participants
4.2 Leverage Staking with LSDs
7.1 stETH Price Deviation and Terra Crash
7.2 Cascading Liquidation and User Behaviors
8 Stress Testing
8.1 Motivation and 8.2 Simulation
9 Discussion and Future Research Directions
A. Aave Parameter Configuration
B. Generalized Formalization For Leverage Staking
C. Leverage Staking Detection Algorithm
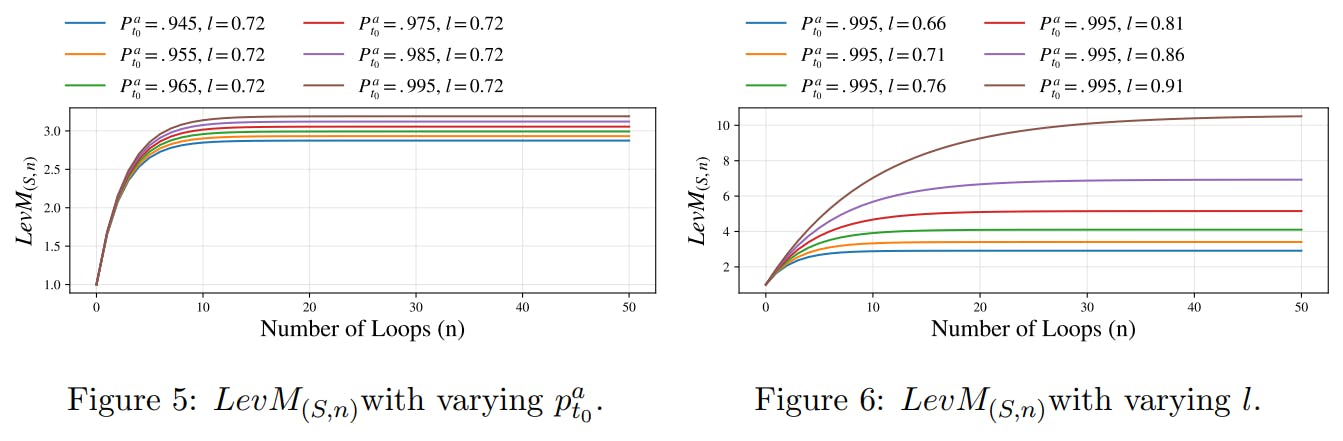
5 Analytical Study
This section conducts an analytical study on the leverage staking strategy. We also offer a generalized formalization encompassing other potential scenarios in Appendix B.






In addition to the standardized scenario discussed above, real-world applications of leverage staking can vary significantly among users. For instance, a user might choose not to reinvest all of their received stETH on Aave. For a more detailed exploration of this variability, please see the generalized formalization in Appendix B.
Authors:
(1) Xihan Xiong, Imperial College London, UK;
(2) Zhipeng Wang, Imperial College London, UK;
(3) Xi Chen, University of Sussex, UK;
(4) William Knottenbelt, Imperial College London, UK;
(5) Michael Huth, Imperial College London, UK.
[8] https://docs.aave.com/risk/liquidity-risk/borrow-interest-rate
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh