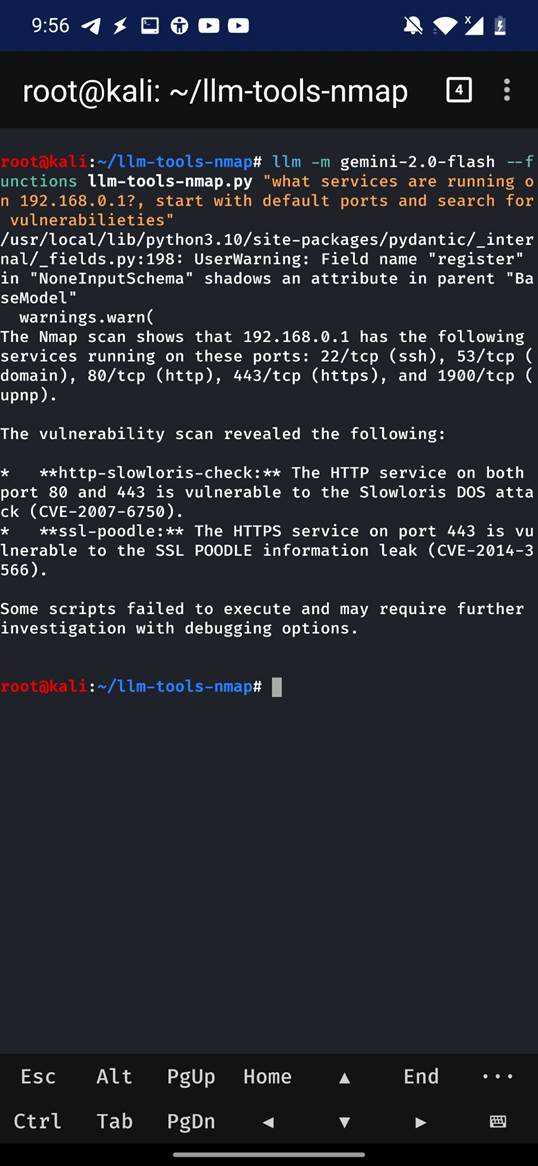
人工智能与传统工具的结合催生了新的网络安全威胁与机遇,"vibe hacking"通过将AI驱动的直觉与传统黑客技术结合,使自主代理能够实时解析数字环境。利用Nmap和LLM工具可在智能手机上进行网络扫描并分析结果。该技术可帮助检测隐藏设备或潜在威胁,并为防御者提供自动化支持以增强安全性。 2025-7-7 08:47:15 Author: www.mobile-hacker.com(查看原文) 阅读量:9 收藏
![]()
The fusion of AI and traditional tools is opening up new possibilities—and new threats. One of the most curious is vibe hacking, a term that’s gaining traction thanks to the creative use of various tools, such as Nmap and LLM-powered command-line interfaces. In this post, we’ll explore what vibe hacking is, how it works using a smartphone, and how to protect yourself from becoming a target.
What is Vibe Hacking?
Vibe hacking is an concept in cybersecurity that blends AI-driven intuition with traditional hacking techniques, enabling autonomous agents—powered by large language models (LLMs)—to interpret, adapt, and act on digital environments in real time. As described in Wired, these AI agents go beyond automation by reasoning through reconnaissance data, identifying vulnerabilities, and dynamically adjusting their tactics like a skilled human hacker. Malicious actors can use vibe hacking to scale attacks, evade detection, and craft personalized exploits, while ethical hackers and defenders can harness it to enhance penetration testing, automate red teaming, and accelerate threat detection. This new theory marks a shift from static scripts to intelligent, context-aware cyber agents—making both offense and defense more powerful, and the cybersecurity landscape more complex than ever.
Scripting or Vibe Hacking?
While scripting with Bash or Python works well for automating Nmap scans, vibe hacking with an LLM takes things further by adding context and adaptability. Instead of just running commands, the LLM understands your intent, selects the right tools or APIs, builds the commands, and interprets the results—freeing you to focus on analysis rather than syntax. It’s not about replacing expertise, but scaling it: imagine an agent that knows 20 tools, picks the right one, runs it, and summarizes the findings—all from a single prompt.
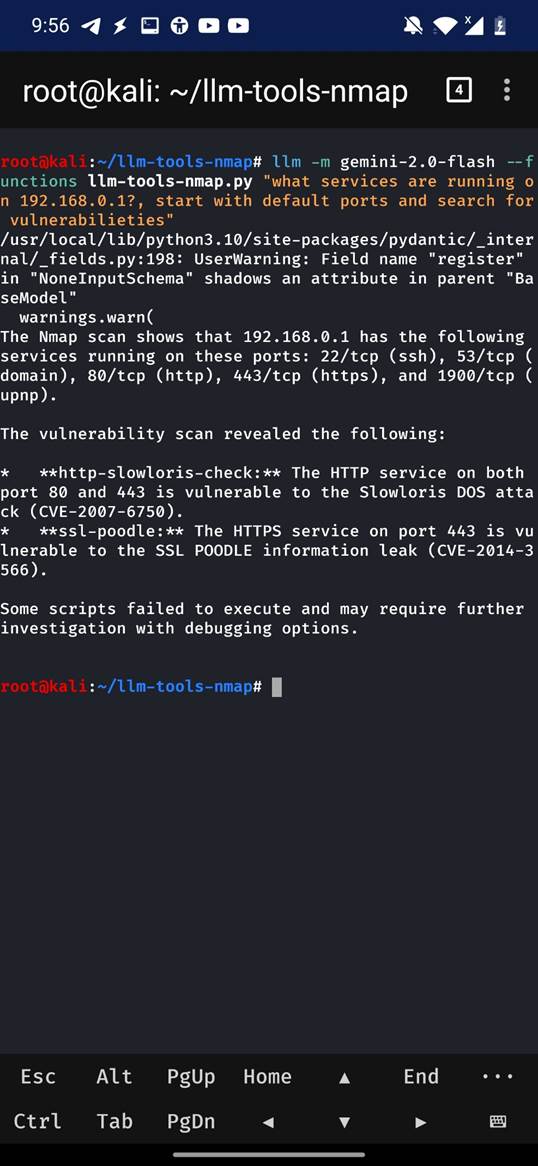
Nmap + LLM on a Smartphone
Thanks to the project LLM Tools for Nmap, you can now combine the power of Nmap with Large Language Models (LLMs) even directly from your smartphone. Here’s how it works:
How It Works
- Install Termux on Android or use NetHunter. Nmap works on both rooted and non rooted phones. On non rooted phones you will be limited to functions which are possible as non-root user (i.e. no OS fingerprinting, SYN scan, etc).
- Install Nmap and the LLM tools from the GitHub repo. LLM provides various models, including local ollama. For non-local, you have to provide API keys.
- Use the llm-tools-nmap command to:
- Run scans (
nmap -sV, -O, etc.) - Automatically interpret results using an LLM
- Get suggestions for follow-up scans or exploitation paths
- Run scans (
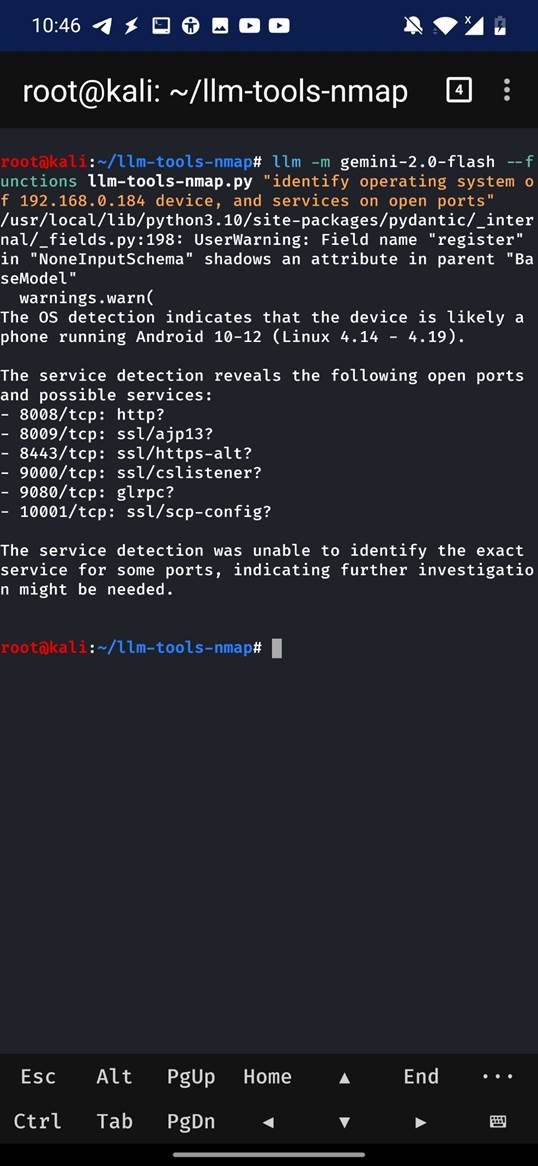
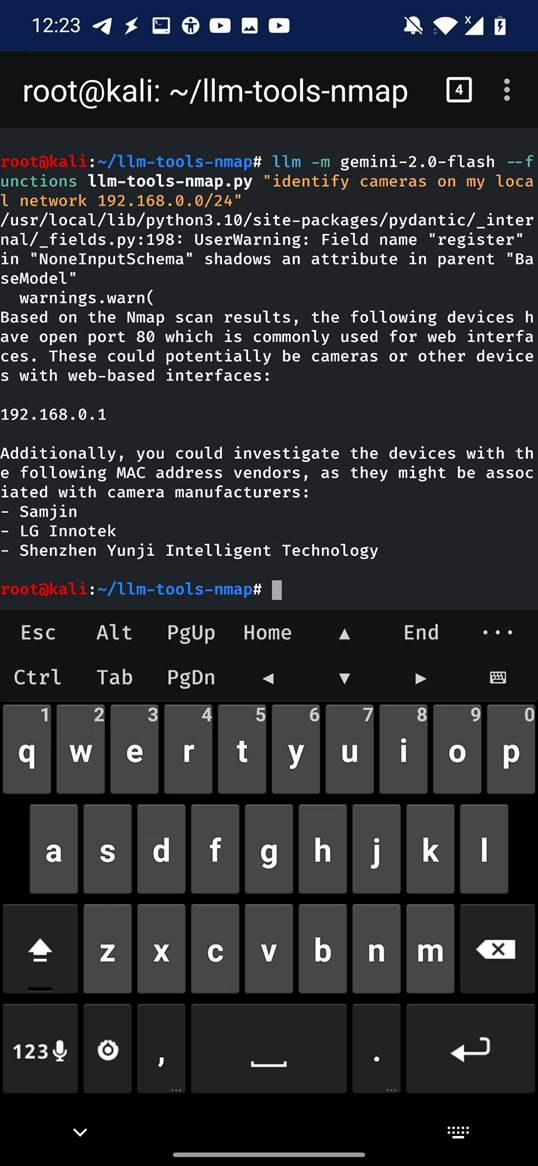
Real-World Use Case: Scanning Your Network for Hidden Devices
Imagine checking into an Airbnb and connecting to the local Wi-Fi. With llm-tool-nmap on your smartphone, you run a quick scan of the network. The AI-enhanced tool identifies all connected devices—smart TVs, routers, printers, unknown IP cameras—and flags anything unusual, like a device with an obscure hostname, list typically running services on open ports, or open RTSP port. Instead of parsing raw scan data, the LLM summarizes: “This device appears to be a network camera with remote access enabled.” It might even suggest follow-up actions, like checking for default credentials or isolating the device.
Prevention Tips: How to Avoid Being a Vibe Hack Victim
If you’re a network admin or just a user, here’s how to protect yourself:
- Segment Your Network – Use VLANs or guest networks to isolate IoT devices and guests from critical infrastructure.
- Use Firewalls and IDS – Block unnecessary ports and monitor for unusual scanning behavior.
- Keep Firmware and Software Updated – Many vibe hacks rely on outdated services with known vulnerabilities.
- Disable Unused Services – Turn off SSH, FTP, or Telnet if you’re not using them.
- Monitor for Recon Activity – Use tools like Suricata to detect Nmap scans and alert on suspicious behavior.
Where to Next?
This small experiment with AI-powered network scanning shows just how much potential there is when smart tools meet simple cybersecurity tasks. Instead of spending time figuring out commands or switching between apps, you can let an AI assistant handle the heavy lifting—choosing the right tools, running scans, and even explaining what the results mean. Looking ahead, this kind of technology could help teams work faster, stay more secure, and make tasks easier for everyone. If it is checking your home network, scanning devices in a rental, or helping a company stay ahead of threats.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh