安全研究人员发现Ulefone和Krüger&Matz安卓手机预装应用中的多个关键漏洞,包括允许第三方应用执行工厂重置、窃取PIN码和注入系统级intent的权限。这些漏洞源于组件未正确导出,可能导致数据泄露和设备操控风险。 2025-6-2 09:32:6 Author: www.mobile-hacker.com(查看原文) 阅读量:35 收藏
![]()
Security researchers have uncovered several critical vulnerabilities in applications preloaded on Ulefone and Krüger&Matz Android smartphones. These flaws, reported by CERT Polska, expose users to significant risks, including potential data theft and device manipulation by malicious applications. In specific, third party app installed on the same device could by misusing these vulnerabilities without authentication perform factory reset of device, exfiltrate PIN code and inject an arbitrary intent with system-level privileges.
The Vulnerabilities Explained
Here’s a breakdown of the three specific vulnerabilities:
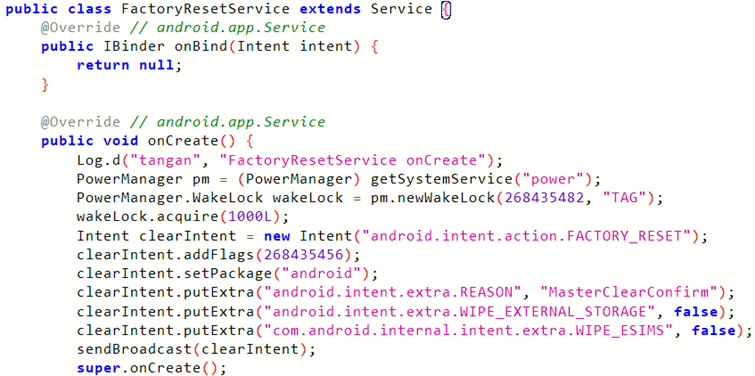
CVE-2024-13915: Factory Reset Service Exposure
- This vulnerability affects the
com.pri.factorytestapplication, which is preloaded on Android smartphones from vendors like Ulefone and Krüger&Matz during the manufacturing process. - The vulnerable application, specifically version 1.0, exposes a service called
com.pri.factorytest.emmc.FactoryResetService.

- This improperly exposed service allows any other application installed on the device to perform a factory reset.
- Updates to the application did not change the APK version but were bundled in later OS builds (after December 2024 for Ulefone and likely after March 2025 for Krüger&Matz).
CVE-2024-13916: AppLock PIN Exfiltration
- This issue resides in the
com.pri.applockapplication, preloaded on Krüger&Matz smartphones, which is designed to encrypt other applications using a PIN or biometric data. - The vulnerability lies in an exposed content provider,
com.android.providers.settings.fingerprint.PriFpShareProvider.

- A public method of this content provider,
query(), allows any other malicious application, without needing any specific Android system permissions, to exfiltrate (steal) the user’s PIN code.

query() method - This directly impacts the confidentiality of sensitive information (the PIN).
- The vendor did not provide information on all vulnerable versions; testing confirmed that version 13 (version code 33) is vulnerable.
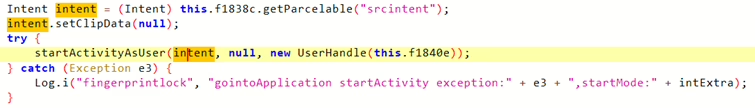
CVE-2024-13917: AppLock Activity Intent Injection
- Also affecting the
com.pri.applockapplication on Krüger&Matz smartphones, this vulnerability involves an exposed activity calledcom.pri.applock.LockUI.

- This vulnerability allows any other malicious application, also with no granted Android system permissions, to inject an arbitrary intent with system-level privileges into an application protected by AppLock.
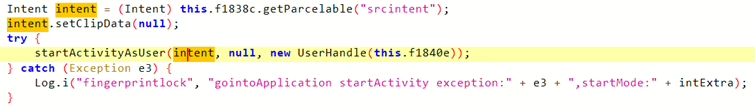
- To fully exploit this, the malicious application would need to know the protecting PIN number (which could potentially be revealed by exploiting CVE-2024-13916) or trick the user into providing it.
- Exploiting an exposed activity can allow malicious apps to gain access to sensitive information, modify the application’s internal state, or trick the user.
- Similar to CVE-2024-13916, the vendor did not provide information on all vulnerable versions; version 13 (version code 33) was confirmed to be vulnerable.
Understanding CWE-926: Improper Export of Android Application Components
Two vulnerabilities described above are relate to CWE-926: Improper Export of Android Application Components. This is a weakness where an Android application exports a component (Activity, Service, or Content Provider) for use by other applications but fails to properly restrict which applications can launch that component or access the data it contains.
There are three main types of Android components that can be improperly exported:
- Activity: Provides a user interface. If improperly exported, any app can launch it, potentially exposing sensitive information or allowing malicious interaction.
- Service: Runs operations in the background without a UI. If improperly exported, any app can start or bind to it, potentially performing unauthorized actions or corrupting internal state.
- Content Provider: Mechanism for sharing data within the app or with other apps. If improperly exported, malicious apps can read or modify sensitive data. In Android versions before 4.2, Content Providers were automatically exported unless explicitly marked otherwise.
A simple example of exploitation involves an Activity or Service that is intended for internal use or trusted partners but has an intent-filter defined in the AndroidManifest.xml and does not explicitly set android:exported="false". By default, the presence of an intent-filter automatically exports the component. A malicious application could then simply create an Intent matching this filter and launch the exported Activity or start the Service, gaining access to functionality or data it shouldn’t have. Similarly, if a Content Provider is not restricted, another app could use a ContentResolver to query, insert, update, or delete data within that provider, reading or modifying sensitive information.
Other Publicly Disclosed Issues Based on CWE-926
Here are some publicly disclosed security issues related to Improper Export of Android Application Components, which occurs when Android app components (like Activities, Services, or Content Providers) are exported without proper access restrictions:
Imou Life (CVE-2023-42470)
Description: The com.mm.android.easy4ip.MainActivity activity within the com.mm.android.smartlifeiot app blindly loads URLs provided through intent data. A malicious third-party app can exploit this oversight to trigger the loading of malicious web content, initiating unauthorized JavaScript web browser mining operations or remote code execution within the WebView.
Impact: An attacker can exploit this vulnerability to:
- Execute arbitrary JavaScript within the app’s context, leading to remote code execution.
- Start unauthorized web browser mining operations, consuming device resources and potentially earning cryptocurrency for the attacker.
- Access the internet from a victim’s device without necessary permissions in the malicious app’s manifest.
PoC: Analysis
Samsung Mobile (CVE-2025-20975)
Description: Improper Export of Android Application Components in AODService prior to version 8.8.28.12 allows local attackers to launch arbitrary activity with systemui privilege.
Android Agent on Kiosk (CVE-2023-41960)
Issue: The vulnerability allows an unprivileged (untrusted) third-party application to interact with a content-provider unsafely exposed by the Android Agent application, potentially modifying sensitive settings of the Android Client application itself.
Description: The Advantech TPC-110W HMI is designed to be controlled remotely. This capability is implemented with a specific Android application named Android Agent (package name com.adv.client), preinstalled on the operating system. This application runs with high privileges, to allow a remote administrator to perform specific operations on the device such as enabling the debug interface or remote login through VNC and installing or removing applications.
Source: Bosch Rexroth ctrlX HMI WR21 Browser-based HMI Affected by Multiple Security Flaws
PrinterShare Android (CVE-2025-5098)
Description: PrinterShare Android application (com.dynamixsoftware.printershare) allows the capture of Gmail authentication tokens that can be reused to access a user’s Gmail account without proper authorization.
Source: Mobile Dynamix PrinterShare Mobile Print Gmail Oauth Token Disclosure
Samsung Mobile (CVE-2024-20860)
Description: Improper export of android application components vulnerability in TelephonyUI prior to SMR May-2024 Release 1 allows local attackers to reboot the device without proper permission.
BLU View 2 and Sharp Rouvo V (CVE-2023-38290)
Description: Certain software builds for the BLU View 2 and Sharp Rouvo V Android devices include a pre-installed app (com.evenwell.fqc) that is vulnerable due to improper access control. The app exposes exported components that can be triggered by any third-party app without requiring special permissions or user interaction.
Impact: This allows attackers to:
- Grant arbitrary permissions
- Install apps silently
- Record the screen
- Wipe the device
- Inject input events
- Call emergency numbers
- Disable apps
- Access notifications
Source: Still Vulnerable Out of the Box: Revisiting the Security of Prepaid Android Carrier Devices
Conclusion for Developers
To protect applications from CWE-926 vulnerabilities like those found in Ulefone and Krüger&Matz devices, developers should focus on reducing the attack surface. Key mitigation strategies during the Build and Compilation or Architecture and Design phases include:
- Explicitly mark components as not exported: For components not intended for use by other applications, developers should explicitly set android:exported=”false” in the application’s manifest. This is a critical step to prevent unintended access.
- Use signature-based restrictions: If components must be shared, but only among related applications under the developer’s control, use android:protectionLevel=”signature” in the manifest XML. This restricts access to only applications signed with the same certificate.
- Limit Content Provider permissions: For Content Providers that are exported, carefully limit read and write permissions as appropriate.
By following these practices, developers can prevent unauthorized access to their application components and protect user data from malicious applications.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh