Cyble分析了26个漏洞及14个暗网利用声明,其中10个高危漏洞影响Fortinet设备、WordPress插件等。研究人员发现多个零日攻击及恶意技术,建议企业加强补丁管理、网络分段及安全监控,以应对日益复杂的网络安全威胁。 2025-4-21 12:46:9 Author: cyble.com(查看原文) 阅读量:21 收藏
Overview
Cyble’s vulnerability intelligence unit examined 26 vulnerabilities and 14 dark web exploit claims in recent reports to clients and flagged 10 of the vulnerabilities as meriting high-priority attention by security teams.
The vulnerabilities, which can lead to system compromise and data breaches, affect Fortinet products, WordPress plugins, Linux and Android systems, and more.
The Top IT Vulnerabilities
Here are some of the vulnerabilities highlighted by Cyble vulnerability intelligence researchers in recent reports.
CVE-2022-42475, CVE-2023-27997, and CVE-2024-21762 are critical vulnerabilities in Fortinet FortiGate devices that have been actively exploited to gain unauthorized remote access. CVE-2022-42475 is a heap-based buffer overflow vulnerability in the SSL-VPN component that allows remote code execution, while the other two enable initial access and privilege escalation.
Recently, Fortinet revealed that attackers exploited these vulnerabilities to gain initial access and then used a novel post-exploitation technique to maintain persistent read-only access even after patches were applied. This technique involves creating a symbolic link (symlink) in the SSL-VPN language files folder that connects the user file system to the root file system, allowing attackers to evade detection and continue accessing device configurations.
CVE-2024-48887 is a critical unverified password change vulnerability in the Fortinet FortiSwitch GUI that could allow a remote, unauthenticated attacker to change administrator passwords without prior access by sending specially crafted HTTP requests to the set_password endpoint, which lacks proper input validation and authentication checks. This could enable the attacker to gain administrative privileges on the vulnerable FortiSwitch device, potentially allowing them to manipulate configurations or move laterally within internal networks.
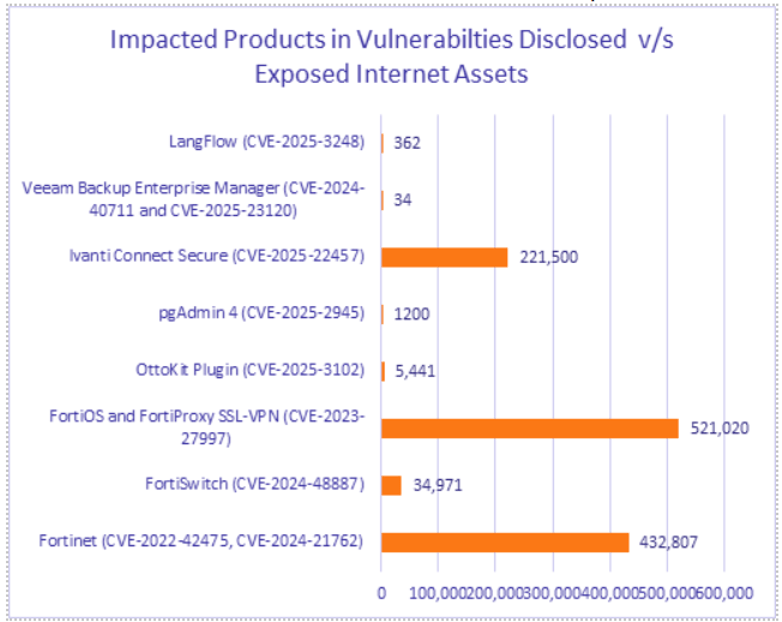
Cyble’s ODIN vulnerability search tool has identified nearly 1 million potentially exposed Fortinet instances:

CVE-2025-3102 is a critical authentication bypass vulnerability in the SureTriggers: All-in-One Automation Platform plugin for WordPress, affecting versions up to and including 1.0.78. The flaw could allow unauthenticated attackers to create administrator accounts on websites where the plugin is installed and activated but not configured with an API key. The issue arises due to a missing empty value check on the ‘secret_key’ parameter in the plugin’s authentication function, potentially enabling attackers to bypass authentication by sending an empty authorization header.
CVE-2024-53197 is a vulnerability in the Linux kernel’s ALSA USB audio driver. It affects systems using USB audio devices, particularly Extigy and Mbox devices. The vulnerability involves potential out-of-bounds memory access that could occur when a malicious USB device provides an invalid bNumConfigurations value, potentially leading to system crashes or privilege escalation if an attacker has physical access to the system. Serbian authorities reportedly exploited the flaw to unlock confiscated Android devices as part of a zero-day exploit chain.
CVE-2025-31334 is a vulnerability affecting WinRAR, a popular file archiver utility for Windows, that could allow attackers to bypass the Windows “Mark of the Web” (MotW) security feature. This feature is designed to flag files downloaded from the internet as potentially unsafe and prompt users with a warning before executing them. Attackers could craft a malicious archive containing a symbolic link (symlink) pointing to an executable file. When opened using a vulnerable version of WinRAR, the MotW warning is bypassed, allowing the executable to run without user confirmation.
CVE-2025-30065 is a critical remote code execution (RCE) vulnerability in the Apache Parquet Java library, specifically affecting the parquet-avro module. Attackers could potentially create a malicious Parquet file that allows them to execute arbitrary code when imported into a vulnerable system. This typically requires social engineering tactics to convince users to open the malicious file. The vulnerability has a maximum CVSS score of 10.0, indicating high severity and ease of exploitation.
Vulnerabilities and Exploits on Underground Forums
Cyble researchers also observed multiple threat actors on dark web forums discussing exploits and weaponizing different vulnerabilities, including some claimed zero-day vulnerabilities. Some of the vulnerabilities under discussion include:
- CVE-2025-23120: A critical vulnerability in Veeam Backup & Replication that could allow an authenticated, remote attacker with valid domain privileges to execute code on the target system.
- CVE-2025-24071: A high-severity vulnerability in Microsoft Windows File Explorer that could allow unauthorized attackers to steal NTLM hashes without user interaction by exploiting the automatic processing of .library-ms files within RAR/ZIP archives. When such a file containing a malicious SMB path is extracted, Windows Explorer triggers an SMB authentication request, leading to the disclosure of the user’s NTLM hash.
- CVE-2025-22457: A critical stack-based buffer overflow vulnerability affecting multiple Ivanti products, including Ivanti Connect Secure, Policy Secure, and ZTA Gateways, that could allow remote, unauthenticated attackers to execute arbitrary code on vulnerable devices, leading to remote code execution (RCE).
- CVE-2025-2005: A vulnerability affecting the Front-End Users plugin for WordPress that allows unauthenticated arbitrary file uploads, which attackers could exploit to upload malicious files, potentially leading to code execution or other security breaches on affected websites.
Cyble Recommendations
To protect against vulnerabilities and exploits, Cyble recommends that organizations implement the following best practices:
- Regularly update all software and hardware systems with the latest patches from official vendors.
- Develop a comprehensive patch management strategy that includes inventory management, patch assessment, testing, deployment, and verification. Automate the process where possible to ensure consistency and efficiency.
- Divide your network into distinct segments to isolate critical assets from less secure areas. Use firewalls, VLANs, and access controls to limit access and reduce the attack surface exposed to potential threats.
- Create and maintain an incident response plan that outlines procedures for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security incidents, including ransomware-resistant backups. Regularly test and update the plan to ensure its effectiveness and alignment with current threats.
- Implement comprehensive monitoring and logging solutions to detect and analyze suspicious activities. Use SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems to aggregate and correlate logs for real-time threat detection and response.
- Subscribe to security advisories and alerts from official vendors, CERTs, and other authoritative sources. Regularly review and assess the impact of these alerts on your systems and take appropriate actions.
- Conduct regular vulnerability assessment and penetration testing (VAPT) exercises to identify and remediate system vulnerabilities. Complement these exercises with periodic security audits to ensure compliance with security policies and standards.
Conclusion
Security teams should prioritize actively exploited vulnerabilities—and those at high risk of exploitation—when determining their patching efforts. They should also consider other indicators of risk, such as web exposure, data, and application sensitivity.
Implementing strong security practices is essential for protecting sensitive data and maintaining system integrity. A comprehensive attack surface management solution like Cyble can monitor for threats, vulnerabilities, and leaks specific to your environment, helping you harden cyber defenses and respond quickly to events before they become bigger incidents.
To access full IT vulnerability and other reports from Cyble, click here.
Disclaimer: This blog is based on our research and the information available at the time of writing. It is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal, financial, or professional advice. While we strive for accuracy, we do not guarantee the completeness or reliability of the content. If any sensitive information has been inadvertently included, please contact us for correction. Cyble is not responsible for any errors, omissions, or decisions made based on this content. Readers should verify findings and seek expert advice where necessary. All trademarks, logos, and third-party content belong to their respective owners and do not imply endorsement or affiliation. All content is presented “as is” without any guarantee that it is free of confidential, proprietary, or otherwise sensitive information. If you believe any portion of this content contains inadvertently shared or sensitive data, please contact us immediately so that we may address and rectify the issue. No Liability for Errors or Omissions Due to the dynamic nature of cyber threat activity, this [blog/report/article] may include partial, outdated, or otherwise incorrect information due to unverified sources, evolving security threats, or human error. We expressly disclaim any liability for errors or omissions or any potential consequences arising from the use, misuse, or reliance on this information.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh