

|
Claude RobitailleCEO and Founder of NearEDGE |
Secrets management remains one of the hardest problems in application security. With over 12.8 million secrets detected in GitHub public repos in 2023, it’s even fair to say hard-coded plaintext credentials are a serious problem!
In this blog post, I'm going to introduce a new way to deliver encrypted secrets anywhere in your infrastructure without having to worry about managing the decryption key, which has been a headache for many sysadmins for too long.
The Challenge of Secure Secret Delivery
Different secret management architectures exist, but ultimately, they all follow the same principle: a secret is provisioned, delivered to the runtime execution environment, and consumed by a legitimate application. The problem is that whether you provision secrets through a Kubernetes secret operator or an SDK, pull them from a vault, or share them via a mounted volume, the secret ends up exposed via an environment variable or a file.
Therefore, this approach has a gap: “What if a container gets compromised, and malware gets the same access to a secret as my legitimate app running in the container?” Once inside your container, a malicious payload can read your secrets in many ways and cause havoc.
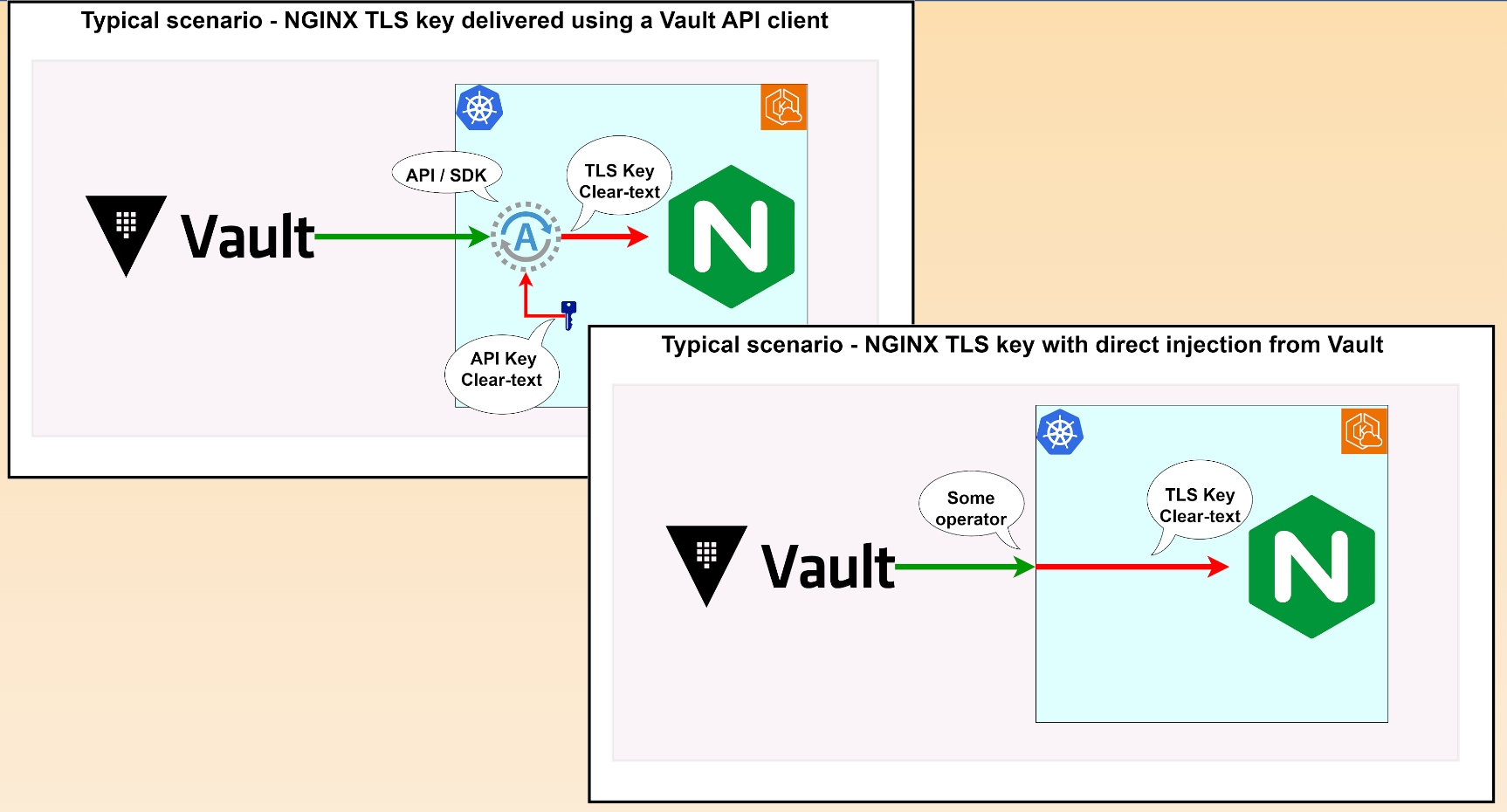
What line of defense can we adopt to mitigate this risk?
A No-Secret Model?
The absolute best secrets security strategy is not using secrets at all. But how can we manage access to resources without secrets? One solution is to rely on infrastructure configuration or tools like Istio to restrict resources a container instance has access to, negating the need for the application to use tokens or other secure identifiers.
Since it's externally managed, a malicious container cannot access it. However, this approach still has a problem: how do you distinguish malware from a legitimate application running on your container fleet?
Most security controls and policies look at container behavior, not what runs inside, meaning they are not able to discriminate malicious calls from legitimate ones. The orchestrator isn’t in control of the runtime inside the containers, either.
The Solution: Shift Right and Extend Protection to the Execution Environment
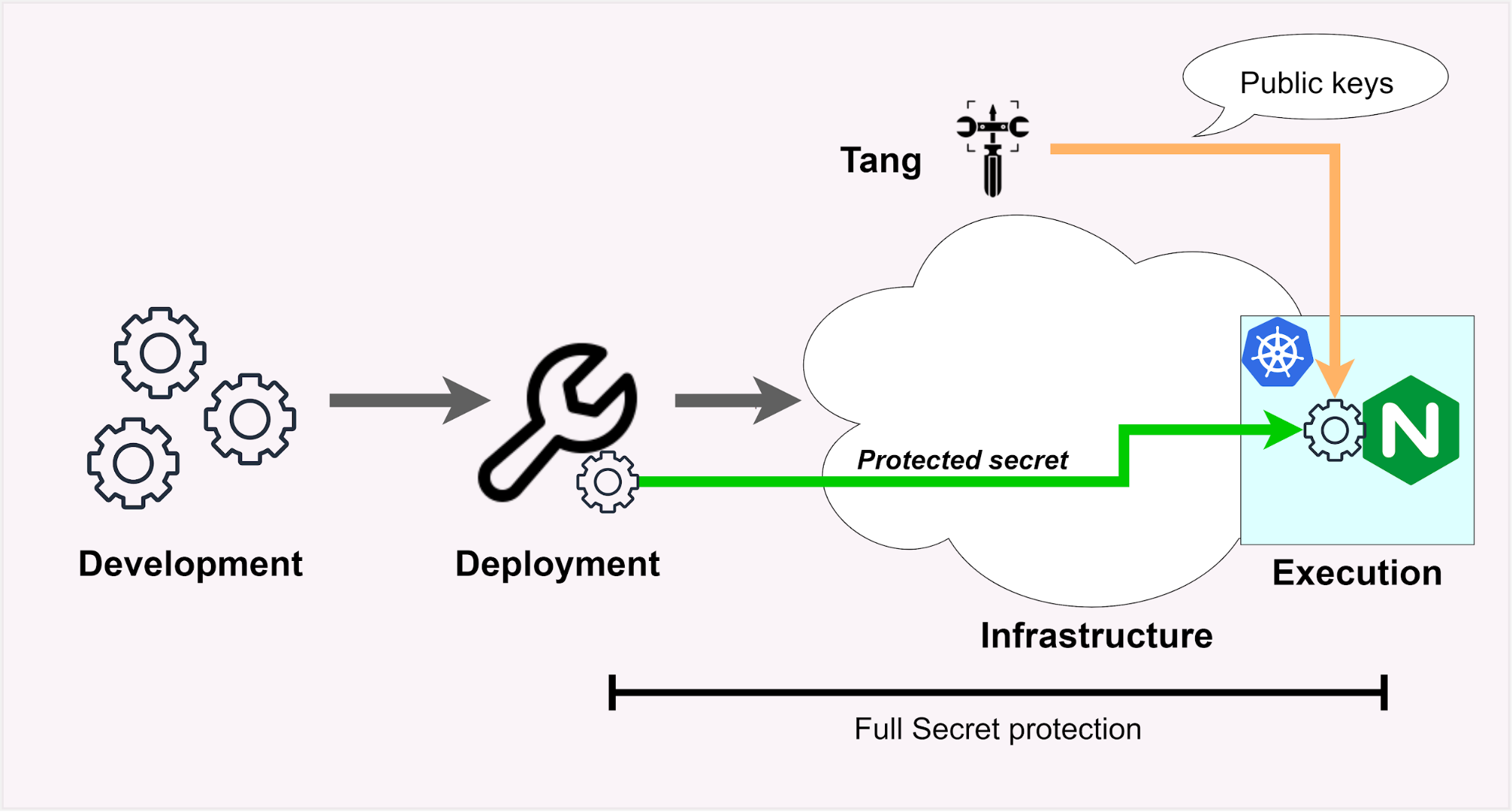
To solve this problem, we need to expand our security model to include the execution environment. This means removing plaintext secrets from files and environment variables. Instead, we deliver secrets directly into the application's memory.
By doing this, you can keep your unsealed secrets hard to reach in memory. You'll only use the filesystem or environment for storing sealed secrets.
This can be implemented by using innovative open-source tools: tang, clevis, and latchy.
tang
Put simply, tangis is a very basic server that makes data available only when the system containing the data is connected to a specific, secure network.
It exposes only 2 endpoints that work like this:
- First, the client gets a list of public keys with a simple
HTTP GETto the/adv("advertise") endpoint to encrypt the data. Since the keys are asymmetric, this is not a sensitive call. - The client then uses one of these keys to generate a unique, cryptographically strong encryption key. The data is then encrypted using this key. Once the data is encrypted, the key is discarded. Yes, you read that right; the unique key used to encrypt the data is destroyed. This is why this protocol is called "no-secret".
- When the client needs to access its data, it simply performs an
HTTP POSTcall (sending a bit of metadata generated during the previous step) to the "recovery" endpoint/recto recover the encryption key.
This process ensures that sensitive information is only accessible when the client is on a secure network.
There are two big advantages compared to key escrow systems, where the encryption key is stored and then retrieved:
- This protocol is stateless: you don't need to manage as many keys as there are client requests, but only two key pairs, which is very convenient in terms of secrets management. This way, you avoid a large swath of infrastructure typically required to secure a key management system: secure backup of keys, use of SSL/TLS everywhere, and comprehensive authentication policy.
- Communication is not sensitive, meaning that you don't need to manage certificates to implement the TLS protocol between
tangand your workloads.
Using tang in production means that we can encrypt all the secrets required by our container fleet immediately after they are generated, and decrypt them on the fly before delivery directly to the application's memory. This way, no files are ever written, and no environment variables are created. The secrets can never be compromised and malware only ever sees encrypted data.
tang can be found on most popular Linux distributions. Docker images are also available on Docker Hub. You can install it via apt on Debian-based distros:
sudo apt install tangAnd run it via systemctl:
sudo systemctl enable tangd.socket --nowThe service listens on port 80; you can alter this by changing the tangd.socket file.
Check that all is up and running with curl:
curl localhost:80/advYou should see a JWS (a signed object) that contains public keys in the form of a JWKSet. See https://github.com/latchset/tang (or man tang) for more information (note that with this systemd service definition, the location for the keys is /var/lib/tang).
clevis
clevis is our encryption tool. It is fully compatible with tang. Secrets are protected by encrypting them and putting the result into a JWE file:
$ echo “Hello World” | clevis encrypt tang '{"url": "http://localhost:80"}' > mysecret.jwe
The advertisement is signed with the following keys:
kWwirxc5PhkFIH0yE28nc-EvjDY
Do you wish to trust the advertisement? [yN] yIn this example, we encrypt the message "Hello World" using the tang pin. The only parameter needed in this case is the URL of the Tang server. During the encryption process, the tang pin requests the key advertisement from the server and asks you to trust the keys. This works similarly to SSH.
💡
Note: it's also possible to work offline by preparing the advertisement from Tang beforehand (a JWS file) and then using it.
latchy
Secrets need to be decrypted to be useful. To do this, the secret value is extracted from the JWE.
While technically, we could use clevis for decryption as well, it comes with some caveats:
- It only tries one attempt at connecting to
tang. You must implement your own retry logic. - The output (decrypted secret) is only available on stdout.
- It is a bash script that requires a shell and depends on
JOSEandcURL. This may make it more difficult to use in containers, particularly the distroless variants.
Enter latchy. It addresses all our concerns out of the box:
- Retry capability.
- Output via named pipes or other suitable means to directly feed a wider range of end applications without creating files or environment variables.
- Fully static binary suitable for all kinds of containers, including lightweight and distroless.
With tang as our key provider, clevis and latchy as our encryption and decryption mechanisms, we can now:
- Store sealed (encrypted) versions of our secrets in our vault or other secrets manager (we can even put them directly in git!)
- Deliver the encrypted secrets to our workload or CI/CD build process, and
- Unseal them at the service or app start using memory-only mechanisms.
By ensuring no secrets are left in clear-text files or environment variables, we are adding a layer of protection to our end-to-end secrets security strategy.
Managing tang Access with NearEDGE Secret Lock
The ultimate trust mechanism in the suggested architecture is controlling access to tang for recovering the private key to unseal the secret: it is crucial at this point that only legitimate clients can recover the key.
There are many ways to implement this control. You can create your own mechanism or use NearEDGE's Secret Lock (NSL).
NSL operates as an API gateway that simply allows or blocks access to the tang /rec API endpoint. (the/adv endpoint is always allowed).
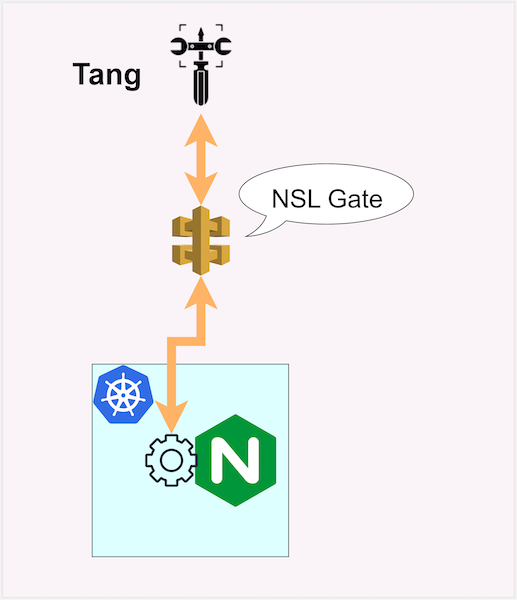
Internally, NSL works with a grant request mechanism, which is processed via a business logic engine that allows you to implement your own custom access control rules to allow workloads to get the private to unseal their secrets.
Ultimately, this solution allows you to use sealed secrets everywhere in your infrastructure, significantly reducing your attack surface linked to exposed secrets and encryption in transit.
To try it, NearEDGE offers hosted tang servers. You can create a perpetual free account at https://nsl.trial.nearedge.io/createprofile
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from GitGuardian Blog - Code Security for the DevOps generation authored by Guest Expert. Read the original post at: https://blog.gitguardian.com/the-runtime-secrets-security-gap/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
