
Executive SummaryOn July 1, 2024, a critical signal handler race condition vulnera 2024-7-3 02:28:47 Author: unit42.paloaltonetworks.com(查看原文) 阅读量:42 收藏
Executive Summary
On July 1, 2024, a critical signal handler race condition vulnerability was disclosed in OpenSSH servers (sshd) on glibc-based Linux systems. This vulnerability, called RegreSSHion and tracked as CVE-2024-6387, can result in unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) with root privileges. This vulnerability has been rated High severity (CVSS 8.1).
This vulnerability impacts the following OpenSSH server versions:
- Open SSH version between 8.5p1-9.8p1
- Open SSH versions earlier than 4.4p1, if they’ve not backport-patched against CVE-2006-5051 or patched against CVE-2008-4109
The SSH features in PAN-OS are not affected by CVE-2024-6387.
Using Palo Alto Networks Xpanse data, we observed 23.0 million instances of OpenSSH servers including all versions. We saw over 7 million exposed instances of OpenSSH versions 8.5p1-9.7p1 globally as of July 1, 2024. Including older versions (4.3p1 and earlier), we see 7.3 million total. However, this is likely to be an overcount of vulnerable versions as there is no reliable way to account for backporting, in which instances are running patched versions but displaying impacted version numbers. These numbers also do not account for OS-level specifications or configurations that could be required for the vulnerability.
While there is PoC code for this vulnerability, there is no known activity in the wild as of July 2, 2024. Our testing of this code suggests it is not functional. We have been unable to successfully exploit the CVE-2024-6387 vulnerability with this PoC to achieve remote code execution.
Palo Alto Networks also recommends updating all OpenSSH instances to the latest version of OpenSSH, later than v9.8p1.
Palo Alto Networks customers receive protections from and mitigations for CVE-2024-6387 in the following ways:
The Unit 42 Incident Response team can also be engaged to help with a compromise or to provide a proactive assessment to lower your risk.
Palo Alto Networks customers are better protected from the malware samples in this article through Cortex XDR and XSIAM. Customers are also better protected through our Next-Generation Firewall with Cloud-Delivered Security Services, including Advanced WildFire. Customers can access external SSH exposure detection from Cortex Xpanse and XSIAM. Customers are also better protected by Prisma Cloud through tooling such as Prisma Cloud’s agent or agentless vulnerability scanning and Software Composition Analysis (SCA) tools, which assist in identifying vulnerable resources across the cloud development lifecycle.
| Vulnerabilities Discussed | CVE-2024-6387 |
Details of the Vulnerability
Researchers at Qualys discovered that the OpenSSH server process sshd is vulnerable to a signal handler race condition, enabling unauthenticated remote code execution with root privileges on glibc-based Linux systems in its default configuration. OpenSSH is an open-source suite of tools for remote sign-in and data transfer, using the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol.
This vulnerability can be exploited remotely on glibc-based Linux systems due to syslog() calling async-signal-unsafe functions like malloc() and free(), leading to unauthenticated remote code execution as root.
This occurs because sshd's privileged code is not sandboxed and runs with full privileges. OpenBSD is not vulnerable because its signal alarm (SIGALRM) handler uses syslog_r(), an async-signal-safe version of syslog().
Table 1 shows the vulnerable versions associated with CVE-2024-6387.
| Version | Vulnerability Determination |
| OpenSSH < 4.4p1 | YES |
| If backport-patched against CVE-2006-5051 and CVE-2008-4109: NO | |
| 4.4p1 <= OpenSSH < 8.5p1 | NO |
| 8.5p1 <= OpenSSH < 9.8p1 | YES |
Table 1. Breakdown of vulnerable OpenSSH versions associated with CVE-2024-6387.
According to OpenSSH’s release notes on July 1, 2024, successful exploitation has been shown on 32-bit Linux/glibc systems with address space layout randomization (ASLR). This exploitation typically requires 6-8 hours of continuous connections under lab conditions up to the server's maximum capacity.
A public PoC for CVE 2024-6387 was committed to the repository of GitHub user zgzhang by user 7etsuo on July 1, 2024. We have been unable to successfully exploit the CVE-2024-6387 vulnerability with this PoC to achieve remote code execution in our testing environment.
Using Palo Alto Networks Xpanse data, we observed 23 million instances of OpenSSH servers including all versions. We saw over 7 million exposed instances of OpenSSH versions 8.5p1-9.7p1 globally as of July 1, 2024. Including older versions (4.3p1 and earlier), we see 7.3 million total. However, this is likely to be an overcount of vulnerable versions as there is no reliable way to account for backporting, in which instances are running patched versions but displaying impacted version numbers. These numbers also do not account for OS-level specifications or configurations that could be required for the vulnerability.
Table 2 shows the geographic distribution of our observations of vulnerable versions 8.5p1-9.7p1.
| Country | Unique IP Addresses |
| United States | 2,173,896 |
| Germany | 905,859 |
| China | 435,490 |
| Singapore | 296,226 |
| Russia | 275,197 |
| The Netherlands | 261,212 |
| France | 248,153 |
| United Kingdom | 237,329 |
| India | 230,320 |
| Japan | 227,663 |
| Korea | 136,852 |
| Canada | 119,924 |
| Finland | 110,516 |
| Hong Kong | 103,685 |
| Australia | 100,780 |
Table 2. Top 15 Countries Exposed to CVE-2024-6387 as of July 1, 2024.
Current Scope of the Attack
While there is PoC code for this vulnerability, there is no known activity in the wild as of July 2, 2024. Our testing of this code suggests it is not functional in our testing environment. We have been unable to successfully exploit the CVE-2024-6387 vulnerability with this PoC to achieve remote code execution.
Interim Guidance
Palo Alto Networks recommends updating all OpenSSH instances to the latest version of OpenSSH, later than v9.8p1.
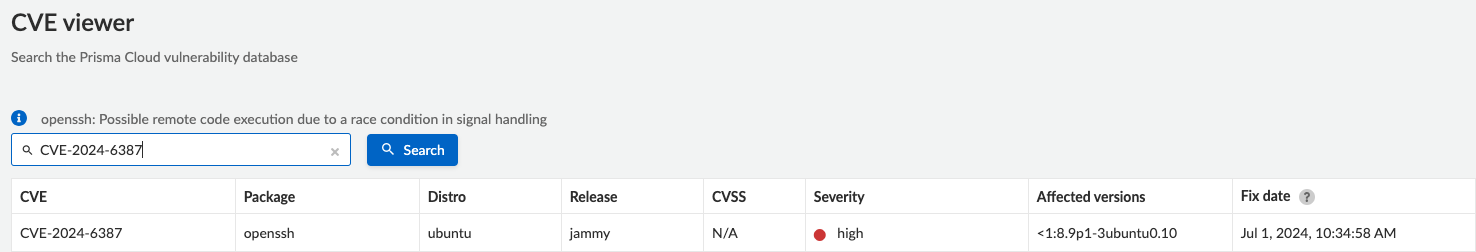
Prisma Cloud detects the presence of any cloud resource that is vulnerable to CVE-2024-6387 as shown in Figure 1, including VM, serverless, container resources and cloud image repositories.
Prisma Cloud customers can query their cloud environments for cloud resources that contain the CVE-2024-6387 vulnerability that are also internet accessible, as shown in Figure 2.
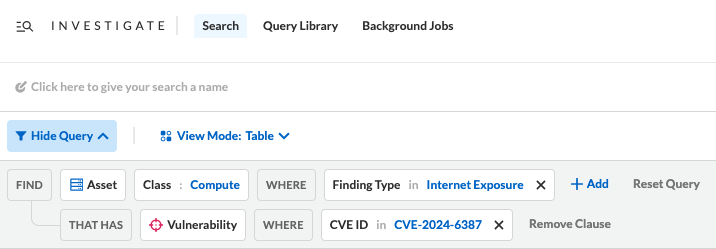
If instances of the RegreSSHion vulnerability are found within cloud resources, they should be updated to the latest version of OpenSSH and an investigation should be started to ensure no malicious connections were established with the vulnerable cloud resources.
Unit 42 Managed Threat Hunting Queries
The Unit 42 Managed Threat Hunting team continues to monitor any developments related to the exploitation of this CVE. Cortex XDR customers can use the XQL query below to identify hosts running an affected version of OpenSSH.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 |
// Query to identify hosts vulnerable to CVE-2024-6387 preset = host_inventory_applications | filter endpoint_type = ENUM.AGENT_TYPE_SERVER | filter lowercase(application_name) ~= "openssh(-server)?" | alter product_major_version = to_number(arrayindex(split(raw_version, "."), 0)), product_minor_version_stage_1 = arrayindex(split(raw_version, "."), 1), product_rev = to_number(arrayindex(split(raw_version, "p"), 1)) | alter product_minor_version = to_number(arrayindex(split(product_minor_version_stage_1, "p"), 0)) // (name:"openssh" and version<4.4) or (name:"openssh" and version<9.8 and version>=8.5) | filter product_major_version < 4 or (product_major_version = 4 and product_minor_version < 4) or (product_major_version = 8 and product_minor_version >= 5) or (product_major_version = 9 and product_minor_version < 8) | fields endpoint_name, application_name, raw_version, product_major_version, product_minor_version, product_rev | dedup endpoint_name |
Conclusion
CVE-2024-6387 (aka RegreSSHion) is a signal handler race condition vulnerability in OpenSSH servers (sshd) on glibc-based Linux systems. This vulnerability is rated High severity (CVSS 8.1), and can result in unauthenticated remote code execution (RCE) with root privileges.
This vulnerability impacts all OpenSSH server versions between 8.5p1-9.8p1, as well as versions earlier than 4.4p1, if they’ve not backport-patched against CVE-2006-5051 or patched against CVE-2008-4109. The SSH features in PAN-OS are not affected by CVE-2024-6387.
While there is PoC code for this vulnerability, there is no known activity in the wild as of July 2, 2024. Our testing of this code suggests it is not functional in our testing environment. We have been unable to successfully exploit the CVE-2024-6387 vulnerability with this PoC to achieve remote code execution.
Palo Alto Networks Product Protections for CVE-2024-6387
Palo Alto Networks customers can leverage a variety of product protections and updates to identify and defend against this threat.
If you think you may have been compromised or have an urgent matter, get in touch with the Unit 42 Incident Response team or call:
- North America Toll-Free: 866.486.4842 (866.4.UNIT42)
- EMEA: +31.20.299.3130
- APAC: +65.6983.8730
- Japan: +81.50.1790.0200
Cortex XDR and XSIAM
Cortex XDR and XSIAM agents have multiple layers of defense protecting our customers from activities that might be performed after exploiting this vulnerability.
Thanks to our multi-layer security approach, we have different capabilities in place to prevent those activities, such as Behavioral Threat Protection (BTP), Advanced WildFire (AWF), Local Analysis (LA) and Reverse Shell Protection.
Cortex Xpanse
Cortex Xpanse has the ability to identify exposed vulnerable OpenSSH devices on the public internet and escalate these findings to defenders. Customers can enable alerting on this risk by ensuring that the Insecure OpenSSHAttack Surface Rule is enabled. Identified findings can either be viewed in the Threat Response Center or in the incident view of Expander. These findings are also available for Cortex XSIAM customers who have purchased the ASM module. Cortex Xpanse and XSIAM also have the ability to automatically mitigate vulnerable exposed OpenSSH servers.
Prisma Cloud
Prisma Cloud has detection capabilities in place for CVE-2024-6387. Prevention capabilities also exist with Prisma Cloud Agent and Agentless vulnerability scanning. Additionally, Prisma Cloud Software Composition Analysis (SCA) can detect vulnerable cloud resources throughout the cloud development lifecycle, including within cloud image repositories.
Additional Resources
- OpenSSH Vulnerability: CVE-2024-6387 FAQs and Resources – Qualys
- CVE-2024-6387 – Ubuntu
- CVE-2024-6387 – CVE.org, The MITRE Corporation
- CVE-2024-6387 Informational Bulletin: Impact of OpenSSH regreSSHion Vulnerability – Palo Alto Networks
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh