2024-6-28 22:14:26 Author: hackernoon.com(查看原文) 阅读量:2 收藏
Author:
(1) David Novoa-Paradela, Universidade da Coruña, CITIC, Campus de Elviña s/n, 15008, A Coruña, Spain & Corresponding author (Email: [email protected]);
(2) Oscar Fontenla-Romero, Universidade da Coruña, CITIC, Campus de Elviña s/n, 15008, A Coruña, Spain (Email: [email protected]);
(3) Bertha Guijarro-Berdiñas, Universidade da Coruña, CITIC, Campus de Elviña s/n, 15008, A Coruña, Spain (Email: [email protected]).
Table of Links
References
[1] B. von Helversen, K. Abramczuk, W. Kopeć, R. Nielek, Influence of consumer reviews on online purchasing decisions in older and younger adults, Decision Support Systems 113 (2018) 1–10. doi:https://doi. org/10.1016/j.dss.2018.05.006.
[2] Amazon targets fake review fraudsters on social media, https://www.aboutamazon.com/news/policy-news-views/ amazon-targets-fake-review-fraudsters-on-social-media.
[3] Tripadvisor review transparency report 2021, https://www. tripadvisor.com/TransparencyReport2021.
[4] V. Chandola, A. Banerjee, V. Kumar, Anomaly detection: A survey, ACM Comput. Surv. 41 (3) (jul 2009). doi:10.1145/1541880.1541882.
[5] A. Chernyavskiy, D. Ilvovsky, P. Nakov, Transformers:“the end of history” for natural language processing?, in: Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Research Track: European Conference, ECML PKDD 2021, Bilbao, Spain, September 13–17, 2021, Proceedings, Part III 21, Springer, 2021, pp. 677–693.
[6] S. Tabinda Kokab, S. Asghar, S. Naz, Transformer-based deep learning models for the sentiment analysis of social media data, Array 14 (2022) 100157. doi:10.1016/j.array.2022.100157.
[7] Y. Kim, S. Bang, J. Sohn, H. Kim, Question answering method for infrastructure damage information retrieval from textual data using bidirectional encoder representations from transformers, Automation in Construction 134 (2022) 104061. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2021. 104061.
[8] Amazon customer reviews dataset, https://nijianmo.github.io/ amazon/index.html.
[9] P. Schneider, F. Xhafa, Chapter 9 - anomaly detection, classification and cep with ml methods: Machine learning pipeline for medicine, in: P. Schneider, F. Xhafa (Eds.), Anomaly Detection and Complex Event Processing over IoT Data Streams, Academic Press, 2022, pp. 193–233. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-823818-9.00020-1.
[10] H. T. Truong, B. P. Ta, Q. A. Le, D. M. Nguyen, C. T. Le, H. X. Nguyen, H. T. Do, H. T. Nguyen, K. P. Tran, Light-weight federated learning-based anomaly detection for time-series data in industrial control systems, Computers in Industry 140 (2022) 103692. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2022.103692.
[11] W. Hilal, S. A. Gadsden, J. Yawney, Financial fraud: A review of anomaly detection techniques and recent advances, Expert Systems with Applications 193 (2022) 116429. doi:10.1016/j.eswa.2021.116429.
[12] T. T. Huong, T. P. Bac, D. M. Long, T. D. Luong, N. M. Dan, L. A. Quang, L. T. Cong, B. D. Thang, K. P. Tran, Detecting cyberattacks using anomaly detection in industrial control systems: A federated learning approach, Computers in Industry 132 (2021) 103509. doi:10.1016/j.compind.2021.103509.
[13] R. Mohawesh, S. Xu, S. N. Tran, R. Ollington, M. Springer, Y. Jararweh, S. Maqsood, Fake reviews detection: A survey, IEEE Access 9 (2021) 65771–65802. doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3075573.
[14] N. Jindal, B. Liu, Opinion spam and analysis, in: Proceedings of the 2008 International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining, WSDM ’08, Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 2008, p. 219–230. doi:10.1145/1341531.1341560.
[15] J. Salminen, C. Kandpal, A. M. Kamel, S. gyo Jung, B. J. Jansen, Creating and detecting fake reviews of online products, Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services 64 (2022) 102771. doi:10.1016/j.jretconser. 2021.102771.
[16] A. Radford, J. Wu, R. Child, D. Luan, D. Amodei, I. Sutskever, et al., Language models are unsupervised multitask learners, OpenAI blog 1 (8) (2019) 9.
[17] Y. Liu, M. Ott, N. Goyal, J. Du, M. Joshi, D. Chen, O. Levy, M. Lewis, L. Zettlemoyer, V. Stoyanov, Roberta: A robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach, CoRR abs/1907.11692 (2019). arXiv:1907.11692.
[18] Şule Öztürk Birim, I. Kazancoglu, S. Kumar Mangla, A. Kahraman, S. Kumar, Y. Kazancoglu, Detecting fake reviews through topic modelling, Journal of Business Research 149 (2022) 884–900. doi:10.1016/ j.jbusres.2022.05.081.
[19] L. Breiman, Random forests, Machine Learning 45 (1) (2001) 5–32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324.
[20] D. Vidanagama, A. Silva, A. Karunananda, Ontology based sentiment analysis for fake review detection, Expert Systems with Applications 206 (2022) 117869.
[21] L. Ruff, Y. Zemlyanskiy, R. Vandermeulen, T. Schnake, M. Kloft, Self-attentive, multi-context one-class classification for unsupervised anomaly detection on text, in: Proceedings of the 57th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Association for Computational Linguistics, Florence, Italy, 2019, pp. 4061–4071. doi: 10.18653/v1/P19-1398.
[22] J. Mu, X. Zhang, Y. Li, J. Guo, Deep neural network for text anomaly detection in siot, Computer Communications 178 (2021) 286–296. doi: 10.1016/j.comcom.2021.08.016.
[23] B. Song, Y. Suh, Narrative texts-based anomaly detection using accident report documents: The case of chemical process safety, Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries 57 (2019) 47–54. doi:10.1016/j. jlp.2018.08.010.
[24] S. Seo, D. Seo, M. Jang, J. Jeong, P. Kang, Unusual customer response identification and visualization based on text mining and anomaly detection, Expert Systems with Applications 144 (2020) 113111. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.113111.
[25] K. Song, X. Tan, T. Qin, J. Lu, T.-Y. Liu, Mpnet: Masked and permuted pre-training for language understanding, in: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS’20, Curran Associates Inc., Red Hook, NY, USA, 2020.
[26] D. Novoa-Paradela, O. Fontenla-Romero, B. Guijarro-Berdiñas, Fast deep autoencoder for federated learning, Pattern Recognition 143 (2023) 109805. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109805. URL https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/ S0031320323005034
[27] T. Mikolov, K. Chen, G. Corrado, J. Dean, Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space (2013). doi:10.48550/ARXIV.1301. 3781.
[28] J. Pennington, R. Socher, C. Manning, GloVe: Global vectors for word representation, in: Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Association for Computational Linguistics, Doha, Qatar, 2014, pp. 1532–1543. doi: 10.3115/v1/D14-1162.
[29] A. Vaswani, N. Shazeer, N. Parmar, J. Uszkoreit, L. Jones, A. N. Gomez, Ł. Kaiser, I. Polosukhin, Attention is all you need, Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017).
[30] J. Devlin, M.-W. Chang, K. Lee, K. Toutanova, Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding (2018). doi: 10.48550/ARXIV.1810.04805.
[31] Z. Yang, Z. Dai, Y. Yang, J. Carbonell, R. R. Salakhutdinov, Q. V. Le, Xlnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding, Advances in neural information processing systems 32 (2019).
[32] T. Brown, B. Mann, N. Ryder, M. Subbiah, J. D. Kaplan, P. Dhariwal, A. Neelakantan, P. Shyam, G. Sastry, A. Askell, et al., Language models are few-shot learners, Advances in neural information processing systems 33 (2020) 1877–1901.
[33] OpenAI, GPT-4 technical report (2023). arXiv:2303.08774.
[34] Hugging face, https://huggingface.co/, accessed: 2023-05-09.
[35] S. S. Khan, M. G. Madden, One-class classification: taxonomy of study and review of techniques, The Knowledge Engineering Review 29 (3) (2014) 345–374.
[36] P. Vincent, H. Larochelle, I. Lajoie, Y. Bengio, P.-A. Manzagol, L. Bottou, Stacked denoising autoencoders: Learning useful representations in a deep network with a local denoising criterion., Journal of machine learning research 11 (12) (2010).
[37] A. Barredo Arrieta, N. Díaz-Rodríguez, J. Del Ser, A. Bennetot, S. Tabik, A. Barbado, S. Garcia, S. Gil-Lopez, D. Molina, R. Benjamins, R. Chatila, F. Herrera, Explainable artificial intelligence (xai): Concepts, taxonomies, opportunities and challenges toward responsible ai, Information Fusion 58 (2020) 82–115. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2019. 12.012.
[38] N.-y. Liang, G.-b. Huang, P. Saratchandran, N. Sundararajan, A fast and accurate online sequential learning algorithm for feedforward networks, IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 17 (6) (2006) 1411–1423. doi:10.1109/TNN.2006.880583.
[39] Y. Wang, J. Wong, A. Miner, Anomaly intrusion detection using one class svm, in: Proceedings from the Fifth Annual IEEE SMC Information Assurance Workshop, 2004., 2004, pp. 358–364. doi:10.1109/IAW. 2004.1437839.
[40] S. M. Lundberg, S.-I. Lee, A unified approach to interpreting model predictions, in: I. Guyon, U. V. Luxburg, S. Bengio, H. Wallach, R. Fergus, S. Vishwanathan, R. Garnett (Eds.), Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vol. 30, Curran Associates, Inc., 2017. URL https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/ file/8a20a8621978632d76c43dfd28b67767-Paper.pdf
[41] P. Hase, M. Bansal, Evaluating explainable AI: Which algorithmic explanations help users predict model behavior?, in: Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Association for Computational Linguistics, Online, 2020, pp. 5540–5552. doi:10.18653/v1/2020.acl-main.491.
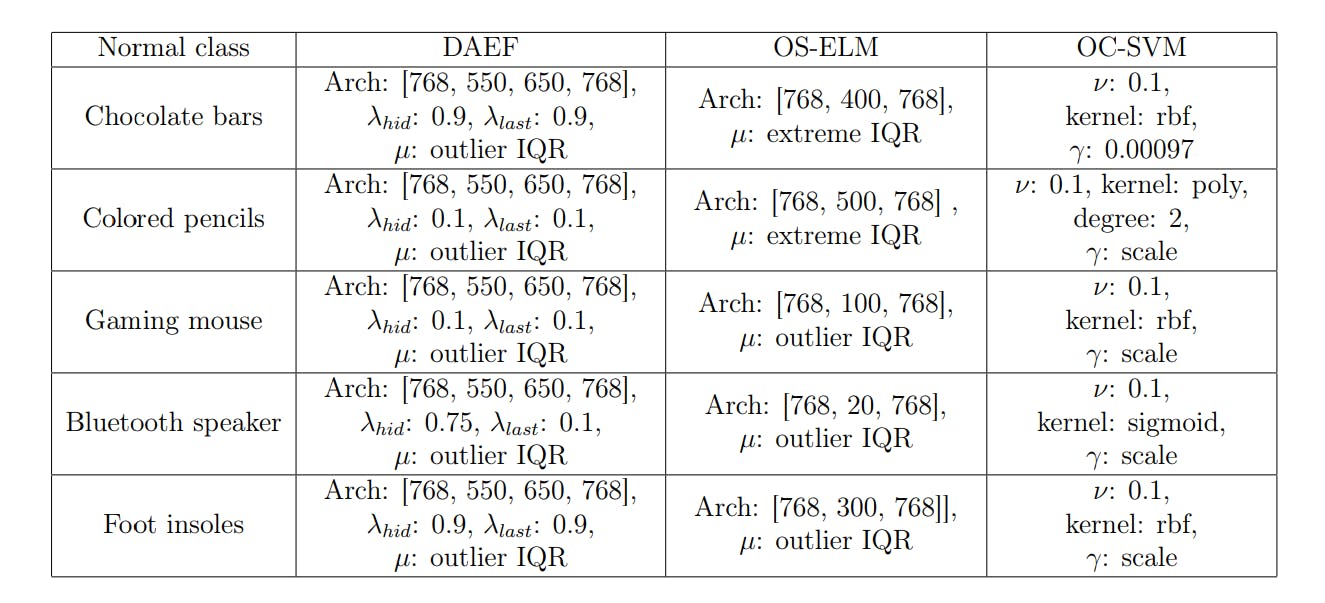
Appendix A. Hyperparameters used during training.
This appendix contains the values of the hyperparameters finally chosen as the best for each method and dataset, listed in Tables A.9 and A.10. DAEF [26], OS-ELM [38], and OC-SVM [39] respectively.
• Deep Autoencoder for Federated learning (DAEF)[26].
– Architecture: Neurons per layer.
– λhid: Regularization hyperparameter of the hidden layer.
– λlast: Regularization hyperparameter of the last layer.
– µ: Anomaly threshold.
• Online Sequential Extreme Learning Machine (OS-ELM)[38]
– Architecture: Neurons per layer.
– µ: Anomaly threshold.
• One-Class Support Vector Machine (OC-SVM)[39].
– An upper bound on the fraction of training errors and a lower bound of the fraction of support vectors (ν).
– Kernel type: Linear, Polynomial or RBF.
– Kernel coefficient γ (in the case of polynomial and RBF kernels).
– Degree (in the case of polynomial kernel).


如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh