
2024-2-13 14:5:47 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:6 收藏
Do you know there are 2.9 million applications on the Google Play Store, which indicates that the Android market is growing quickly? Although there are many benefits and opportunities associated with it, concerns over data security will also grow. The Google Play Store’s tracking, in contrast to the iPhone App Store, will make it more likely that risky apps can be downloaded. Developers must prioritize security due to the prevalence of tasks like banking, shopping, and reservations conducted through mobile apps. They must incorporate robust records safety protocols to guarantee a seamless and secure user experience. While many mobile app developers incorporate advanced data security measures, some overlook less obvious aspects that contribute to data processing. If you’re among them, review the following points to grasp the concept of data leakage and prevent data breaches.
Brief About Mobile App Security
It entails safeguarding mobile apps and digital identities from fraudulent attacks, including tampering, reverse engineering, malware, keyloggers, and manipulation. A strong mobile app security strategy combines technology like app shielding with best usage and corporate practices. Since the industry uses mobile devices on a regular basis, mobile application security has become more and more important. The increasing reliance on mobile devices for banking, shopping, and other activities mirrors the rise in mobile devices, apps, and users.
Book a Free Consultation with our Cyber Security Experts

What Was Wrong With Mobile Apps in Latin America?
In collaboration with SocialTIC, eight heavily used mobile apps underwent extensive analysis. Apps from telco, government, and marketplace categories were selected for their widespread usage and user incentives, such as data rewards. SocialTIC used advanced reverse engineering to uncover security and privacy flaws in critical apps, including cellular connectivity.
The research revealed significant issues across all three threat categories outlined in the analysis. SocialTIC engaged with app developers, issuing two vulnerability disclosures about cleartext HTTP usage and unauthorized data sharing with third-party servers. Findings highlight the urgent need for strong security measures and privacy standards to safeguard user data and ensure app integrity.
How Kratikal Helps in Preventing Such Attacks?
Kratikal being a CERT-In empanelled auditor is committed to securing data through the latest methodologies. We offer manual and automated testing services that address many different types of vulnerabilities, such as problems with login and authorization, data leaks, and malware attacks. The testing methodology combines with black and grey box techniques to locate vulnerabilities that different testing methods would miss. Mobile application security testing is essential to prevent security breaches, data theft, and other vulnerabilities that could harm users.
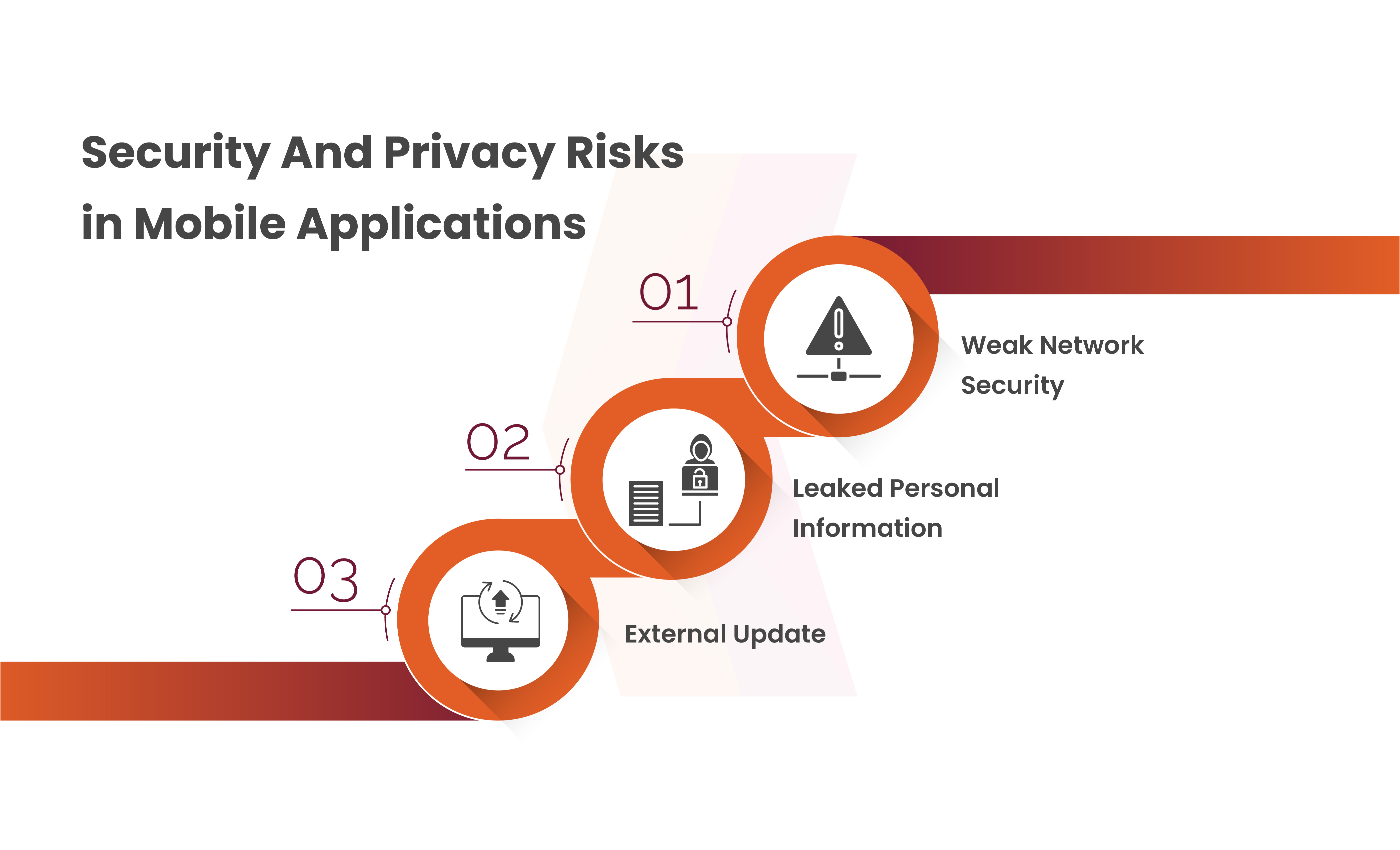
Analysis of Security and Privacy Risks in Mobile Apps
There are 3 primary, security and privacy threats mentioned below which were assessed in mobile apps:
Weak Network Security
The security exposes vulnerabilities that enables a local or in-path adversary to intercept or alter network traffic, potentially influencing the app’s behavior. Vulnerability encompasses the use of unencrypted communication protocols like HTTP for interactions between the app, application servers, and third-party services. This suggests that user’s ISP-managed routers could exploit the security flaw to manipulate app network traffic.
Leaked Personal Information
The second concern was that in each app there was a potential leakage of personally identifiable information (PII). Sensitive data, like phone numbers or emails, sent to non-developer servers can confirm a user’s identity. Many apps utilize various third-party services in the background for functions like payments, analytics, and ad serving. However, these third parties should not receive personal information about individual users unless explicitly stated in the app’s privacy policy, app store description, or user agreement.
During the internal research, it was found that most were leaking login credentials, vulnerable to man in the middle attacks, and exposing their secrets.
(SSL Strip leaking login credential)
External Update
The third risk involves the capability to perform external updates to the APK, bypassing the official channels of the Google Play Store or iOS App Store. Official platform updates undergo rigorous review to ensure security and privacy compliance. If an app can modify its behavior and code without undergoing this verification process, it poses a significant threat to users. For instance, such an app could update to a version that tracks and shares the user’s location without their knowledge. Moreover, an app with this functionality could selectively target specific users with updates, leaving others unaware of the changes made.
Conclusion
The growing percentage of cyber attacks poses an extensive threat to data security and consumer privacy in mobile apps. Through collaborative efforts with groups like SocialTIC, the vulnerabilities in famous mobile apps have been brought to light, emphasizing the crucial need for sturdy security measures. The analysis highlights the importance of prioritizing user trust and data integrity in developing and deploying mobile apps, especially in regions like Latin America. Cybersecurity firms like Kratikal take proactive steps to mitigate cyber attack risks, offering data security solutions to safeguard organizations.
Ref: https://www.opentech.fund/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/ICFP_Beau_Kujath_Final_Report.pdf
The post How Your Mobile Apps Leak Sensitive Data? appeared first on Kratikal Blogs.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Kratikal Blogs authored by Shikha Dhingra. Read the original post at: https://kratikal.com/blog/how-your-mobile-apps-leak-sensitive-data/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh