
2023-11-15 06:38:55 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:2 收藏
In the digital age, data breaches and cyber-attacks are increasingly common. Understanding the cyber security glossary is crucial for small business managers. This knowledge will empower you to communicate effectively with IT personnel. It also enables you to make informed decisions to protect your business assets. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll decode the essential cybersecurity terms that will help you navigate the complexities of cyber threats and defenses. Thus, ensuring your business’s digital safety.
Understanding Cyber Threats: The Foundation of Cyber Security
Grasping the nature of cyber threats is the first step toward robust cybersecurity. Small businesses are often targets due to the perception of weaker defenses. This section will illuminate the common threats that lurk in the digital shadows. Helping to prevent their goal to compromise your business’s integrity and security.
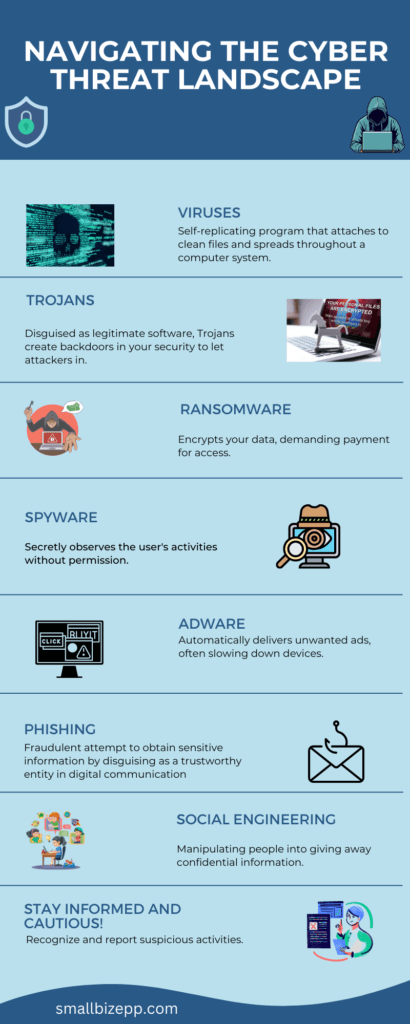
The Menace of Malware: From Viruses to Worms
Malware is a term that’s an amalgamation of ‘malicious software’. It is an umbrella term for any software intentionally designed to cause damage to a computer, server, client, or network. Let’s break down the types:
- Viruses: These are malicious programs that, when executed, replicate themselves by modifying other computer programs and inserting their own code.
- Worms: Similar to viruses, worms replicate across networks but operate independently without needing to attach to a program.
Understanding these terms is pivotal as they form the basis of many cyber attacks.
Phishing and Social Engineering: The Human Factor
Beyond the software-based threats, phishing and social engineering represent the psychological side of cyber threats. They exploit human error and social manipulation to gain unauthorized access to valuable information.
- Phishing: A technique of fraudulently obtaining private information by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication.
- Social Engineering: The art of manipulating people so they give up confidential information. This can include anything from passwords to bank information.
Recognizing these tactics is essential for small business managers to train their teams in identifying and avoiding such deceptive maneuvers.
Building Your Cyber Defense: Tools and Techniques
With an understanding of the threats, it’s time to construct your digital fortress. This section explores the essential cybersecurity tools and techniques that fortify your business against cyber onslaughts.
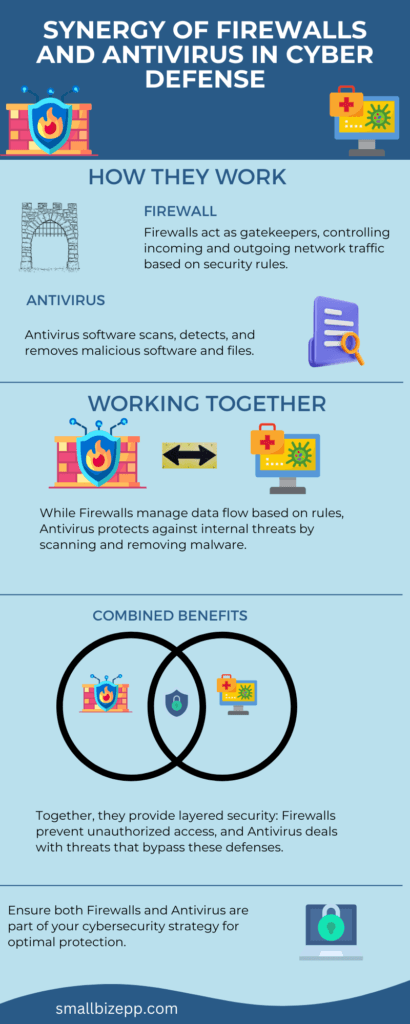
Firewalls and Antivirus: Your First Line of Defense
Firewalls act as gatekeepers for your network. They control incoming and outgoing traffic based on security rules. On the other hand, antivirus software scans, detects, and removes malicious software.
- Firewalls: These network security devices monitor and filter incoming and outgoing network traffic. They achieve this goal based on an organization’s previously established security policies.
- Antivirus Software: Programs designed to detect and eradicate malware from computers, smartphones, and other devices.
Both are critical in creating a defensive barrier against cyber threats.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention: Keeping Watch
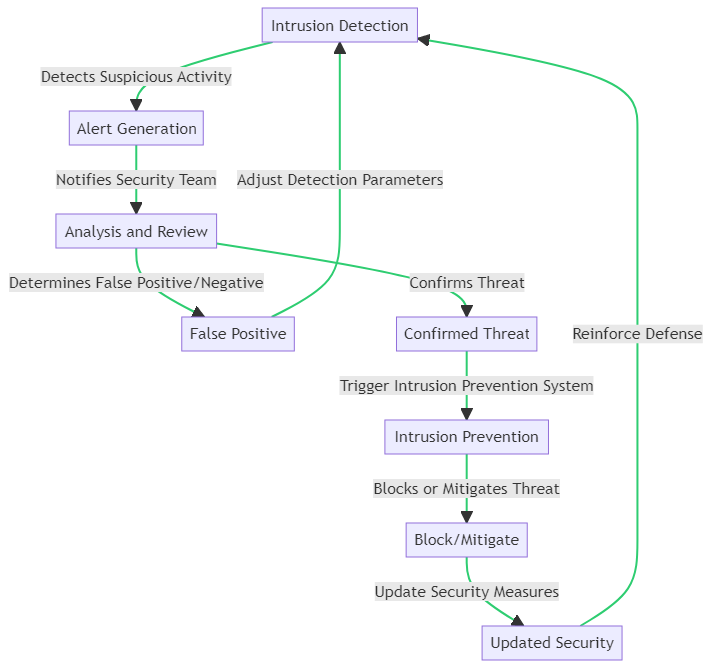
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are the watchtowers and guards. They work together to detect potential threats and taking action to prevent a breach.
- Intrusion Detection System (IDS): These systems monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and issue alerts when such activity is discovered.
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS): They go a step further beyond just detecting threats. They also taking preventive action to block the traffic from reaching the network.
Incorporating these systems ensures that you’re not just aware of potential threats but are also prepared to stop them in their tracks.
The process of intrusion detection and prevention is a critical component of any robust cyber defense strategy. It begins with Intrusion Detection, where systems monitor network traffic and activities for signs of suspicious behavior. Upon detecting potential threats, the system generates Alerts to notify the security team.
These alerts undergo Analysis and Review to determine whether they are false positives or confirm a genuine threat. If an alert is deemed a false positive, the detection parameters are adjusted to refine the system’s accuracy. However, if a real threat is confirmed, it triggers the Intrusion Prevention System.
The Intrusion Prevention System then takes action to Block or Mitigate the Threat, effectively neutralizing the risk to the network. Following this, Security Measures are Updated to reinforce defenses against similar future threats, thereby completing the cycle and enhancing the overall security posture.
Data Protection: Safeguarding Your Business’s Lifeline
Data is the lifeblood of any small business in the digital realm. Protecting this vital asset is not just a technical necessity but a business imperative. This section delves into the strategies and technologies that ensure your data remains confidential, integral, and available.
The Role of Encryption in Data Security
Encryption is the process of converting information or data into a code, especially to prevent unauthorized access. It’s the equivalent of a secret language that only those with the ‘key’ can understand.
- Data Encryption: This refers to the method of using algorithms to transform readable data into a secured form, which can only be reverted to its original form with the correct decryption key.
By encrypting data, you ensure that even if it falls into the wrong hands, it remains unreadable and secure.
The Blueprint of Cyber Security Management
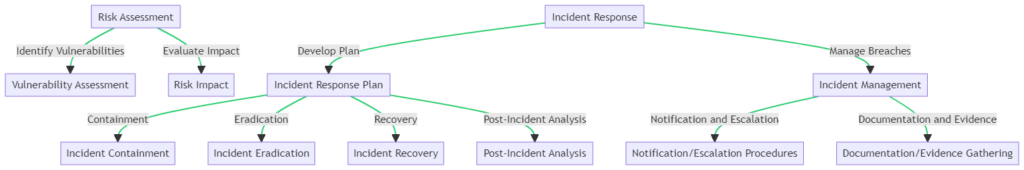
Effective cybersecurity management is a blueprint for safeguarding your digital assets. It’s about establishing a framework that encompasses policies, tools, and procedures to manage the cyber defense lifecycle.
An effective cybersecurity management strategy is akin to a well-drawn map; it guides you through the terrain of digital threats and safeguards. At the heart of this strategy lies a thorough Risk Assessment, where potential vulnerabilities are identified and their impact evaluated. This proactive approach is crucial in fortifying your defenses against cyber threats.
When an incident occurs, a well-prepared Incident Response Plan is activated, encompassing containment, eradication, and recovery processes, followed by a detailed post-incident analysis. This plan is supported by robust Incident Management procedures that ensure proper notification, escalation, and documentation are in place.
The accompanying flowchart visualizes these interconnected processes, providing a clear path from risk assessment to incident resolution.
Risk Assessment: Identifying Your Vulnerabilities
Risk Assessment is a systematic process of evaluating the potential risks that may be involved in a projected activity or undertaking. In cybersecurity, this means identifying the various vulnerabilities in your systems and the potential impact of different cyber threats.
- Vulnerability Assessment: This involves the identification and quantification of security vulnerabilities in a company’s environment.
A thorough risk assessment is the cornerstone of any solid cybersecurity strategy, as it informs the security measures you put in place.
Incident Response: When Breaches Happen
Incident Response is a plan for dealing with intrusions, cyber-theft, data breaches, and other security incidents. A well-structured incident response plan can be the difference between a minor disruption and a major crisis.
- Incident Management: This refers to the organization’s overarching process for managing security incidents and breaches.
Understanding and preparing for incident response ensures that your business can quickly recover from any security event, minimizing damage and restoring operations as swiftly as possible.
Authentication and Access: The Gatekeepers of Cyber Security
In the realm of cybersecurity, ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to your business’s data is paramount. This section will guide you through the concepts of authentication and access control, which are critical in verifying user identities and maintaining data integrity.
Biometrics and Digital Certificates: Beyond Passwords
Moving beyond traditional passwords, biometrics and digital certificates provide a more secure and user-friendly way to authenticate users.
- Biometrics: Utilizes unique physical characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, to verify identity.
- Digital Certificates: Acts as a digital passport to establish credentials when doing business or other transactions on the web.
These advanced authentication methods are becoming the standard due to their enhanced security features.
he Digital Battleground: Network and Internet Security
The network is the backbone of your business’s digital presence, and securing it is a battle against ever-evolving threats. This section focuses on the strategies and tools that protect your network and internet connections, which are vital for the safe operation of your business online.
VPNs and Cloud Security: Protecting Data in Transit
In the fight to secure data on the move, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and cloud security measures are your allies.
- VPNs: Create a secure tunnel between your device and the internet, encrypting data as it travels to ensure privacy and prevent interception.
- Cloud Security: Encompasses a set of policies, controls, and technologies that work together to protect cloud-based systems and data.
These technologies are essential for maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of your data as it traverses the digital expanse.
Proactive Measures: Software and Application Security
Taking proactive steps in software and application security is crucial for thwarting attacks before they can exploit vulnerabilities. This section will outline the proactive defenses that small business managers can implement to enhance their cybersecurity posture.
Secure Coding Practices: The First Line of Software Defense
Secure coding is the practice of writing software with security in mind, aiming to prevent vulnerabilities at the source.
- Code Review: A systematic examination of computer source code intended to find and fix mistakes overlooked in the initial development phase, improving both the overall quality of software and the developers’ skills.
Application Security Testing: Uncovering Hidden Weaknesses
Application security testing involves the processes used to find, fix, and prevent security vulnerabilities in applications.
- Static Application Security Testing (SAST): A set of technologies designed to analyze application source code, byte code, and binaries for coding and design conditions that are indicative of security vulnerabilities.
- Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): Techniques that are used to detect conditions indicative of a security vulnerability in an application in its running state.
Patch Management: Keeping Software Up to Date
Patch management is the process of distributing and applying updates to software. These patches are often necessary to correct errors (known as “bugs”) in the software.
- Automated Patching Tools: Software that helps automate the process of updating software with patches to ensure that programs are up-to-date and secure from known vulnerabilities.
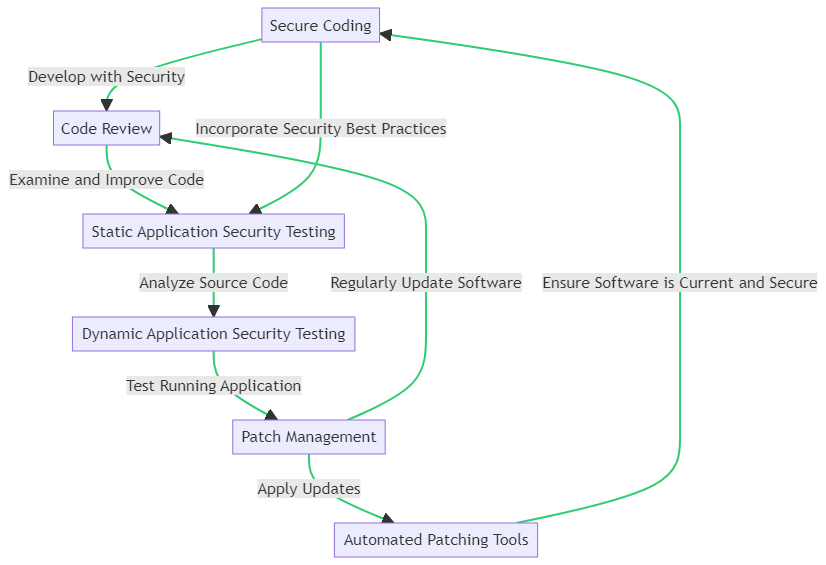
Proactive measures in software and application security form a multi-layered defense strategy. It begins with Secure Coding, where developers are mindful of security risks during the coding process. This is followed by a Code Review, a crucial step where peers examine the code for potential security issues.
Next, Static Application Security Testing (SAST) analyzes the source code for known vulnerabilities, while Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) assesses the application in its running state, identifying real-time security flaws.
The cycle is completed with Patch Management, where software updates are applied to address identified security issues. Automated Patching Tools can streamline this process, ensuring that applications remain up-to-date and protected against known threats.
This flowchart visualizes the interconnected steps of a comprehensive software security strategy, highlighting the importance of each phase in maintaining the integrity and security of software applications.
Cyber Security Intelligence: Staying Ahead of Threats
In the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats, staying informed is as crucial as having strong defenses. This section will cover how cyber security intelligence acts as a radar system, detecting threats before they can cause harm.
Threat Intelligence Platforms: The Informants of Cyber Security
Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs) are sophisticated systems that gather, analyze, and disseminate information about emerging or existing threat actors and threats.
- Threat Feeds: These provide real-time information about threats, often derived from global sources and security communities.
- Threat Analysis: Involves the evaluation of threat data to understand the potential impact on your business.
Security Information and Event Management: The Central Hub
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems provide a holistic view of an organization’s information security.
- Log Management: The SIEM’s log management capabilities are essential for tracking and analyzing security events.
- Event Correlation: This feature allows SIEM systems to link related records and identify potential security incidents.
Graphic suggestion: An infographic that illustrates how Threat Intelligence Platforms gather data, analyze threats, and feed this information into SIEM systems for event correlation and incident response.
Fostering a Culture of Security Within Your Organization
Creating a security-conscious culture is not just about implementing technology; it’s about shaping behavior and mindset. This section will discuss how to instill a sense of responsibility for cybersecurity in every team member.
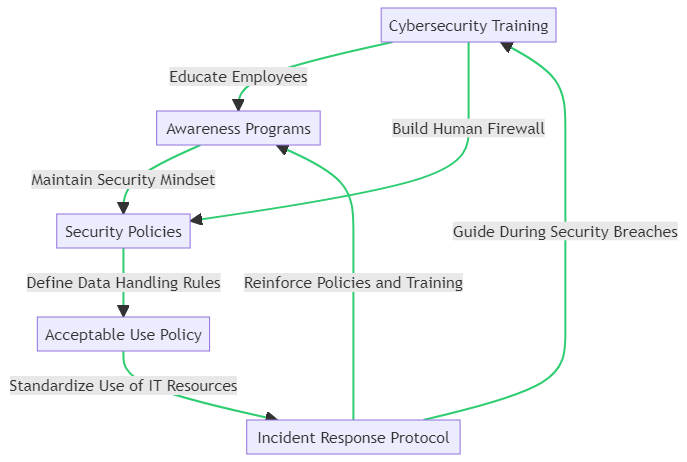
To foster a culture of security, the cycle begins with Cybersecurity Training, where employees are educated on the latest security practices and threats. This knowledge is reinforced through ongoing Awareness Programs, which keep security top of mind and encourage vigilant behavior.
The foundation of this culture is laid by comprehensive Security Policies, which provide clear guidelines on data protection and IT resource usage. These policies are crystallized into everyday practice through the Acceptable Use Policy, ensuring that all team members understand and adhere to the organization’s security standards.
In the event of a security incident, the Incident Response Protocol offers a predefined action plan, enabling a swift and effective response. This protocol not only guides staff during breaches but also serves to reinforce the importance of the training and policies previously established.
The accompanying diagram illustrates this cyclical process, highlighting how each component contributes to building a resilient human firewall and a robust culture of security within the organization.
Training and Awareness: The Human Firewall
Cybersecurity Training: Regular training sessions can significantly reduce the risk of breaches by educating employees on the importance of security and the role they play in maintaining it.
- Awareness Programs: These are designed to keep security at the forefront of employees’ minds, helping them to recognize and respond to threats effectively.
Policies and Protocols: The Rulebook of Cybersecurity
Security Policies: Clearly defined policies are the rulebook that governs how data should be handled and protected within the organization.
- Acceptable Use Policy: This outlines the standards for employee use of the provided Internet and IT equipment.
- Incident Response Protocol: A set of instructions that guide staff on what to do in the event of a security breach.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Business Through Knowledge
In the digital age, where cyber threats loom large, solidifying your cybersecurity stance is not just a technical necessity but a business imperative. Throughout this post, we’ve navigated the complex landscape of cybersecurity, from understanding threats to implementing robust defenses, and fostering a culture of security awareness.
Small business managers and IT personnel must recognize that cybersecurity is a continuous journey, not a one-time fix. By staying informed, adopting proactive measures, and cultivating a vigilant workforce, businesses can not only defend against cyber threats but also build a reputation for reliability and trustworthiness.
Remember, a strong cybersecurity strategy integrates technology, processes, and people. It’s about creating a resilient framework that adapts to new threats while supporting business growth and innovation.
As you move forward, keep these principles in mind, and revisit them often. Cybersecurity is an evolving challenge, but with the right approach, it’s one that can be met with confidence and competence.
The post Cyber Security Glossary: Terms Every Small Business Manager Must Know appeared first on Endpoint Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Endpoint Security authored by Michael Toback. Read the original post at: https://smallbizepp.com/cyber-security-glossary/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=cyber-security-glossary
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
