2023-10-3 01:0:0 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:14 收藏
Introduction
Endpoint security is a critical component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, especially for small businesses. It focuses on safeguarding various endpoints in a network from potential cyber threats. Endpoints include devices such as laptops, smartphones, and other connected devices. Endpoint security solutions come with a range of features designed to protect your business, including antispam, antimalware, and antivirus capabilities. It’s tempting to invest in the most advanced solutions. However, it’s crucial to perform a cost-benefit analysis to ensure you’re optimizing your security investments. This ensures that you’re not only secure but also budget conscious.
Why Hardened Secure Endpoint is Crucial: Prevent Attacks
It’s crucial to stay updated on the evolving threats and trends in cybersecurity. Our latest infographic provides a comprehensive overview of the most pressing issues you should be aware of:
- Endpoint Attacks: Our infographic highlights the increasing vulnerabilities in endpoint devices. These are often the weakest links in a security chain and are prime targets for cybercriminals.
- Data Breach Costs: The financial repercussions of data breaches are escalating. According to our infographic, the global average cost of a data breach in 2023 has risen to $4.45 million. This marks a 15% increase over the past three years.
- Rising Incidents: The infographic also sheds light on the growing number of cyber incidents. This includes supply chain attacks, which have seen a significant uptick recently.
- Email Attacks: Phishing and other email-based attacks remain a persistent threat. Our infographic offers actionable insights on how incident responders can identify indicators. These indicators can be used to prevent these attacks from impacting an entire organization.
By understanding these key areas, you’ll be better equipped to protect your organization and respond effectively to cybersecurity challenges. For a more detailed look, refer to our full infographic.

Why Endpoint Hardening is Crucial: Layered Security

Endpoint hardening is a foundational element of cybersecurity, but it shouldn’t be your only line of defense. In today’s complex and ever-evolving threat landscape, a multi-layered approach known as “Defense in Depth” is essential for robust protection.
The Limitations of Endpoint Hardening Alone
While endpoint hardening fortifies your devices against common vulnerabilities, it’s not foolproof. Cybercriminals are continually developing new methods to bypass these defenses. That’s where the concept of Defense in Depth comes into play.
Introducing Defense in Depth
As illustrated in the graphic, Defense in Depth involves multiple layers of security controls and measures. Each layer serves as a backup for the others. This ensures that even if one fails, the subsequent layers remain intact to thwart potential breaches.
- Network Security: This is the first line of defense. Firewalls and intrusion detection systems monitor and control the incoming and outgoing network traffic based on an organization’s security policies.
- Data Encryption: Should your network security fail, encrypted data serves as a second layer. Doing so renders the information useless to unauthorized users.
- Behavioral Analytics: This layer monitors user behavior to identify abnormal patterns, which could signify a security threat.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra verification step to prove the user’s identity. This makes it harder for attackers to gain access.
- Regular Audits: Regular security audits help you identify and fix vulnerabilities, ensuring all other layers are effective.
For a more in-depth look at each layer refer to our previous post on Defense in Depth: A Layered Approach.
The Synergy of Endpoint Hardening and Defense in Depth
When combined with endpoint hardening, Defense in Depth provides a comprehensive security strategy. Endpoint hardening fortifies the individual nodes. Defense in Depth ensures that the network and data are secure, offering a holistic approach to cybersecurity.
By understanding and implementing both endpoint hardening and Defense in Depth, you’re not just adding more locks to your doors. You are also building an impenetrable fortress around your digital assets.
Understanding Security Vulnerabilities
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, understanding common security vulnerabilities is crucial for safeguarding your systems. Our infographic below provides a comprehensive overview of these vulnerabilities. However, let’s delve deeper into some real-world examples to grasp their impact fully.
Real-World Case Studies
1. Equifax Data Breach: The Cost of Ignoring Known Vulnerabilities
In 2017, Equifax, a major credit reporting agency, suffered a catastrophic data breach affecting 147 million Americans. The breach was attributed to a known vulnerability in the Apache Struts web application framework. Despite patches being available, Equifax failed to update their systems. This lead to the exposure of sensitive data like Social Security numbers and birth dates.
Key Takeaway: Regularly updating and patching your systems can prevent exploitation of known vulnerabilities, safeguarding your data and your reputation.
2. Sony Pictures Hack: The Perils of SQL Injection
Sony Pictures Entertainment fell victim to a devastating cyber-attack in 2014. The attack resulted in the theft and release of confidential data, including unreleased films and internal emails. The attackers exploited an SQL injection vulnerability to gain unauthorized access to Sony’s network.
Key Takeaway: Proper input validation and secure coding practices can mitigate the risks associated with SQL injection. Doing so protects your data and intellectual property.
Conclusion
Understanding common security vulnerabilities and their real-world implications is essential for any organization. As the case studies of Equifax and Sony Pictures illustrate, the failure to address these vulnerabilities can have dire consequences. Therefore, it’s imperative to stay updated on the latest security threats and to implement robust security measures to protect your systems and data.
By being proactive and learning from past mistakes, you can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to similar security breaches.
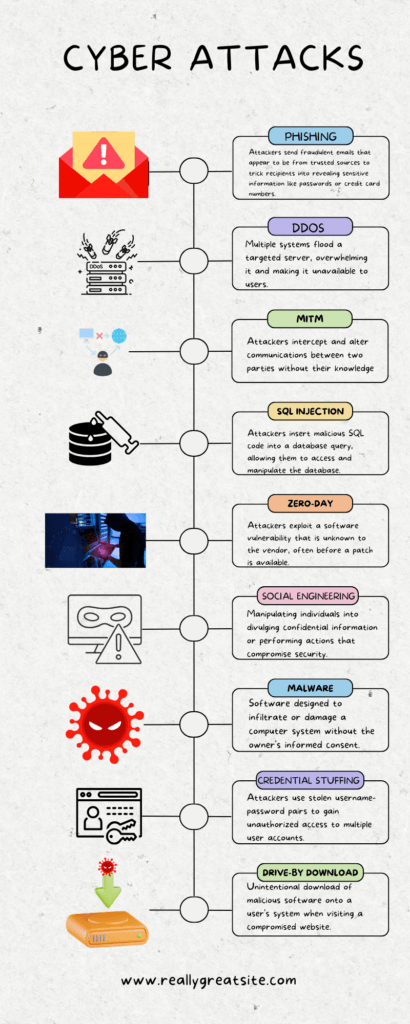
The Anatomy of Cyber Attacks
In today’s digital landscape, understanding the various types of cyber-attacks is crucial for both individuals and organizations. To help you grasp the complexity and diversity of these attacks, we’ve created an infographic that outlines each type. Below, we delve into more detail.
Types of Cyber Attacks and How They Work
Phishing
Phishing is a deceptive technique where attackers pose as trustworthy entities to steal sensitive information. Emails are the most common medium for this type of attack. Always be cautious of unsolicited communications asking for personal information.
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service)
DDoS attacks overwhelm a network or service with excessive traffic, rendering it unusable. These attacks often use multiple compromised systems to flood the target. It’s essential to have robust security measures in place to mitigate such attacks.
Ransomware
Ransomware is malicious software that encrypts files on a victim’s computer, demanding a ransom for their release. Regularly updating your software and keeping backups can help you avoid the damaging effects of ransomware.
Man-in-the-Middle
In Man-in-the-Middle attacks, the attacker secretly intercepts and possibly alters the communication between two parties. Using secure and encrypted connections can help prevent these attacks.
SQL Injection
SQL Injection involves inserting malicious SQL code into a database query. This can give attackers access to sensitive information. Employing input validation methods can help protect against SQL injection attacks.
Zero-Day Exploit
Zero-Day Exploits take advantage of vulnerabilities in software that are unknown to the vendor. These are particularly dangerous because they are hard to defend against. Keeping your software updated can offer some protection.
Social Engineering
Social Engineering attacks manipulate individuals into divulging confidential information. Being aware and skeptical can go a long way in defending against these attacks.
Malware
Malware is software designed to infiltrate or damage a computer system. Installing a reputable antivirus program and keeping it updated can help protect against malware.
Credential Stuffing
Credential Stuffing involves automated attempts to gain unauthorized access using pairs of usernames and passwords. Using unique and strong passwords for different accounts can help prevent these attacks.
Drive-By Download
Drive-By Downloads involve unintentionally downloading malicious software by visiting a compromised website. Keeping your browser and plugins updated can offer some level of protection.
Understanding these types of cyber-attacks can help you take proactive steps to protect yourself and your organization. Stay vigilant and always keep your security measures up to date.
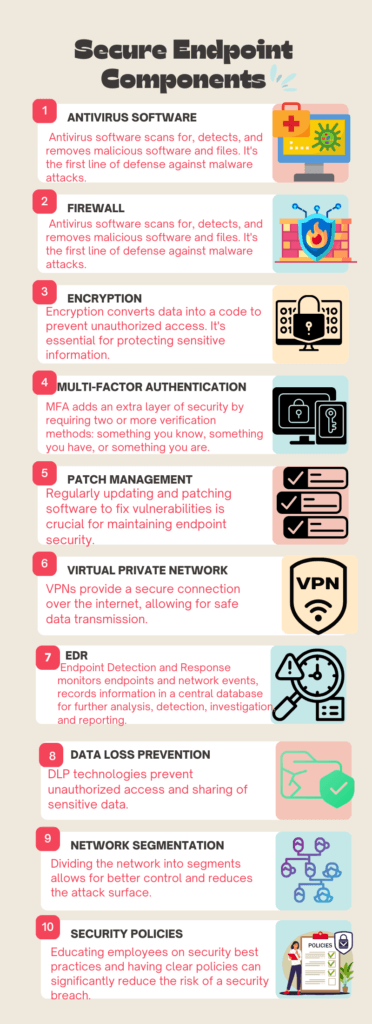
Endpoint Security Essentials
Endpoint security is not just a one-time setup but an ongoing process. One of the critical aspects of this process is endpoint hardening, which involves fortifying each endpoint device to make it more resistant to cyber-attacks. The components of a secure endpoint serve as the building blocks for effective endpoint hardening. Below, we delve into each of these components to give you a comprehensive understanding of what it takes to secure an endpoint effectively.
Antivirus Software
Antivirus software is your first line of defense against malware and other malicious software. It scans, detects, and removes threats, thereby serving as a foundational element in endpoint hardening.
Firewall
A firewall monitors and controls the data packets that move in and out of the network. It acts as a barrier between your secure internal network and untrusted external networks, a crucial component for hardening your endpoints.
Encryption
Encryption is the process of converting data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. It is especially vital for protecting sensitive data and is a key aspect of endpoint hardening.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring two or more forms of verification before granting access. This makes it more challenging for unauthorized users to gain access to your network, thereby hardening your endpoints.
Patch Management
Patch Management involves regularly updating and patching software to fix vulnerabilities. Keeping your systems up to date is an essential part of endpoint hardening.
VPN (Virtual Private Network)
A VPN provides a secure tunnel for data transmission over the internet. It’s an essential tool for remote workers and adds an extra layer of security, contributing to endpoint hardening.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions continuously monitor and collect data from endpoints. This aids in detecting, investigating, and preventing potential threats, making it a vital component in hardening endpoints.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP)
Data Loss Prevention (DLP) technologies help in controlling and managing data, preventing unauthorized access and data breaches. This is crucial for the endpoint hardening process.
Network Segmentation
Network Segmentation involves dividing the network into various segments to control traffic and reduce the attack surface, thereby contributing to endpoint hardening.
Security Policies and Training
Last but not least, Security Policies and Training are essential for educating employees about best practices in cybersecurity. A well-informed team can be your best defense in hardening endpoints.
By understanding and implementing these components, you’re well on your way to effective endpoint hardening, ensuring a more secure and resilient environment against cyber threats.

Operating Systems and Their Risks
In today’s digital landscape, the choice of operating system (OS) can significantly impact your endpoint security. Let’s delve into the market share of major operating systems and their inherent security features to understand the risks and benefits.
Market Share of Operating Systems in 2023
Our pie chart visual illustrates the current market share of major operating systems:
- Windows: 72%
- Linux: 14%
- Unix: 6%
- Other: 8%
This data is crucial because the more widely used an OS is, the more likely it becomes a target for cybercriminals.

Security Features Across Operating Systems
Our table visual provides a comprehensive look at the security features of Windows, Linux, and Unix:
- Windows: Known for its user-friendly interface, Windows also offers robust security features like BitLocker Drive Encryption and Windows Defender Firewall.
- Linux: Although it has a smaller market share, Linux is lauded for its security. Features like SELinux and IPTables Firewall make it a secure choice for enterprises.
- Unix: With features like Role-Based Access Control and Solaris Auditing, Unix is often used in environments that require high-level security.
Relation to Endpoint Hardening
Understanding the security features of these operating systems is integral to endpoint hardening. For instance, using BitLocker in Windows or SELinux in Linux can significantly enhance the security posture of your endpoints. Therefore, when hardening your endpoints, it’s crucial to leverage these built-in OS security features effectively.
By choosing an OS with robust security features and understanding its market share risks, you can make informed decisions that align with your endpoint hardening strategy.
So, the next time you’re evaluating operating systems, remember that your choice will play a pivotal role in your overall cybersecurity posture. Choose wisely.
In today’s digital landscape, the choice of operating system (OS) can significantly impact your endpoint security. Let’s delve into the market share of major operating systems and their inherent security features to understand the risks and benefits.
Security Features Across Operating Systems
| Operating System | Security Features |
|---|---|
| Windows | – BitLocker Drive Encryption – Windows Defender Firewall – User Account Control (UAC) – Windows Hello – Secure Boot – Windows Information Protection (WIP) |
| Linux | – SELinux (Security-Enhanced Linux) – AppArmor – IPTables Firewall – PAM (Pluggable Authentication Modules) – Chroot Jails<br>- Secure Boot Support |
| Unix | – Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) – Basic Audit Reporting Tool (BART) – Solaris Auditing – Trusted Extensions – Process Rights Management |
The above table provides a comprehensive look at the security features of Windows, Linux, and Unix:
- Windows: Known for its user-friendly interface, Windows also offers robust security features like BitLocker Drive Encryption and Windows Defender Firewall.
- Linux: Although it has a smaller market share, Linux is lauded for its security. Features like SELinux and IPTables Firewall make it a secure choice for enterprises.
- Unix: With features like Role-Based Access Control and Solaris Auditing, Unix is often used in environments that require high-level security.
Relation to Endpoint Hardening
Understanding the security features of these operating systems is integral to endpoint hardening. For instance, using BitLocker in Windows or SELinux in Linux can significantly enhance the security posture of your endpoints. Therefore, when hardening your endpoints, it’s crucial to leverage these built-in OS security features effectively.
By choosing an OS with robust security features and understanding its market share risks, you can make informed decisions that align with your endpoint hardening strategy.
There are procedures for hardening operating systems and pre-made hardened operating systems for many variants of common operating systems. One source of this is the Center For Internet Security.
So, the next time you’re evaluating operating systems, remember that your choice will play a pivotal role in your overall cybersecurity posture. Choose wisely.
Industry Standards for Endpoint Security
In the realm of endpoint security, adhering to industry standards is not just a best practice but a necessity. These standards serve as a guideline for organizations to ensure that their endpoint security measures are up to par with global requirements. Let’s take a look at some of the key certifications and what they signify.
Important Certifications and Their Significance
| Certification | Description |
|---|---|
| ISO/IEC 27001 | This international standard outlines the requirements for establishing, implementing, and maintaining an Information Security Management System (ISMS). |
| NIST SP 800-53 | Developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology, this standard provides guidelines for federal organizations on security controls for information systems. |
| PCI DSS | The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard is crucial for organizations that handle credit card transactions. It focuses on securing cardholder data. |
| HIPAA | The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act is essential for healthcare providers. It sets the standard for protecting sensitive patient data. |
| GDPR | The General Data Protection Regulation applies to organizations operating within the EU. It focuses on data protection and privacy. |
| CIS Controls | Developed by the Center for Internet Security, these controls provide a prioritized set of actions for improving system and data security. |
| FISMA | The Federal Information Security Management Act applies to federal agencies and their contractors, focusing on information security management. |
| SOC 2 Type II | This certification assures that a service organization’s controls are effectively designed and operating over a period of time, often relevant for cloud service providers. |
Why These Standards Matter for Endpoint Security
Adhering to these certifications ensures that your endpoint security measures are robust and in line with global best practices. For instance, following NIST guidelines can help you in the effective hardening of your endpoints. Similarly, being PCI DSS compliant ensures that your endpoints are secure enough to handle financial transactions safely.
In summary, these industry standards serve as a roadmap for organizations to secure their endpoints effectively. They provide a framework that, when followed, can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. Therefore, understanding and implementing these standards should be a cornerstone of your endpoint security strategy.
The Strategy for Endpoint Security
In today’s digital landscape, having a comprehensive endpoint security strategy is not just an option but a necessity. The following steps, illustrated in the flowchart, guide you through creating a robust security strategy that aligns with the concept of endpoint hardening.
Identify Assets
The first step in creating a security strategy is identifying all the assets that require protection. This includes hardware like servers and workstations, software applications, and crucial data. Knowing what you have is the foundation for understanding what needs to be secured. This step is vital as it sets the stage for the risk assessment.
Risk Assessment
Once you’ve identified your assets, the next step is to perform a risk assessment. This involves evaluating the vulnerabilities and threats that could potentially impact your assets. The risk assessment is crucial because it builds upon the asset identification to give you a clear picture of where your security might be lacking.
Define Objectives
Based on the risk assessment, you’ll need to define your security objectives. What are you trying to achieve with your security strategy? Whether it’s data protection, compliance with regulations, or safeguarding intellectual property, these objectives will guide the rest of your strategy.
Select Tools & Technologies
After defining your objectives, the next step is to select the appropriate tools and technologies that will help you achieve those objectives. This could range from antivirus software to intrusion detection systems. The tools you choose are instrumental in shaping your policies and procedures.
Develop Policies & Procedures
With the right tools and technologies in place, you’ll need to develop policies and procedures that dictate how these will be used. These guidelines serve as the rulebook for your organization’s security, outlining what is acceptable and what is not. They are developed to ensure that the selected tools and technologies are used effectively.
Implementation
The implementation phase involves putting your policies and procedures into action. This is where the rubber meets the road. You’ll deploy the selected tools and technologies according to the guidelines you’ve established, making sure that they are correctly configured and installed.
Monitoring & Auditing
After implementation, continuous monitoring and auditing become crucial. This step ensures that your security measures are effective and alerts you to any potential issues before they become significant problems. Monitoring and auditing are ongoing processes that feed into the review and update phase.
Review & Update
Security is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. The landscape is continually changing, and new threats emerge regularly. Therefore, it’s essential to periodically review and update your security strategy to adapt to new challenges and technologies.
By following these steps, you not only create a comprehensive security strategy but also contribute to the hardening of your endpoints, making them less susceptible to attacks.
Industry-Specific Solutions
The need for robust endpoint security is universal, but the approach to it can vary significantly depending on the industry. Different sectors have unique challenges and regulatory requirements that dictate how they implement and manage endpoint security.
The table below is not meant to be exact, but rather give examples of different industries might look like.
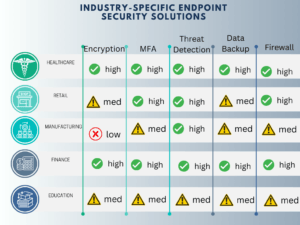
Here is more advice based on several sources by industry.
Sources:
Financial Sector
In the financial sector, the focus is often on compliance with regulations like GDPR and PCI DSS. Endpoint security solutions here are geared towards data encryption and secure transaction processing.
Energy Sector
For the energy sector, the emphasis is on securing critical infrastructure. Solutions often include advanced threat detection mechanisms and incident response capabilities to protect against potential sabotage.
Government
Government organizations prioritize national security and thus require endpoint solutions with advanced encryption and multi-factor authentication features.
Retail
Retail businesses are prime targets for data breaches. Endpoint security solutions in this sector focus on securing point-of-sale (POS) systems and customer data.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, the focus is on protecting intellectual property and ensuring the integrity of automated processes. Endpoint security solutions often include features like application vetting and device control.
Software Companies
Software companies need to protect their source code and customer data. Endpoint security solutions often include advanced threat detection and response capabilities.
Healthcare
In healthcare, compliance with regulations like HIPAA is crucial. Endpoint security solutions focus on securing patient data and medical records.
The approach to endpoint security can differ significantly between industries, but the goal remains the same: to protect your organization from cyber threats. By understanding the unique needs and challenges of your industry, you can implement a more effective and compliant endpoint security strategy.
Case Studies to Consider
For a deeper understanding of these industry-specific solutions, consider these case studies:
- JP Morgan Chase implemented advanced threat detection algorithms to safeguard against fraudulent activities.
- ExxonMobil focused on securing their SCADA systems to protect against potential cyber-attacks on their energy grids.
- U.S. Department of Defense utilized multi-layered endpoint security solutions to protect sensitive military data.
These case studies demonstrate the necessity of tailoring endpoint security solutions to industry-specific requirements. For a more visual representation, refer to the bar graph comparing industry-specific security measures.
By customizing your endpoint security measures to fit your industry’s unique challenges, you not only bolster your defenses but also enhance operational efficiency.
So, what industry do you belong to, and how are you customizing your endpoint security solutions? We’d love to hear from you.
Conclusion
In today’s rapidly evolving cyber landscape, endpoint security is not just a buzzword—it’s a necessity. From understanding the escalating threats targeting small businesses to recognizing the importance of tailored, industry-specific solutions, this guide has walked you through the essentials of implementing a robust endpoint security strategy.
Whether you’re grappling with the challenges of remote work or seeking to fortify your network with advanced technologies like encryption and multi-factor authentication, remember that endpoint security is an ongoing process. Staying updated with the latest security technologies is not just advisable; it’s imperative.
So, what’s your next move? Don’t just read—act. Evaluate your current security posture, consider the unique needs of your industry, and take proactive steps to safeguard your business. And as you embark on this journey, we invite you to share your thoughts, questions, and experiences with our community. Your insights could be the missing puzzle piece for someone else striving to achieve comprehensive endpoint security.
Join the conversation today and become an active participant in the collective effort to secure our digital world.
The post Unlocking the Secrets of Hardened Secure Endpoint in 2023 appeared first on Endpoint Security.
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Endpoint Security authored by Michael Toback. Read the original post at: https://smallbizepp.com/hardened-secure-endpoint/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=hardened-secure-endpoint
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
