【Linux命令】每天一个Linux命令(5):cp命令
每天一个Linux命令(5):cp命令命令:cp描述:cp(copy)用于复制文件或目录。语法:cp [选项] 源文件 目标文件常用选项:-r:复制目录及其内容。-i:在复制文件之前进行交互式确认。- 2023-6-3 00:4:11 Author: 利刃信安攻防实验室(查看原文) 阅读量:21 收藏
每天一个Linux命令(5):cp命令命令:cp描述:cp(copy)用于复制文件或目录。语法:cp [选项] 源文件 目标文件常用选项:-r:复制目录及其内容。-i:在复制文件之前进行交互式确认。- 2023-6-3 00:4:11 Author: 利刃信安攻防实验室(查看原文) 阅读量:21 收藏
每天一个Linux命令(5):cp命令
cpcp [选项] 源文件 目标文件-r:复制目录及其内容。 -i:在复制文件之前进行交互式确认。 -v:显示每个复制操作的详细信息。
cp file1.txt file2.txt这将复制 file1.txt 文件并将其命名为 file2.txt。
2.
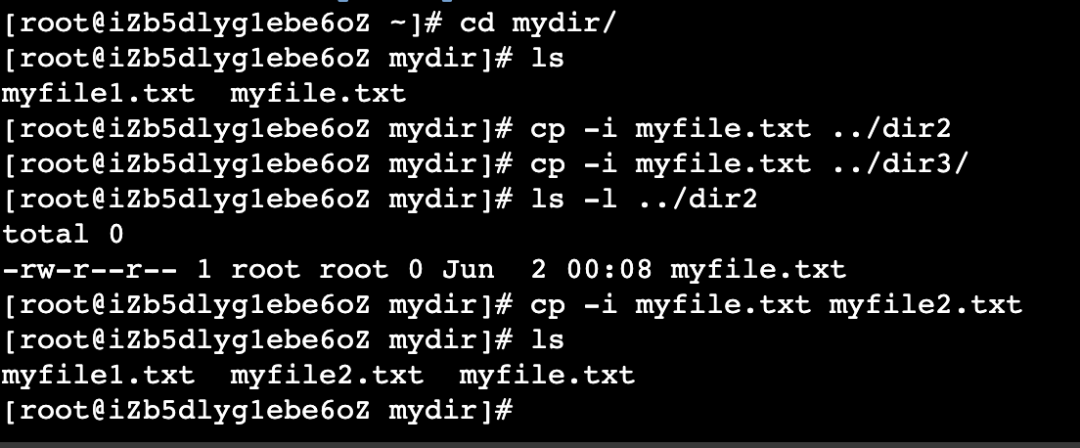
cp file1.txt file2.txt directory/cp -r sourcedir/ destination/cp -i file.txt destination/特别提醒:
[[email protected] ~]# cp --helpUsage: cp [OPTION]... [-T] SOURCE DESTor: cp [OPTION]... SOURCE... DIRECTORYor: cp [OPTION]... -t DIRECTORY SOURCE...Copy SOURCE to DEST, or multiple SOURCE(s) to DIRECTORY.Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.-a, --archive same as -dR --preserve=all--attributes-only don't copy the file data, just the attributes--backup[=CONTROL] make a backup of each existing destination file-b like --backup but does not accept an argument--copy-contents copy contents of special files when recursive-d same as --no-dereference --preserve=links-f, --force if an existing destination file cannot beopened, remove it and try again (this optionis ignored when the -n option is also used)-i, --interactive prompt before overwrite (overrides a previous -noption)-H follow command-line symbolic links in SOURCE-l, --link hard link files instead of copying-L, --dereference always follow symbolic links in SOURCE-n, --no-clobber do not overwrite an existing file (overridesa previous -i option)-P, --no-dereference never follow symbolic links in SOURCE-p same as --preserve=mode,ownership,timestamps--preserve[=ATTR_LIST] preserve the specified attributes (default:mode,ownership,timestamps), if possibleadditional attributes: context, links, xattr,all-c deprecated, same as --preserve=context--no-preserve=ATTR_LIST don't preserve the specified attributes--parents use full source file name under DIRECTORY-R, -r, --recursive copy directories recursively--reflink[=WHEN] control clone/CoW copies. See below--remove-destination remove each existing destination file beforeattempting to open it (contrast with --force)--sparse=WHEN control creation of sparse files. See below--strip-trailing-slashes remove any trailing slashes from each SOURCEargument-s, --symbolic-link make symbolic links instead of copying-S, --suffix=SUFFIX override the usual backup suffix-t, --target-directory=DIRECTORY copy all SOURCE arguments into DIRECTORY-T, --no-target-directory treat DEST as a normal file-u, --update copy only when the SOURCE file is newerthan the destination file or when thedestination file is missing-v, --verbose explain what is being done-x, --one-file-system stay on this file system-Z set SELinux security context of destinationfile to default type--context[=CTX] like -Z, or if CTX is specified then set theSELinux or SMACK security context to CTX--help display this help and exit--version output version information and exitBy default, sparse SOURCE files are detected by a crude heuristic and thecorresponding DEST file is made sparse as well. That is the behaviorselected by --sparse=auto. Specify --sparse=always to create a sparse DESTfile whenever the SOURCE file contains a long enough sequence of zero bytes.Use --sparse=never to inhibit creation of sparse files.When --reflink[=always] is specified, perform a lightweight copy, where thedata blocks are copied only when modified. If this is not possible the copyfails, or if --reflink=auto is specified, fall back to a standard copy.Use --reflink=never to ensure a standard copy is performed.The backup suffix is '~', unless set with --suffix or SIMPLE_BACKUP_SUFFIX.The version control method may be selected via the --backup option or throughthe VERSION_CONTROL environment variable. Here are the values:none, off never make backups (even if --backup is given)numbered, t make numbered backupsexisting, nil numbered if numbered backups exist, simple otherwisesimple, never always make simple backupsAs a special case, cp makes a backup of SOURCE when the force and backupoptions are given and SOURCE and DEST are the same name for an existing,regular file.GNU coreutils online help: <https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>Full documentation <https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/cp>or available locally via: info '(coreutils) cp invocation'[[email protected] ~]# cp --helpUsage: cp [OPTION]... [-T] SOURCE DESTor: cp [OPTION]... SOURCE... DIRECTORYor: cp [OPTION]... -t DIRECTORY SOURCE...Copy SOURCE to DEST, or multiple SOURCE(s) to DIRECTORY.Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.-a, --archive same as -dR --preserve=all--attributes-only don't copy the file data, just the attributes--backup[=CONTROL] make a backup of each existing destination file-b like --backup but does not accept an argument--copy-contents copy contents of special files when recursive-d same as --no-dereference --preserve=links-f, --force if an existing destination file cannot beopened, remove it and try again (this optionis ignored when the -n option is also used)-i, --interactive prompt before overwrite (overrides a previous -noption)-H follow command-line symbolic links in SOURCE-l, --link hard link files instead of copying-L, --dereference always follow symbolic links in SOURCE-n, --no-clobber do not overwrite an existing file (overridesa previous -i option)-P, --no-dereference never follow symbolic links in SOURCE-p same as --preserve=mode,ownership,timestamps--preserve[=ATTR_LIST] preserve the specified attributes (default:mode,ownership,timestamps), if possibleadditional attributes: context, links, xattr,all-c deprecated, same as --preserve=context--no-preserve=ATTR_LIST don't preserve the specified attributes--parents use full source file name under DIRECTORY-R, -r, --recursive copy directories recursively--reflink[=WHEN] control clone/CoW copies. See below--remove-destination remove each existing destination file beforeattempting to open it (contrast with --force)--sparse=WHEN control creation of sparse files. See below--strip-trailing-slashes remove any trailing slashes from each SOURCEargument-s, --symbolic-link make symbolic links instead of copying-S, --suffix=SUFFIX override the usual backup suffix-t, --target-directory=DIRECTORY copy all SOURCE arguments into DIRECTORY-T, --no-target-directory treat DEST as a normal file-u, --update copy only when the SOURCE file is newerthan the destination file or when thedestination file is missing-v, --verbose explain what is being done-x, --one-file-system stay on this file system-Z set SELinux security context of destinationfile to default type--context[=CTX] like -Z, or if CTX is specified then set theSELinux or SMACK security context to CTX--help display this help and exit--version output version information and exitBy default, sparse SOURCE files are detected by a crude heuristic and thecorresponding DEST file is made sparse as well. That is the behaviorselected by --sparse=auto. Specify --sparse=always to create a sparse DESTfile whenever the SOURCE file contains a long enough sequence of zero bytes.Use --sparse=never to inhibit creation of sparse files.When --reflink[=always] is specified, perform a lightweight copy, where thedata blocks are copied only when modified. If this is not possible the copyfails, or if --reflink=auto is specified, fall back to a standard copy.Use --reflink=never to ensure a standard copy is performed.The backup suffix is '~', unless set with --suffix or SIMPLE_BACKUP_SUFFIX.The version control method may be selected via the --backup option or throughthe VERSION_CONTROL environment variable. Here are the values:none, off never make backups (even if --backup is given)numbered, t make numbered backupsexisting, nil numbered if numbered backups exist, simple otherwisesimple, never always make simple backupsAs a special case, cp makes a backup of SOURCE when the force and backupoptions are given and SOURCE and DEST are the same name for an existing,regular file.GNU coreutils online help: <https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>Full documentation <https://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/cp>or available locally via: info '(coreutils) cp invocation'
文章来源: http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU1Mjk3MDY1OA==&mid=2247504399&idx=2&sn=b698695c5918223c1280c7127248036b&chksm=fbfb62c2cc8cebd4537007c0184a66f6f9f5b3ef303721715d51123ed04ec629c623749d4ce1#rd
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh