
RSA
使用openssl模块 rsa -pubin -text -modulus -in pub.key得到n值,在 factordb.com上分解大素数得到p,q值,脚本生成private.pem。
# coding=utf-8 import math import sys from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA keypair = RSA.generate(1024) keypair.p = 2859604688904516379356294403726392834xx keypair.q = 3040087416046019244943281559752724184xx keypair.e = 65537 keypair.n = keypair.p Qn = long((keypair.p - 1) * (keypair.q - 1)) i = 1 while (True): x = (Qn * i) + 1 if (x % keypair.e == 0): keypair.d = x / keypair.e break i += 1 private = open('private.pem', 'w') private.write(keypair.exportKey()) private.close()
再使用openssl模块 rsautl -decrypt -in flag.enc -inkey private.pem得到flag。
Youngter-drive
多线程题目,首先有upx加壳,脱壳后发现堆栈不平衡,调整平衡后发现主要有两个线程函数,StartAddress函数和sub_41119F函数
CreateThread(0, 0, (LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)StartAddress, 0, 0, 0); hObject = (HANDLE)sub_41116D(); CreateThread(0, 0, sub_41119F, 0, 0, 0);
StartAddress函数主要是对输入逐位加密,将字符串进行了替换,当字符是大写字母时,替换为off_418000处-38,小写则替换后-96
if ( dword_418008 > -1 ) { sub_41112C(&Source, dword_418008); --dword_418008; Sleep(0x64u); sub_41116D(); }
sub_41119F函数是使StartAddress函数的dword_418008再减一位
while ( 1 ) { WaitForSingleObject(hObject, 0xFFFFFFFF); sub_41116D(); if ( dword_418008 > -1 ) { Sleep(0x64u); sub_41116D(); --dword_418008; } ReleaseMutex(hObject); sub_41116D(); }
这就导致了源程序的间隔加密,奇数位加密,偶数位不变,脚本解密得到flag
off_418000 = "QWERTYUIOPASDFGHJKLZXCVBNMqwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnm" off_418004 = "TOiZiZtOrYaToUwPnToBsOaOapsyS" flag='' for i in range(len(off_418004)): if i %2 == 0: flag += off_418004[i] continue for j,k in enumerate(off_418000): if off_418004[i] == k: if chr(j+38).isupper(): flag += chr(j+38) else: flag += chr(j+96) print flag
相册
使用apktool box反编译apk,使用ida加载里面的.so文件搜索字符串,其中几串base64值分别是邮箱用户名密码,邮箱即为flag。
CrackMe
首先依据你的用户名创建一个xor表,然后用这个表和密码经过异或计算,得到一个长度为8的checksum(unsigned char checksum[8]),最后检查checksum是否满足一些条件。满足则通过注册,不满足不通过。checksum进入check2进行验证,最终得到check_num == 43924则成功。
分析check2:
_DWORD *__usercall check2@<eax>(int a1@<ebx>, _BYTE *key, _DWORD *a3) { int v3; // ST28_4 int v4; // ecx int v6; // edx int v8; // ST20_4 int v9; // eax int v10; // edi int v11; // ST1C_4 int v12; // edx char v13; // di int v14; // ST18_4 int v15; // eax int v16; // ST14_4 int v17; // edx char v18; // al int v19; // ST10_4 int v20; // ecx int v23; // ST0C_4 int v24; // eax _DWORD *result; // eax int v26; // edx if ( *key == 100 ) { *a3 |= 4u; v4 = *a3; } else { *a3 ^= 3u; } v3 = *a3; if ( key[1] == 98 ) { _EAX = a3; *a3 |= 0x14u; v6 = *a3; } else { *a3 &= 0x61u; _EAX = (_DWORD *)*a3; } __asm { aam } if ( key[2] == 97 ) { *a3 |= 0x84u; v9 = *a3; } else { *a3 &= 0xAu; } v8 = *a3; v10 = ~(a1 >> -91); if ( key[3] == 112 ) { *a3 |= 0x114u; v12 = *a3; } else { *a3 >>= 7; } v11 = *a3; v13 = v10 - 1; if ( key[4] == 112 ) { *a3 |= 0x380u; v15 = *a3; } else { *a3 *= 2; } v14 = *a3; if ( *(_DWORD *)(*(_DWORD *)(__readfsdword(0x30u) + 24) + 12) != 2 ) { if ( key[5] == 102 ) { *a3 |= 0x2DCu; v17 = *a3; } else { *a3 |= 0x21u; } v16 = *a3; } if ( key[5] == 115 ) { *a3 |= 0xA04u; v18 = (char)a3; v20 = *a3; } else { v18 = (char)a3; *a3 ^= 0x1ADu; } v19 = *a3; _AL = v18 - v13; __asm { daa } if ( key[6] == 101 ) { *a3 |= 0x2310u; v24 = *a3; } else { *a3 |= 0x4Au; } v23 = *a3; if ( key[7] == 99 ) { result = a3; *a3 |= 0x8A10u; v26 = *a3; } else { *a3 &= 0x3A3u; result = (_DWORD *)*a3; } return result; }
发现满足条件的key值只有[100, 98, 97, 112, 112, 115, 101, 99],即"dbappsec"
xor函数是将key和user每位对应异或。在013b1b3e处下断点动态调试扣出和密码异或计算的值

需要主要的是,动态调试和执行得到的异或值是不一样的,需要把类似反调试的代码nop掉,
if ( *(_DWORD *)(__readfsdword(48) + 104) & 0x70 ) v13 = v11 + v12; *(&v17 + v6) = byte_13C6050[(unsigned __int8)(v8 + v13)] ^ *(&v15 + v5); if ( *(_DWORD *)(__readfsdword(48) + 2) & 0xFF ) { v11 = -83; v12 = 43; }
然后得到box是[0x2a,0xd7,0x92,0xe9,0x53,0xe2,0xc4,xx],写脚本得到flag。
a=[0x2a,0xd7,0x92,0xe9,0x53,0xe2,0xc4,xx] b=[0x64,0x62,0x61,0x70,0x70,0x73,0x65,0x63] #dbappsec for i in range(8): print hex(a[i]^b[i])
equation
jsfuck代码,发现代码中存在很多l,怀疑l后面是混淆的下标整数,脚本处理,得到多元线性方程组
<script>
function deEquation(str) {
for (let i = 0; i <= 1; i++) {
str = str.replace(/l\[(\D*?)](\+l|-l|==)/g, (m, a, b) => 'l[' + eval(a) + ']' + b);
}
str = str.replace(/==(\D*?)&&/g, (m, a) => '==' + eval(a) + '&&');
return str;
}
s="jsfuck";
ss=deEquation(s);
document.write(ss);
</script>

整理成numpy解方程格式,求出flag数组
from scipy.integrate import odeint import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from scipy.optimize import root,fsolve def f3(l): return np.array([l[40]+l[35]+l[34]-l[0]-l[15]-l[37]+l[7]+l[6]-l[26]+l[20]+l[19]+l[8]-l[17]-l[14]-l[38]+l[1]-l[9]+l[22]+l[41]+l[3]-l[29]-l[36]-l[25]+l[5]+l[32]-l[16]+l[12]-l[24]+l[30]+l[39]+l[10]+l[2]+l[27]+l[28]+l[21]+l[33]-l[18]+l[4]-861, ……, ……, ……] ) sol3_root = root(f3,[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]) sol3_fsolve = fsolve(f3,[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]) print sol3_fsolve
数组转化即为flag。
firmware
固件分析,首先在ubuntu中安装工具firmware-mod-kit
1 #安装依赖 2 sudo apt-get install git build-essential zlib1g-dev liblzma-dev python-magic 3 #安装firmware-mod-kit 4 git clone https://github.com/mirror/firmware-mod-kit.git 5 cd firmware-mod-kit/src 6 ./configure 7 make
使用binwalk提取出固件内容:
1 binwalk -e "firmware.bin"
使用firmware-mod-kit解包固件提取内核和文件系统:
1 cd firmware-mod-kit 2 ./unsquashfs_all.sh '/home/vicen/Desktop/_firmware.bin.extracted/120200.squashfs' 3 cd squashfs-root/tmp/ 4 ls
发现tmp目录下有后门文件backdoor

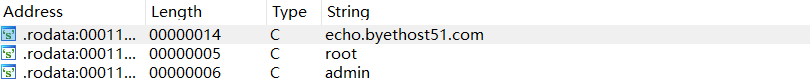
存在upx3.94加壳,脱壳后载入ida,查看字符串发现远程服务器网址,对网址交叉引用查看代码段发现端口值,将md5值提交flag。
达芬奇密码
斐波拉契数列乱序,求出密文对应的正确映射次序即为flag。
a=[0,233,3,2584,1346269,144,5,196418,21,1597,610,377,10946,89,514229,987,8,55,6765,2178309,121393,317811,46368,4181,1,832040,2,28657,75025,34,13,17711] b=[0,1,2,3,5,8,13,21,34,55,89,144,233,377,610,987,1597,2584,4181,6765,10946,17711,28657,46368,75025,121393,196418,317811,514229,832040,1346269,2178309] c=[0 for i in range(len(a))] for i in range(len(a)): for j in range(len(a)): if a[i]==b[j]: c[j]=i s="36968853882116725547342176952286" d='' for i in range(len(s)): d+=s[c[i]] print d
救世捷径
有向图最短路问题,根据各向量的权值,使用Dijkstra算法求出最短路径,然后对照字符串得到flag。
import networkx as nx def Dijkstra(G, start, end): RG = G.reverse(); dist = {}; previous = {} for v in RG.nodes(): dist[v] = float('inf') previous[v] = 'none' dist[end] = 0 u = end while u != start: u = min(dist, key=dist.get) distu = dist[u] del dist[u] for u, v in RG.edges(u): if v in dist: alt = distu + RG[u][v]['weight'] if alt < dist[v]: dist[v] = alt previous[v] = u path = (start,) last = start while last != end: nxt = previous[last] path += (nxt,) last = nxt return path G = nx.DiGraph() G.add_edge(1,2,weight=100) G.add_edge(2,3,weight=87) G.add_edge(2,4,weight=57) G.add_edge(2,5,weight=50) G.add_edge(2,6,weight=51) G.add_edge(3,7,weight=94) G.add_edge(3,8,weight=78) G.add_edge(3,9,weight=85) G.add_edge(4,13,weight=54) G.add_edge(4,14,weight=47) G.add_edge(4,15,weight=98) G.add_edge(5,10,weight=43) G.add_edge(5,11,weight=32) G.add_edge(5,12,weight=44) G.add_edge(6,16,weight=59) G.add_edge(6,17,weight=92) G.add_edge(6,18,weight=39) G.add_edge(6,23,weight=99) G.add_edge(7,19,weight=99) G.add_edge(8,20,weight=96) G.add_edge(9,20,weight=86) G.add_edge(10,21,weight=60) G.add_edge(11,21,weight=57) G.add_edge(12,22,weight=47) G.add_edge(14,10,weight=55) G.add_edge(16,17,weight=59) G.add_edge(18,12,weight=53) G.add_edge(18,24,weight=93) G.add_edge(21,22,weight=33) G.add_edge(19,25,weight=88) G.add_edge(20,25,weight=96) G.add_edge(22,25,weight=23) G.add_edge(25,26,weight=75) rs = Dijkstra(G, 1, 26) print(rs)
EasyProgram
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 int main() 4 { 5 FILE *fp = NULL; 6 char flag[255]; 7 fp = fopen("file.txt", "r"); 8 fscanf(fp, "%s", flag); 9 int i,j,s[256],t[256],p,x; 10 char key[]="whoami"; 11 for (i=0;i<256;i++) 12 s[i]=i; 13 for (i=0;i<256;i++) 14 t[i]=key[i%(strlen(key))]; 15 j=0; 16 for (i=0;i<256;i++){ 17 j=(j+s[i]+t[i])%256; 18 p=s[i];s[i]=s[j];s[j]=p; 19 } 20 i=0;j=0; 21 for (int m=0;m<38;m++){ 22 i=(i+1)%256; 23 j=(j+s[i])%256; 24 p=s[i];s[i]=s[j];s[j]=p; 25 x=(s[i] + s[j]%256)%256; 26 flag[m]=flag[m]^s[x]; 27 } 28 printf("%s\n", flag ); 29 return 0; 30 }
浪里淘沙
分析单词出现频率,然后按次数排序,找出其中第4,8,11,15,16位单词拼接为flag。
a="tonightsuccessnoticenoticewewesuccesstonightweexamplecryptoshouldwebackspacetonightbackspace......"
def d(s): print s,a.count(s) g=a.replace(s,'') return g a=d("tonight") a=d("success") a=d("notice") a=d("example") a=d("should") a=d("crypto") a=d("backspace") a=d("learn") a=d("found") a=d("morning") a=d("we") a=d("system") a=d("sublim") a=d("the") a=d("user") a=d("enter")
SameMod
发现n相同,很明显的RSA共模攻击,随便找个共模攻击脚本得到m=10210897103123119104101110119101116104.....
发现像ascii码拼接在一起,分开为 102,108,97,103......得到flag。
RSA系列
- 已知p、q、e、c系列:RSA、rsarsa、RSAROLL
- 已知p、q、dq、dp、c系列:RSA1
- 已知e、n、dp、c系列:RSA2
- 共模攻击:RSA3、SameMod
- 低解密指数攻击:rsa2
- 低加密指数攻击:Dangerous RSA
- 相同的e与m,gcd(n1,n2)找存在公约数的两个n值得到p,q:RSA5
套路参考https://err0rzz.github.io/2017/11/14/CTF%E4%B8%ADRSA%E5%A5%97%E8%B7%AF/index.html
writeup参考https://beiyuouo.github.io/2019/05/30/ctf-buuctf/
RSA & what
发现相同的明文使用不同e加密,且n相同,想到是共模攻击,攻击得到一堆base64字符串,解密得到这样一段话:
THIS FLAG IS HIDDEN. CAN YOU FIND IT OUT? DO YOU KNOW BASE64? YoungC THINK YOU ARE NOT THAT FAMILIAR WITH BASE64. Base64 is a group of similar binary-to-text encoding schemes that represent binary data in an ASCII string format by translating it into a radix-64 representation. The term Base64 originates from a specific MIME content transfer encoding. The particular set of 64 characters chosen to represent the 64 place-values for the base varies between implementations. The general strategy is to choose 64 characters that are both members of a subset common to most encodings, and also printable. This combination leaves the data unlikely to be modified in transit through information systems, such as E-mail, that were traditionally not 8-bit clean.[1] For example, MIME's Base64 implementation uses A�CZ, a�Cz, and 0�C9 for the first 62 values. Other variations share this property but differ in the symbols chosen for the last two values; an example is UTF-7.
根据这段话给出的提示怀疑是base64加密,验证发现每个base64串解密后再加密果然与原base串不同,于是解密得到一串数值,即为flag。这里给出流程的完整脚本。
1 from libnum import n2s,s2n 2 import base64 3 import codecs 4 from gmpy2 import invert 5 def egcd(a, b): 6 if a == 0: 7 return (b, 0, 1) 8 else: 9 g, y, x = egcd(b % a, a) 10 return (g, x - (b // a) * y, y) 11 12 def bb(c1,c2): 13 n = 14 e1 = 15 e2 = 16 s = egcd(e1, e2) 17 s1 = s[1] 18 s2 = s[2] 19 if s1<0: 20 s1 = - s1 21 c1 = invert(c1, n) 22 elif s2<0: 23 s2 = - s2 24 c2 = invert(c2, n) 25 m = pow(c1,s1,n)*pow(c2,s2,n) % n 26 return hex(m)[2:] 27 #print (n2s(m)) 28 29 def get_base64_diff_value(s1, s2): 30 base64chars = 'ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789+/' 31 res = 0 32 for i in xrange(len(s1)): 33 if s1[i] != s2[i]: 34 return abs(base64chars.index(s1[i]) - base64chars.index(s2[i])) 35 return res 36 37 def main(): 38 c1=[,,,,] 39 c2=[,,,,] 40 ss='' 41 for i in range(6): 42 ss+=bb(c1[i],c2[i]) 43 bases=codecs.decode(ss, 'hex') 44 m=bases.split("\n") 45 bin_str = '' 46 for i in m: 47 steg_line=i 48 norm_line = steg_line.decode('base64').encode('base64') 49 diff = get_base64_diff_value(steg_line, norm_line) 50 pads_num = steg_line.count('=') 51 if diff: 52 bin_str += bin(diff)[2:].zfill(pads_num * 2) 53 else: 54 bin_str += '0' * pads_num * 2 55 res_str = '' 56 57 for i in xrange(0, len(bin_str), 8): 58 res_str += chr(int(bin_str[i:i + 8], 2)) 59 print 'flag{'+res_str+'}' 60 if __name__ == '__main__': 61 main()
Only when you plant the flowers can you really smell their fragrance.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh