New tool: teeplus.py
This new tool, teeplus.py, is an extension of the tee command.
The tools takes (binary) data from stdin, and sends it to stdout, while also writing the data to a file on disk.
While the tee command requires a filename as argument, teeplus.py takes no arguments (only options).
By default, teeplus.py will write the data to a file on disk, with filename equal to the sha256 of the data and extension .vir.
And it will also log this activity in a log file (teeplus.log by default).
Here is an example.
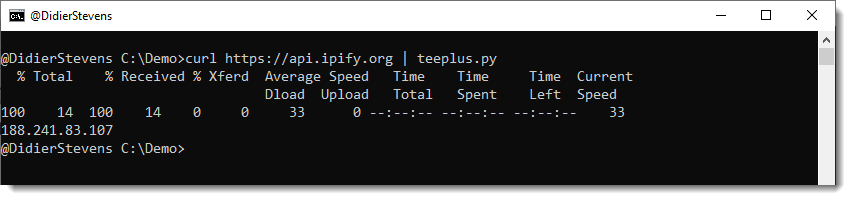
I run curl with a request to ipify to get my current public IPv4 address:

Then I pipe this output to teeplus.py:

This results in the creation of two files inside the current directory:

The first file it the output of the curl command:

The filename is the SHA256 hash of the data with extension .vir:

The second file, teeplus.log, is a log file:

Each line in teeplus.log has 4 fields (comma separated):
- The ISO timestamp when the activity was logged
- The length in bytes of the data
- The SHA256 hash of the data
- An error message (empty string when no error occured)
A line is created for each invocation of the teeplus.py command:

When the IPv4 address changes:

And the command is executed again, a new .vir file is created (since the received data changed):

And this is reflected in the log file:


This allows you to create a log of your public IPv4 address, for example (by scheduling this command as a recurrent task).
I use it for monitoring websites, and saving a copy of the HTML page I downloaded. I will explain how in an upcoming blog post.
teeplus.py has a couple of options: you can change the extension of the saved file, and the filename of the log file. And you can also us option -n to prevent the data to be piped to stdout (or you could redirect to /dev/null).
This is something I would do when the teeplus.py command is not followed by another command.

teeplus_V0_0_1.zip (http)
MD5: 0A3704CD56BD6B3A1FF2B92FD87476FB
SHA256: 9E3CBE7323D83FFC588FD67F7B762F53189391A43EDF465C64BD0E4D8E7E8990
No comments yet.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh