RondoDox expands botnet by exploiting XWiki RCE bug left unpatched since February 202 2025-11-17 08:4:19 Author: securityaffairs.com(查看原文) 阅读量:16 收藏
RondoDox expands botnet by exploiting XWiki RCE bug left unpatched since February 2025
Pierluigi Paganini
November 17, 2025

RondoDox botnet exploits unpatched XWiki flaw CVE-2025-24893 to gain RCE and infect more servers, despite fixes released in February 2025.
RondoDox is targeting unpatched XWiki servers via critical RCE flaw CVE-2025-24893 (CVSS score of 9.8), pulling more devices into its botnet despite patches released in Feb 2025.
The XWiki Platform is a generic wiki framework that provides runtime services for applications built on top of it. The vulnerability CVE-2025-24893 resides in its SolrSearch feature. This flaw allows unauthenticated users, essentially any guest, to execute arbitrary code on the server, posing a severe risk to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the entire XWiki installation. The vulnerability works by injecting Groovy code into the RSS feed generation mechanism through a specially crafted request to the SolrSearch endpoint.
This issue was patched in XWiki versions 15.10.11, 16.4.1, and 16.5.0RC1, and users are strongly advised to upgrade immediately.
At the end of October, the U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) added the XWiki Platform flaw to its Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog.
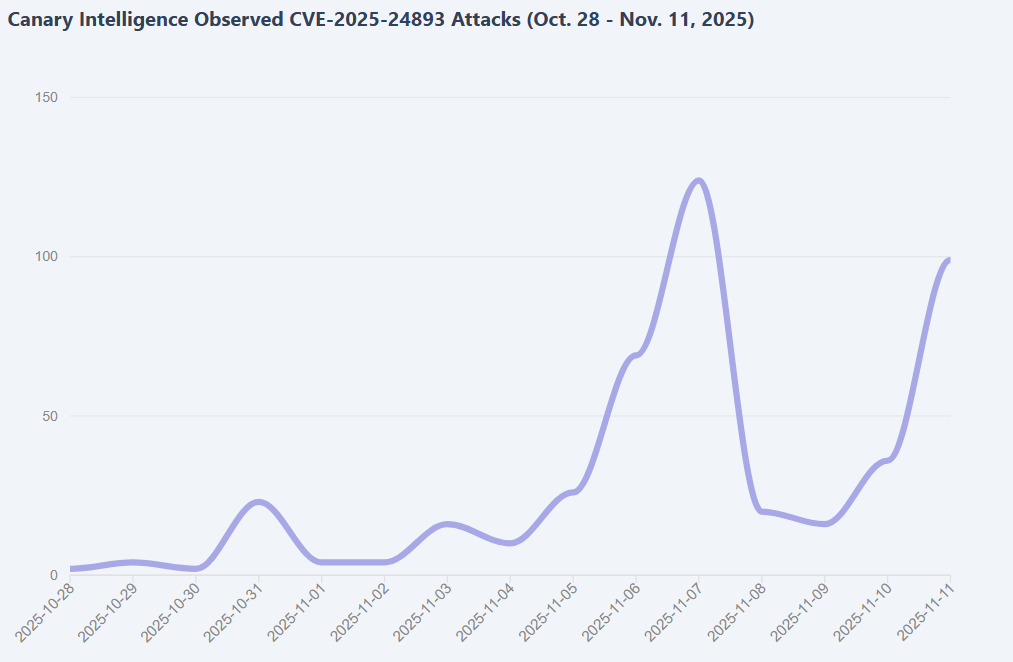
“Since our initial publication, exploitation has expanded quickly. Multiple independent attackers are now actively targeting CVE-2025-24893.” reads the report published by VulnCheck. “We saw a sharp uptick in attacks when the RondoDox botnet added this vulnerability to its repertoire. The first RondoDox exploit was observed on November 3, 2025, and activity has grown steadily since.”

Attacks exploiting CVE-2025-24893 surged after the RondoDox botnet started targeting the flaw on November 3, 2025. Activity is easily linked to RondoDox via its User-Agent and payload names, with servers like 74.194.191[.]52 delivering malicious scripts. Other actors joined in: on November 7, IP 172.245.241[.]123 fetched an obfuscated payload leading to a coin miner, and more miners were deployed through second-stage payloads.
“The obfuscated payload downloads a secondary payload which in turn fetches and executes a coin miner.” continues the report. “There is no lack of coin miner activity. On November 7, 2025, 156.146.56[.]131 fetched a secondary payload from 47.236.194[.]231:81 (the host is now offline). The secondary payload was executed in a second-pass exploit, as discussed in XWiki CVE-2025-24893 Exploited in the Wild.”
Attackers exploiting CVE-2025-24893 tried several reverse shells, showing either manual hacking or automated tools avoiding normal HTTP traffic. An AWS IP (18.228.3[.]224) sent both reverse-shell attempts and special OAST probes, suggesting a more targeted attack.
Another IP (118.99.141[.]178) likely came from a compromised QNAP/DrayTek device and also tried a bash shell. Meanwhile, many others are just scanning the internet for vulnerable XWiki servers using Nuclei and simple commands like id, whoami, and /etc/passwd to confirm exploitation.
“CVE-2025-24893 is a familiar story: one attacker moves first, and many follow. Within days of the initial exploitation, we saw botnets, miners, and opportunistic scanners all adopting the same vulnerability.” concludes the report. “Once again, this highlights the gap between exploitation in the wild and visibility at scale. By the time an issue lands in CISA KEV, attackers are already days ahead, and early detection remains the only real advantage defenders have.”
Follow me on Twitter: @securityaffairs and Facebook and Mastodon
(SecurityAffairs – hacking, RondoDox botnet)
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh