好的,我现在需要帮用户总结一篇文章的内容,控制在100字以内。首先,我得仔细阅读文章,抓住主要信息。 文章主要讲的是2025年勒索软件攻击激增了50%,涉及的团伙包括Qilin和一些新团体。他们利用漏洞,主要攻击美国、韩国等地区。文章还提到Qilin在9月份表现突出,成为最大目标。此外,供应链攻击和数据泄露事件增多,安全团队需要加强防范措施。 接下来,我需要将这些要点浓缩到100字以内。要确保涵盖攻击激增、主要团伙、目标地区、Qilin的表现以及防范建议。 可能会这样组织语言:“2025年勒索软件攻击激增50%,Qilin等团伙利用漏洞,主要针对美国、韩国等地。Qilin在9月成为最大目标,供应链攻击和数据泄露增多。安全团队需加强防范措施。” 这样既涵盖了主要信息,又控制在了字数限制内。 </think> 2025年勒索软件攻击激增50%,Qilin等团伙利用漏洞,主要针对美国、韩国等地。Qilin在9月成为最大目标,供应链攻击和数据泄露增多。安全团队需加强防范措施。 2025-10-24 13:46:11 Author: cyble.com(查看原文) 阅读量:21 收藏
Ransomware attacks surged 50% in 2025, with groups like Qilin and newcomers exploiting vulnerabilities, targeting the U.S., South Korea, and other global regions.
Despite major changes in the leading ransomware groups, ransomware attacks have surged 50% in 2025, as cybercriminals have proven adept at finding new opportunities and exploiting vulnerabilities.
Ransomware attacks were up 50% in 2025 through October 21, according to Cyble data, rising to 5,010 from 3,335 in the same period of 2024. Cyble’s data is based on ransomware group claims on their dark web data leak sites.
From the decline of RansomHub to the rise of Qilin and newcomers like Sinobi and The Gentlemen, ransomware group leadership has been in flux for much of 2025, but affiliates have been quick to find new opportunities, and a steady supply of critical vulnerabilities has helped fuel attacks.
Dramatic changes in the ransomware landscape were among the revelations in Cyble’s just-published September 2025 threat landscape report. The report also documents record data breaches, a surge in supply chain attacks, and the most active threat groups and malware families.
Qilin Led All Ransomware Groups in September 2025
Ransomware attacks rose for the fifth consecutive month in September, and Qilin led all ransomware groups in claimed victims for the fifth time in six months.
Overall, ransomware groups claimed 474 victims in September. That’s up slightly from August and well below February’s record, yet still among the highest monthly ransomware attack totals on record (chart below).

The U.S. remains the biggest target for ransomware groups, with its 259 claimed victims accounting for nearly 55% of attacks in September (chart below). Germany, France, Canada, Spain, Italy, and the UK remain significant targets, but an unexpected change in September was the emergence of South Korea as a major target, in second place behind the U.S. with 32 attacks. That’s largely due to one campaign by Qilin.

All but three of the 32 South Korean attacks came from Qilin’s “KoreanLeak” campaign, which targeted asset management companies in the country. Published data samples for each entity included financial records and scanned personal documents, suggesting exposure of both corporate and individual data. One of the asset management firms said its systems were impacted through a ransomware attack on its IT management provider, indicating a possible supply chain compromise affecting multiple firms simultaneously.
The campaign also made South Korea by far the most attacked country in the APAC region in September, well ahead of India, Thailand, and Taiwan (chart below).

Qilin’s South Korean campaign made Banking, Financial Services and Insurance (BFSI) the third most attacked sector in September, behind Construction and Manufacturing and ahead of Professional Services, IT and Healthcare (chart below).

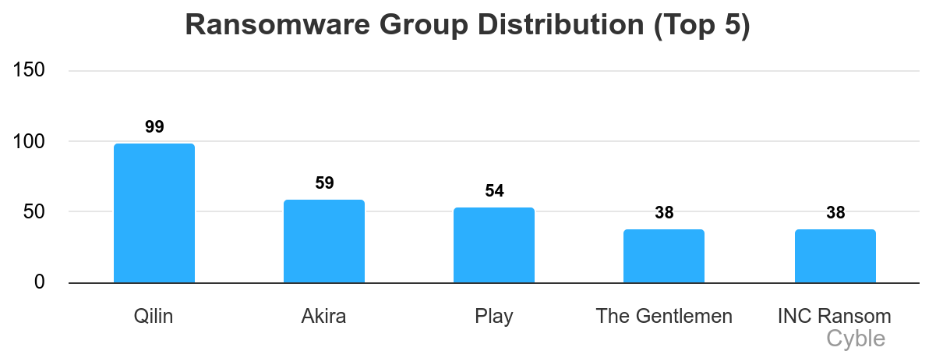
Qilin led all ransomware groups once again, its 99 claimed victims, 40 ahead of second-place Akira (chart below).

Also of note is the emergence of The Gentlemen, a new group that has claimed 46 victims to date. The group’s use of custom tools targeting specific security vendors and the geographic diversity of its targets (chart below) suggest that the group may have the resources to become an enduring threat.

The ransomware incidents in September that attracted by far the most attention were crippling cyberattacks on a major UK automaker and European airports.
Significant Ransomware Attacks in September 2025
Here are some of the key ransomware incidents documented by Cyble in September 2025.
The threat group Scattered LAPSUS$ Hunters claimed responsibility for the crippling cyberattack on the UK automaker, posting multiple screenshots suggesting unauthorized access to the company’s infrastructure. The group has an established pattern of leveraging supply chain vulnerabilities and social engineering, though the specific attack path in this case remains unverified.
Reports suggest that the disruption of operations at European and UK airports was due to a supply-chain ransomware attack affecting widely used check-in and boarding software. While the ransomware attacker remains unclear, the Everest ransomware group has since claimed exfiltration of more than 50GB of data.
The Play ransomware group claimed responsibility for breaches at two notable U.S.-based IT providers that could trigger supply chain risks. The first was a cybersecurity and software assurance firm providing services such as vulnerability assessment and mitigation, supply chain and third-party trust, DevSecOps transformation, cyber resiliency for weapons systems and space architectures, and OT/ICS resilience for both government and private sector clients. The second victim was a company specializing in digital cloud, hybrid, and edge solutions that enable high-speed data access and management across distributed environments.
The Akira ransomware group claimed an attack on an Australian company that provides OT & ICS services for various critical sectors. Akira claimed to have stolen 10GB of corporate data, including employee information (passports, driver’s licenses, medical records, and birth/death certificates), as well as confidentiality agreements, contracts, financial records, and project documentation.
The ArcusMedia ransomware group claimed responsibility for a cyberattack on an Egypt-based company that provides ERP and enterprise software solutions, including accounting, HR, payroll, inventory, and customer management systems.
The Warlock ransomware group claimed responsibility for attacks on a Taiwan-based company that provides automated test equipment and turnkey solutions for power electronics and semiconductor industries and a U.S.-based provider of cloud and managed IT services.
The SafePay ransomware group claimed responsibility for a cyberattack against a U.S.-based artificial intelligence company that develops AI-driven platforms and software designed to optimize business operations. The group did not publish any samples to substantiate the claim.
Akira claimed an attack on a U.S.-based chemical company, alleging the theft of more than 161 GB of data that included financial data, employee and customer information, confidential information, and NDAs. The company provides chemicals for water, air and soil treatments and serves several critical industries such as Municipalities, Semiconductor, Pharmaceutical, Mining, Energy & Utilities, and Manufacturing.
Qilin claimed a cyberattack on a U.S.-based company that provides data storage and data management solutions for enterprises and government agencies. The threat group did not specify the volume of data allegedly stolen but stated that it included information required to log into client vaults, personal data of employees and customers, financial records, and blueprints of network infrastructure. To support its claims, Qilin published five samples, including a confidential agreement between the company’s Australian subsidiary and a client, financial statements and documents from 2021, employee salary proposals from 2023, and technical documentation marked as confidential. However, Cyble noted that the nature of the samples raised questions about the extent of the breach and whether Qilin may be exaggerating its claims.
Conclusion
With cyberattacks of all kinds at or near all-time highs – and becoming dramatically more damaging – security teams must respond with renewed vigilance. The good news is that basic cybersecurity best practices can offer protection against a wide range of cyber threats. Recommended cybersecurity best practices include:
- Prioritizing vulnerabilities based on risk
- Protecting web-facing assets
- Segmenting networks and critical assets
- Hardening endpoints and infrastructure
- Strong access controls, allowing no more access than is required, with frequent verification
- A strong source of user identity and authentication, including multi-factor authentication and biometrics, as well as machine authentication with device compliance and health checks
- Encryption of data at rest and in transit
- Ransomware-resistant backups that are immutable, air-gapped, and isolated as much as possible
- Honeypots that lure attackers to fake assets for early breach detection
- Proper configuration of APIs and cloud service connections
- Monitoring for unusual and anomalous activity with SIEM, Active Directory monitoring, endpoint security, and data loss prevention (DLP) tools
- Routinely assessing and confirming controls through audits, vulnerability scanning, and penetration tests
Cyble’s comprehensive attack surface management solutions can help by scanning network and cloud assets for exposures and prioritizing fixes, in addition to monitoring for leaked credentials and other early warning signs of major cyberattacks.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh