
文章介绍Escape DAST的新功能——多用户测试能力,用于检测多租户SaaS应用中的跨租户访问和数据泄露风险。该功能支持三种场景:独立用户探索、对称权限隔离测试和非对称权限双向测试,并引入自然语言规则生成技术简化配置流程。 2025-10-23 16:15:55 Author: securityboulevard.com(查看原文) 阅读量:16 收藏
Most of today’s SaaS structures are multi-tenant environments. Making sure that each tenant’s data and resources are securely isolated from others is critical. Weaknesses or misconfigurations in tenant isolation can lead to unauthorized access or data leaks between tenants, compromising the security of the entire system.
If you’re serious about maintaining strict isolation and protecting your tenants' data (so you can relax when the Thanksgiving madness hits), this product release is right up your alley!
Our new multi-user testing capabilities in Escape DAST allow you to test security from all angles, ensuring that users with different permissions or roles can’t access unauthorized data.
Why is Multi-User Testing Important?
For multi-tenant SaaS applications, ensuring proper tenant isolation and access control is essential. Vulnerabilities like Broken Access Control (BAC) or Cross-User Data Breaches can arise when tenants or users with the same or different permissions inadvertently access unauthorized data. Our new multi-user testing capabilities are designed to help you detect these vulnerabilities before they become security risks.
The Science Behind Multi-User Security Testing
Multi-user security testing can be systematically categorized into exactly three distinct use cases, each representing a fundamentally different testing objective. These use cases are mathematically comprehensive: they cover all possible combinations of user exploration requirements and permission symmetry.
When testing applications with multiple users, two critical dimensions must be considered:
- Exploration Coverage: Does one or all users require full application crawling?
- Permission Symmetry: Do users possess equivalent or different privilege levels?
These dimensions yield precisely three mutually exclusive scenarios that encompass all possible multi-user testing requirements. Escape has been architected to support all three scenarios by design, ensuring your app is tested from every critical angle.
Use Case 1: Independent User Exploration (Previously Supported)
Scenario: Complete application behavior analysis is required for multiple distinct user roles or personas.
Real-world use case examples:
- SaaS Platform Testing: A project management tool must be validated separately for Account Owners, Project Managers, and Team Members, as each role interacts with fundamentally different features and API endpoints.
- Healthcare Systems: HIPAA compliance requires demonstrating that Physicians, Nurses, and Administrative Staff each have appropriately scoped access to patient records, with distinct workflows that must be independently verified.
- E-commerce Marketplaces: Separate security validation is needed for Buyers, Sellers, and Marketplace Administrators, as each persona accesses different subsets of the platform.
How it works in the Escape DAST platform:
Two or more scan profiles should be created, with each profile configured to perform complete crawling and security testing for a specific user. While the scans operate independently, issues discovered across multiple profiles are automatically deduplicated at the asset level. This ensures that common vulnerabilities appear only once in unified views such as "All Issues" or the "ASM Asset View," while role-specific vulnerabilities remain properly attributed to their respective user contexts.
Use Case 2: Symmetric Permission Tenant Isolation Testing (Now Supported)
This fall, we’re introducing two new multi-user testing approaches to Web Apps that ensure both symmetric and asymmetric permission scenarios are tested and validated for tenant isolation.
With symmetric permission testing, you can validate that users with identical roles or permission levels across tenants cannot access each other’s data. This approach is critical for applications where users across different tenants have the same privileges but should still be properly isolated.
Real-world use case examples:
- Multi-Tenant SaaS Applications: Ensure that, for example, Company A’s sales reps can’t access Company B’s customer data, even though both have identical "Sales Rep" permissions.
- Financial Services Platforms: Prevent standard account holders from accessing each other’s transaction history.
- Educational Platforms: Ensure students in different courses cannot view each other’s grades, submissions, or personal information.
How it works in the Escape DAST platform:
A single scan profile is configured with a primary user for exploration and secondary users as exploitation targets. Escape tests for Broken Access Control, Tenant Isolation, and Cross-User Data Breaches by attempting to replay the primary user’s requests using secondary users’ credentials. Since permission levels are symmetric, this approach ensures violations are automatically detected in both directions.
Use Case 3: Asymmetric Permission Bidirectional Testing (Now Supported)
Asymmetric permission testing is designed for scenarios where users have different privilege levels, such as admins, standard users, or privileged roles in different domains. This type of testing validates that unauthorized access is prevented in both directions between users of different permission levels.
Real-world use case examples:
- Enterprise Applications with RBAC: Ensure that standard users cannot access admin endpoints, while admins cannot access standard user data.
- Healthcare Systems: Ensure that physicians cannot access admin records, while admins cannot view sensitive clinical data.
- Financial Platforms: Verify that portfolio managers can’t access compliance officer audit trails and vice versa.
How it works in the Escape DAST platform:
This testing requires two separate scan profiles to test both directions of authorization:
- Scan Profile A: Primary user is configured for exploration, secondary user as the target.
- Scan Profile B: Secondary user becomes the primary user, with the first user as the target.
This bidirectional approach captures vulnerabilities from both perspectives, ensuring all potential weaknesses are identified.
Multi-User Testing in APIs and Web Apps
Escape's multi-user testing configurations are now supported for both APIs and Web Apps. However, the security issues identified—Broken Access Control (BAC), Tenant Isolation failures, Insecure Direct Object References (IDOR), and Cross-User Data Breaches—are invariably manifestations of API-level authorization deficiencies.
- API DAST: Direct testing of REST, GraphQL, and other API protocols, where requests are constructed and sent directly to API endpoints
- Web App DAST: Browser-based testing where user interactions generate API traffic, which is then intercepted, analyzed, and replayed with modified authentication contexts
In web app DAST scenarios, the primary user is used for exploration and crawling to discover API endpoints through browser interactions. Secondary users are then employed to replay the captured API traffic with different authentication credentials, validating that the underlying APIs properly enforce authorization boundaries.
How to set up the configuration in Escape
Escape provides three configuration strategies for tenant isolation testing, each suited to different levels of specificity and customization requirements:
- Approach 1 (Newly Supported): Natural Language Rule Generation (AI-Assisted)
- Approach 2: Default Fingerprint-Based Detection
- Approach 3: Custom Detection Rules (Precision Targeting)
All configurations are supported for both APIs and web apps. For a detailed overview and step-by-step guide on configuring and using the tenant isolation detection rules, check out our documentation.
Introducing Natural Language Rule Generation to configuration approaches
In this article, we want to highlight one of the standout features we’re introducing this month. Escape DAST users can now use natural language to generate tenant isolation detection rules. With the integration of LLMs, Escape customers can now write detection rules in plain language, without needing to know complex syntax or code. This makes creating custom detection rules more accessible and intuitive than ever before.
How does it work?
- Write a natural language query describing the tenant isolation rule you want to create. Here is a configuration example (Identification issue):
security_tests:
tenant_isolation:
main_user: 'user1' # Primary user for exploration and baseline establishment
natural_language_rule: |
Ensure that a user's notes cannot be accessed by other users.
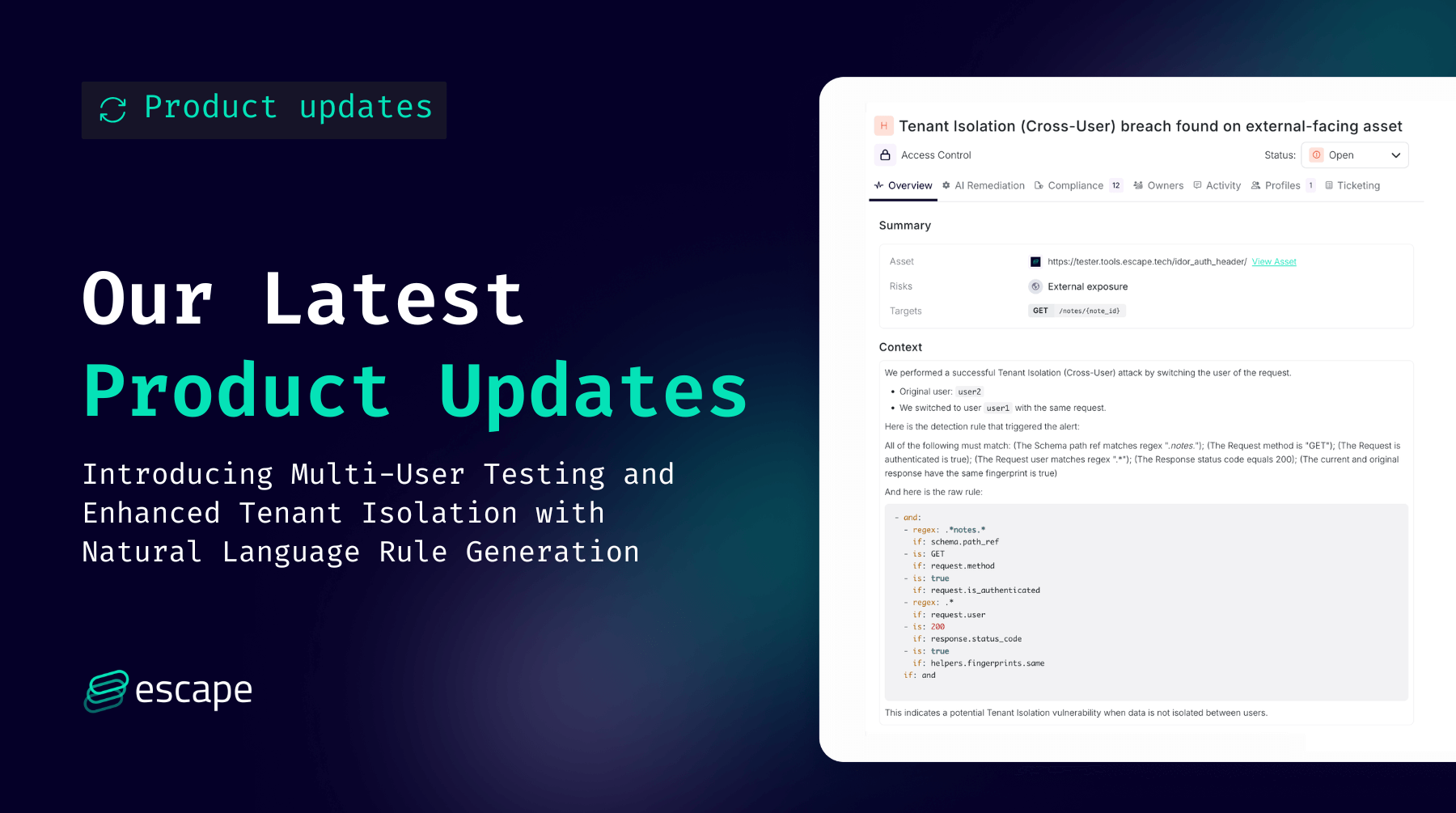
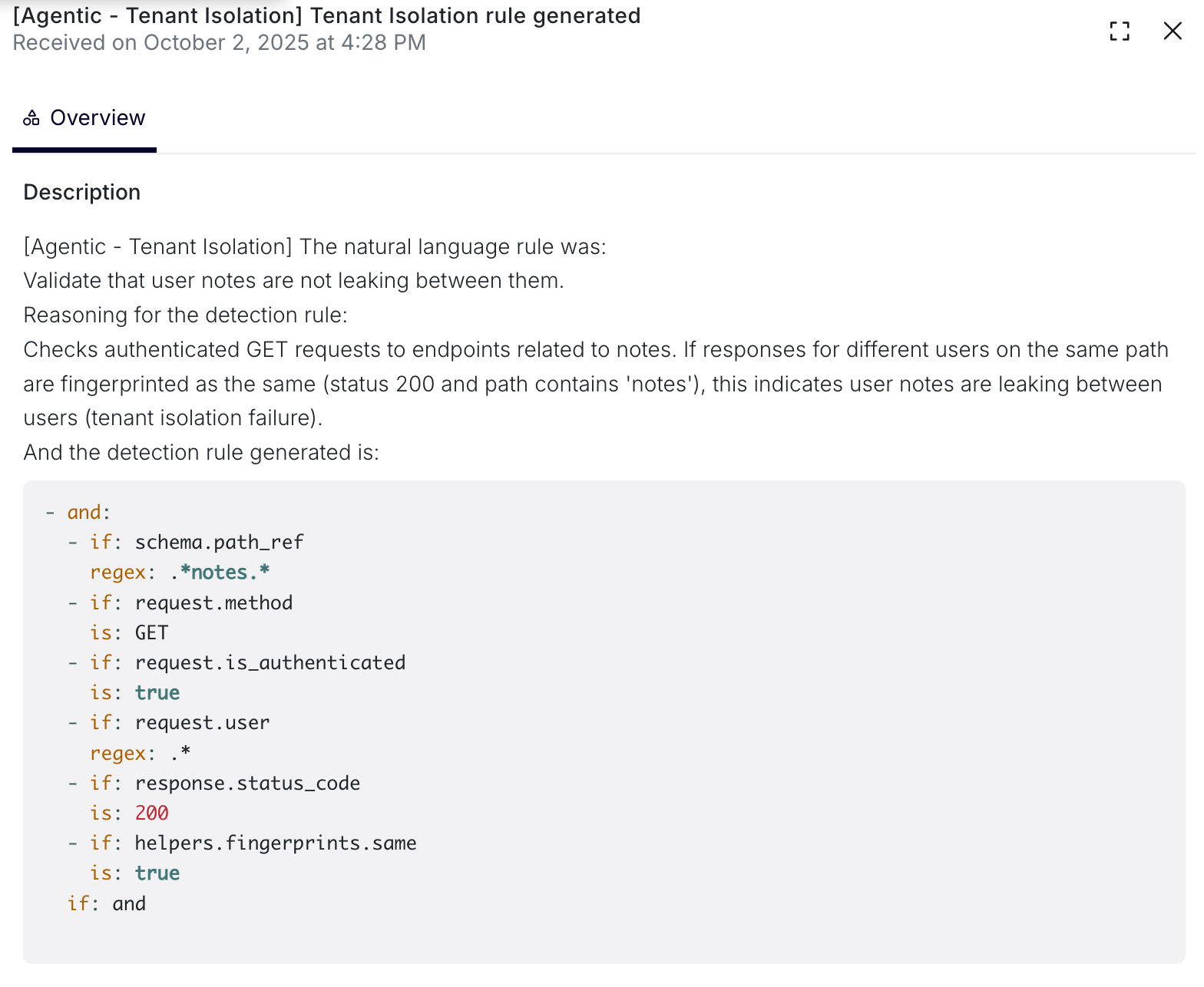
- The natural language description is then processed by Escape's agentic system, which generates a set of detection rules that validate the specified authorization boundary. The AI-generated detection logic is transparently displayed during scan execution:
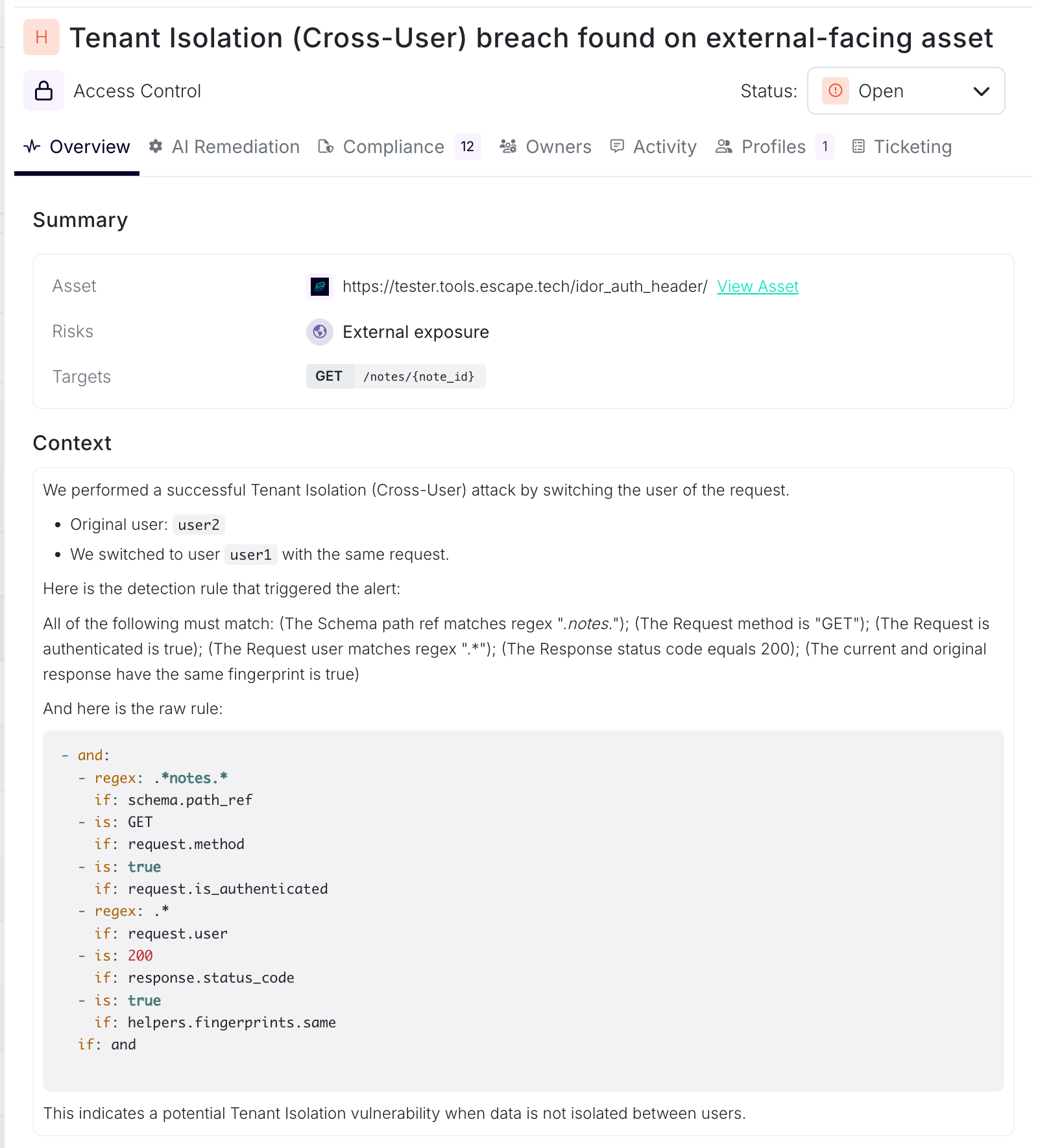
- When a tenant isolation violation is detected, the specific rule that triggered the finding is displayed alongside the vulnerability details:
Log Search and Rule Alerts
Once the detection rule is generated, you can easily track its activity through the logs. To monitor the generated detection rule:
- Search the logs for:
[Agentic - Tenant Isolation]
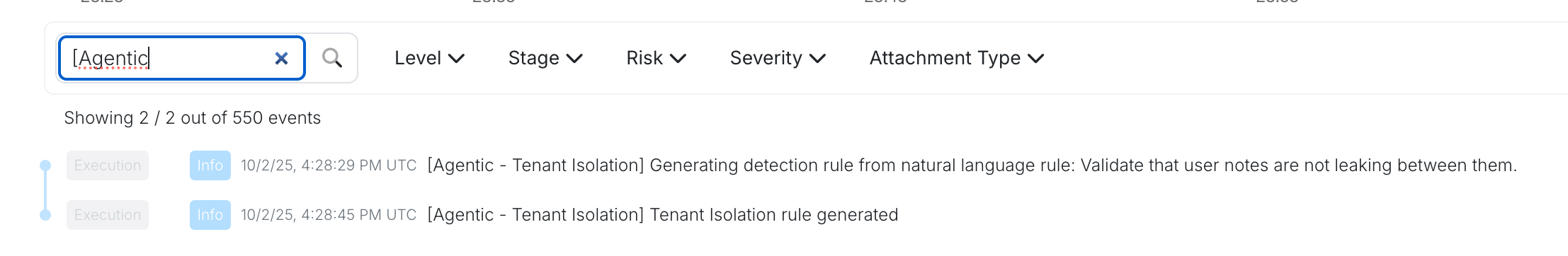
- You’ll find the logs detailing the generation of the tenant isolation rule.
Additionally, any relevant alerts will now contain the generated rule, making it even easier to manage and respond to potential isolation violations in your environment.
💡
When to use this approach?
This method is recommended when authorization boundaries can be clearly articulated in business logic terms, and when rapid configuration without deep technical rule definition is desired. It is particularly effective for domain-specific isolation requirements that would be cumbersome to express in low-level detection predicates.
To learn more about the other two approaches: Default Fingerprint-Based Detection and Custom Detection Rules (Precision Targeting), please visit our documentation.
How Escape Validates Authorization Boundaries
Once multiple users are configured in the scan's authentication settings, Escape automatically orchestrates authorization testing through credential replay and response analysis:
Credential Replay Testing:
API requests discovered or generated during exploration are systematically replayed with the authentication credentials of different users. Responses are compared to detect authorization failures.
Response Analysis and Fingerprinting:
Escape employs sophisticated response fingerprinting algorithms to detect when different users receive substantively identical responses, indicating potential authorization bypass. The analysis accounts for expected variations (timestamps, session identifiers, user-specific metadata) while identifying semantically equivalent data access.
Conclusion: Secure Your Multi-Tenant Environment with Confidence
With Escape DAST's tenant isolation testing, securing your multi-tenant SaaS applications has never been easier or more powerful. Whether you're ensuring that standard account holders can't access each other's transaction histories or preventing different company sales reps from viewing the same organization's customer data, Escape DAST has got you covered.
👉 Ready to get started? Read further about this feature in our documentation, or head to your Escape dashboard and make sure no user can access data they shouldn’t.
💡 Check out more product updates below:
- Introducing AI-Powered Exploit Validation and Remediation Guidelines
- August Product Updates: Enhancements to the Escape Public API and CLI, and the Introduction of Global Configuration Management
- More Support for Complex Authentication Flows: TOTP MFA and Text-Based CAPTCHA
*** This is a Security Bloggers Network syndicated blog from Escape DAST - Application Security Blog authored by Antoine Carossio. Read the original post at: https://escape.tech/blog/escape-dast-multi-user-testing-tenant-isolation/
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh
