As machine identities explode across cloud environments, enterprises report dramatic productivity gains from eliminating static credentials. And only legacy systems remain the weak link.
For decades, organizations have relied on static secrets, such as API keys, passwords, and tokens, as unique identifiers for workloads. While this approach provides clear traceability, it creates what security researchers describe as an "operational nightmare" of manual lifecycle management, rotation schedules, and constant credential leakage risks.
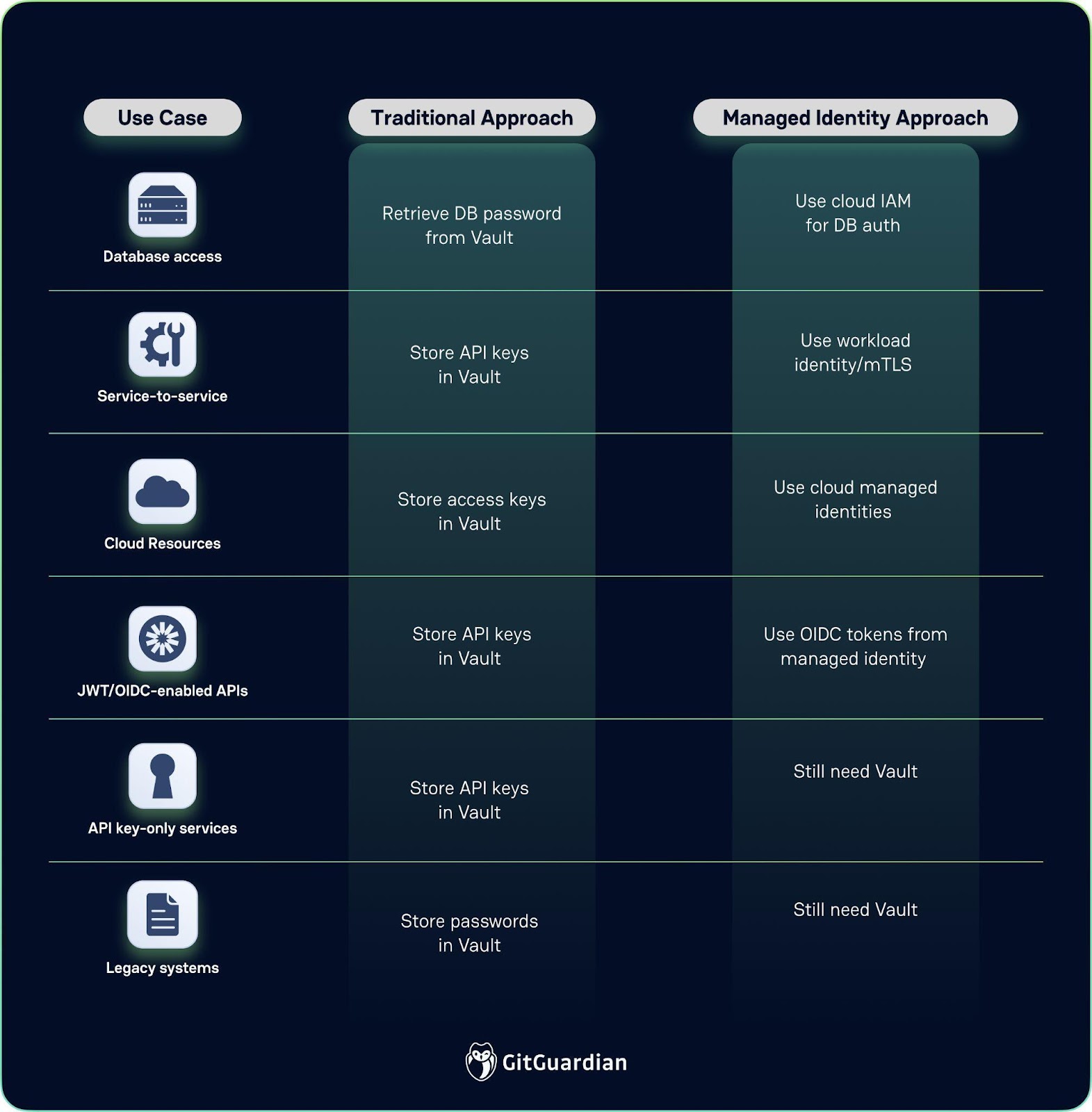
This challenge has traditionally driven organizations toward centralized secret management solutions like HashiCorp Vault or CyberArk, which provide universal brokers for secrets across platforms. However, these approaches perpetuate the fundamental problem: the proliferation of static secrets requiring careful management and rotation.
"Having a workload in Azure that needs to read data from AWS S3 is not ideal from a security perspective," explains one DevOps engineer managing a multicloud environment. "Cross-cloud authentication and authorization complexity make it hard to set this up securely, especially if we choose to simply configure the Azure workload with AWS access keys."
The Business Case for Change
Enterprise case studies document that organizations implementing managed identities report a 95% reduction in time spent managing credentials per application component, along with a 75% reduction in time spent learning platform-specific authentication mechanisms, resulting in hundreds of saved hours annually.
But how to approach the transition, and what prevents us from entirely eliminating static secrets?
Platform-Native Solutions
Managed identities represent a paradigm shift from the traditional "what you have" model to a "who you are" approach. Rather than embedding static credentials into applications, modern platforms now provide identity services that issue short-lived, automatically rotated credentials to authenticated workloads.
The transformation spans major cloud providers:
- Amazon Web Services pioneered automated credential provisioning through IAM Roles, where applications receive temporary access permissions automatically without storing static keys
- Microsoft Azure offers Managed Identities that allow applications to authenticate to services like Key Vault and Storage without developers having to manage connection strings or passwords
- Google Cloud Platform provides Service Accounts with cross-cloud capabilities, enabling applications to authenticate across different cloud environments seamlessly
- GitHub and GitLab have introduced automated authentication for development pipelines, eliminating the need to store cloud access credentials in development tools
The Hybrid Reality
However, the reality is more nuanced. Security experts emphasize that managed identities don't solve every authentication challenge. Third-party APIs still require API keys, legacy systems often can't integrate with modern identity providers, and cross-organizational authentication may still require shared secrets.
"Using a secret manager dramatically improves the security posture of systems that rely on shared secrets, but heavy use perpetuates the use of shared secrets rather than using strong identities," according to identity security researchers. The goal isn't to eliminate secret managers entirely, but to dramatically reduce their scope.
Smart organizations are strategically reducing their secret footprint by 70-80% through managed identities, then using robust secret management for remaining use cases, creating resilient architectures that leverage the best of both worlds.
The Non-Human Identity Discovery Challenge
Most organizations don't have visibility into their current credential landscape. IT teams often discover hundreds or thousands of API keys, passwords, and access tokens scattered across their infrastructure, with unclear ownership and usage patterns.
"You can't replace what you can't see," explains Gaetan Ferry, a security researcher at GitGuardian. "Before implementing modern identity systems, organizations need to understand exactly what credentials exist and how they're being used."
GitGuardian's NHI (Non-Human Identity) Security platform addresses this discovery challenge by providing comprehensive visibility into existing secret landscapes before managed identity implementation.
The platform discovers hidden API keys, passwords, and machine identities across entire infrastructures, enabling organizations to:
- Map dependencies between services and credentials
- Identify migration candidates ready for managed identity transformation
- Assess risks associated with current secret usage
- Plan strategic migrations rather than blind transformations
Found this article interesting? This article is a contributed piece from one of our valued partners. Follow us on Google News, Twitter and LinkedIn to read more exclusive content we post.