文章介绍了一种AI驱动的端口扫描工具LLM-Tools-Nmap,通过自然语言指令简化了Nmap的使用。该工具适用于网络安全专业人士,帮助他们高效执行复杂的网络侦察任务。文章详细讲解了安装、配置和使用方法,并提供了快速扫描、服务检测和漏洞分析等实用技巧。 2025-10-20 16:40:41 Author: www.blackmoreops.com(查看原文) 阅读量:8 收藏
AI-powered port scanning is revolutionising network reconnaissance by enabling cybersecurity professionals to execute complex Nmap commands through simple natural language instructions. This comprehensive guide will walk you through installing, configuring, and using AI-powered port scanning tools to enhance your security assessments. Whether you’re a seasoned penetration tester or developing your cybersecurity skills, this AI-powered port scanning tutorial will help you leverage artificial intelligence for more efficient network reconnaissance. If you want to learn more on NMAP, you would want to check out previous post on top 35 Nmap Commands for Hackers.
What Is AI-Powered Port Scanning?
Before diving into the implementation steps, it’s important to understand what makes AI-powered port scanning different from traditional approaches. For decades, Nmap has been the gold standard for network scanning, accumulating hundreds of command-line options and NSE scripts. Whilst this flexibility is powerful, it requires significant expertise to use effectively.
AI-powered port scanning changes this paradigm by introducing LLM-Tools-Nmap, a plugin that bridges Large Language Models (LLMs) with Nmap functionality. Instead of memorising complex command syntax, you simply describe what you want to discover in plain English, and the AI automatically selects appropriate Nmap commands, parses results, and identifies security issues.
The key innovation is function calling—the ability for an LLM to not just generate text, but to execute actual commands and interpret their results. The AI becomes an intelligent wrapper around Nmap, translating your intent into proper scanning commands and providing actionable insights from the results.
Step 1: Verify Your System Requirements
Before beginning your AI-powered port scanning setup, ensure your system meets the necessary requirements:
System Prerequisites:
- Kali Linux (2025.3 or earlier versions)
- Python 3.8 or higher
- Nmap installed (typically pre-installed on Kali Linux)
- Internet connection for downloading packages and API access
- Root or sudo privileges for Nmap execution
Check Your Kali Linux Version:
Open your terminal and run:
cat /etc/os-release
This displays your Kali version. Kali Linux 2025.3 includes LLM-Tools-Nmap in its repository, making installation simpler. Earlier versions require manual installation from GitHub.
Verify Nmap Installation:
nmap --version
If Nmap isn’t installed, add it using:
sudo apt update sudo apt install nmap
Check Python Version:
python3 --version
Ensure you’re running Python 3.8 or higher for compatibility with the llm CLI tool.
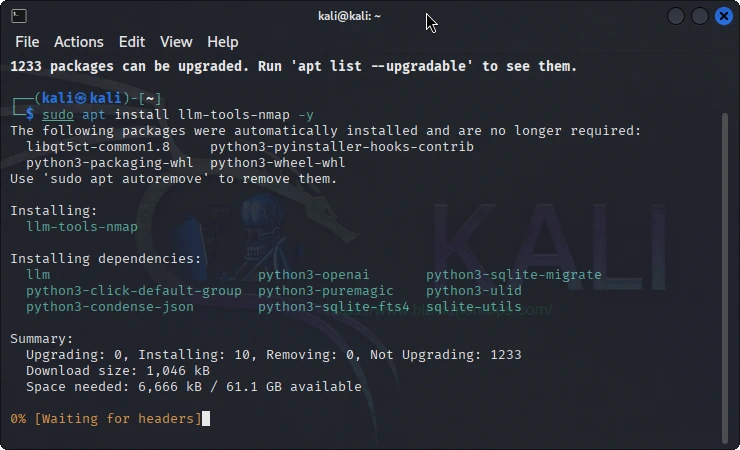
Step 2: Install LLM-Tools-Nmap
The installation process differs slightly depending on your Kali Linux version. Follow the appropriate method for your system.
Method A: Installing on Kali Linux 2025.3 (Repository Installation)
If you’re running Kali Linux 2025.3 or later, the installation is straightforward:
sudo apt update sudo apt install llm-tools-nmap
This automatically installs LLM-Tools-Nmap and its dependencies from the Kali repository.
Method B: Manual Installation from GitHub (Older Kali Versions)
For earlier Kali versions, install manually from the GitHub repository:
cd ~ git clone https://github.com/peter-hackertarget/llm-tools-nmap.git cd llm-tools-nmap
The repository will clone to your home directory, creating a new folder containing all necessary files for AI-powered port scanning.
Step 3: Install the Core LLM CLI Tool
Regardless of your installation method, you need the core llm CLI tool. This tool enables interaction with various Large Language Models and serves as the foundation for AI-powered port scanning.
Install Using pipx (Recommended for Isolated Environment):
Pipx creates isolated environments for Python applications, preventing dependency conflicts:
sudo apt install pipx pipx install llm pipx ensurepath
The ensurepath command ensures the llm tool is accessible from your terminal.
Alternative: Install Using pip:
If you prefer using pip directly:
pip3 install llm
Verify the Installation:
After installation, confirm the llm tool is working:
llm --version
You should see output similar to: llm, version 0.27.1
If the command isn’t recognised, close and reopen your terminal, or run:
source ~/.bashrc
Step 4: Choose and Configure Your LLM Model
AI-powered port scanning requires a Large Language Model to interpret your commands and analyse results. You have several options, each with different requirements and capabilities.
Understanding Your LLM Options
Option 1: OpenAI (Paid Service)
- Most capable and responsive
- Requires paid API key
- Best for professional environments
- Monthly costs based on usage
Option 2: Google Gemini (Free Tier Available)
- Excellent performance with free tier
- API key required (free to obtain)
- Suitable for most AI-powered port scanning tasks
- Recommended for beginners and testing
Option 3: Ollama (Local Models)
- Runs entirely on your machine
- No API costs or internet required
- Requires significant hardware (16GB+ RAM recommended)
- Privacy-focused option
For this guide, we’ll use Google Gemini due to its free tier and excellent performance.
You Might Be Interested In
Installing the Gemini Plugin
Install the llm-gemini plugin to enable Gemini support:
llm install llm-gemini
The installation process downloads and configures the necessary components for AI-powered port scanning with Gemini.
Obtaining Your Gemini API Key
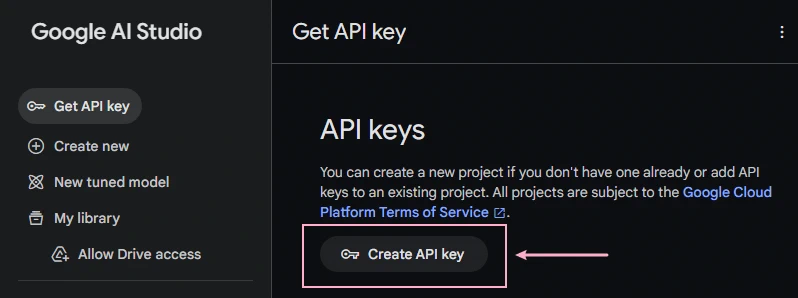
Visit the Google AI Studio to generate your free API key:
- Navigate to https://aistudio.google.com/apikey
- Sign in with your Google account
- Click “Create API Key”
- Select “Create API key in new project” (or choose an existing project)
- Copy the generated API key
Important: Store your API key securely. Don’t share it publicly or commit it to version control systems.
Configuring Your API Key
Set your Gemini API key for AI-powered port scanning:
llm keys set gemini
When prompted, paste your API key and press Enter. The key is stored securely in your system.
Verifying Available Models
List all available LLM models to confirm successful configuration:
llm models
You should see multiple Gemini models listed, including:
- gemini/gemini-2.0-flash
- gemini/gemini-2.5-pro-exp-03-25
- gemini/gemini-2.5-flash
- And several others
Setting Your Default Model
Choose a default model for AI-powered port scanning operations:
llm models default gemini-2.5-flash
The gemini-2.5-flash model offers an excellent balance between speed and capability for most scanning tasks.
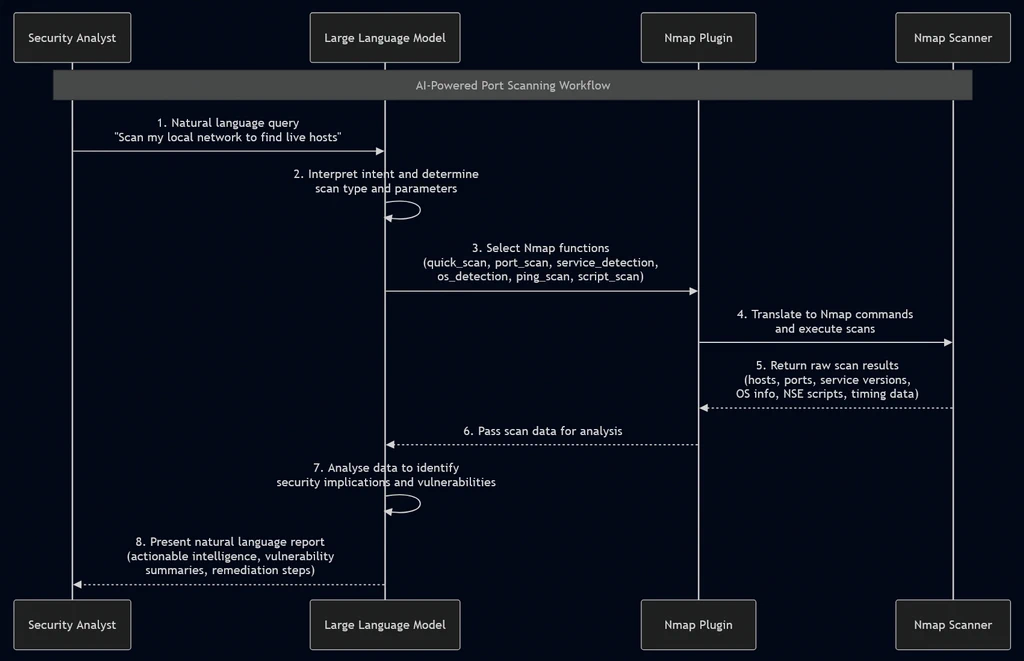
Step 5: Understanding the AI-Powered Port Scanning Architecture
Before executing scans, understanding how AI-powered port scanning works helps you use it more effectively.
The Function-Calling Process
The AI-powered port scanning workflow follows this sequence:
- User Query: You provide a natural-language instruction
- LLM Analysis: The AI interprets your intent and determines required Nmap functions
- Function Selection: The plugin identifies appropriate Nmap commands
- Command Execution: Nmap executes the selected scan against your target
- Output Capture: Results are collected and formatted
- AI Interpretation: The LLM analyses results for security implications
- Natural Language Summary: Findings are presented in clear, actionable language
Available Functions
LLM-Tools-Nmap provides eight core functions for AI-powered port scanning:
1. get_local_network_info():
- Discovers network interfaces on your system
- Identifies network ranges for scanning
- Suggests appropriate scan targets
2. nmap_quick_scan(target):
- Fast scan of common ports (approximately 1,000 most frequent)
- Uses timing template -T4 for speed
- Ideal for rapid initial reconnaissance
3. nmap_port_scan(target, ports):
- Scans specific port numbers or ranges
- Allows targeted investigation
- Useful when you know which services to check
4. nmap_service_detection(target, ports):
- Identifies service versions on open ports
- Attempts to determine exact software and version numbers
- Critical for vulnerability assessment
5. nmap_os_detection(target):
- Performs operating system fingerprinting
- Identifies the target’s OS and version
- Requires elevated privileges (root/sudo)
6. nmap_ping_scan(target):
- Discovers live hosts on a network
- Doesn’t perform port scanning
- Efficient for mapping network topology
7. nmap_script_scan(target, script, ports):
- Executes specific NSE (Nmap Scripting Engine) scripts
- Enables advanced vulnerability detection
- Provides detailed service information
8. nmap_scan(target, options):
- Generic function accepting custom Nmap options
- Provides flexibility for advanced users
- Bridges AI interface with manual control
The AI automatically selects which functions to use based on your natural language query, often chaining multiple functions for comprehensive AI-powered port scanning.
Step 6: Performing Your First AI-Powered Port Scanning Operation
Now that everything is configured, let’s execute your first AI-powered port scanning operation.
Discovering Your Local Network
Begin by identifying devices on your local network:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan my local network to find live hosts"
Understanding the Command Structure:
llm: Invokes the LLM CLI tool--functions llm-tools-nmap.py: Loads AI-powered port scanning functions"Scan my local network to find live hosts": Your natural language instruction
The AI will:
- Identify your network interfaces
- Determine appropriate network ranges
- Execute a ping scan to find live hosts
- Present results in a formatted table
Example Output:
The system might display something like:
Starting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-10-20 09:05 EDT Nmap scan report for Router-XF89-B7A2.lan (10.0.50.1) Host is up (0.00062s latency). MAC Address: 08:7E:3D:AA:72:F3 (ASUSTek Computer) Nmap scan report for 4bc72f9da1b6 (10.0.50.12) Host is up (0.00053s latency). MAC Address: 06:8A:D4:B2:05:1C (Unknown) Nmap scan report for 10.0.50.45 Host is up (0.0027s latency). MAC Address: 44:B9:6C:81:A4:29 (Netgear) Nmap scan report for 10.0.50.68 Host is up (0.12s latency). MAC Address: E2:D6:45:39:B1:7E (Unknown) Nmap scan report for Smart-Speaker-A.lan (10.0.50.71) Host is up (0.058s latency). MAC Address: B8:A4:67:91:2E:5D (Google) Nmap scan report for WRK-PC-08742.lan (10.0.50.74) Host is up. MAC Address: C6:21:5A:8D:E9:43 (Intel Corporate) Nmap scan report for 10.0.50.76 Host is up (0.11s latency). Nmap done: 256 IP addresses (7 hosts up) scanned in 8.84 seconds
Step 7: Conducting Rapid Reconnaissance with AI-Powered Port Scanning
After identifying live hosts, perform a quick port scan on a specific target.
Quick Port Scan
Replace <target_ip> with an IP address from your previous scan:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Do a quick port scan of <target_ip>"
For example:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Do a quick port scan of 192.168.0.100"
This AI-powered port scanning command executes a fast scan (-T4 -F) of approximately 1,000 common ports.
Typical Results:
The quick port scan on 192.168.0.100 shows that two ports are open: * Port 22/tcp - Running SSH (Secure Shell) * Port 80/tcp - Running HTTP (Web server) The host is up, and its MAC address is 11:22:33:44:55:66.
Understanding the Results
The AI interprets Nmap output and presents:
- Open ports and their numbers
- Associated protocols (TCP/UDP)
- Common services running on those ports
- Host status and basic network information
This rapid AI-powered port scanning approach provides a quick overview before conducting deeper investigation.
Step 8: Comprehensive Service Detection and Vulnerability Analysis
For thorough security assessment, request comprehensive reconnaissance combining multiple AI-powered port scanning techniques.
Multi-Stage Reconnaissance Command
Execute an in-depth scan with security analysis:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "What services are running on 192.168.0.100? Gather as much information as you can and identify any security issues or items of interest to a security analyst"
What Happens During Comprehensive AI-Powered Port Scanning
The AI orchestrates multiple scanning phases:
Phase 1: Initial Port Discovery
- Identifies all open ports on the target
- Determines which services are accessible
Phase 2: Service Version Detection
- Probes each open port to identify specific software
- Attempts to determine exact version numbers
- Collects banner information
Phase 3: NSE Script Execution
- Runs relevant Nmap Scripting Engine scripts
- Tests for common vulnerabilities
- Gathers additional service information
Phase 4: Operating System Detection
- Performs OS fingerprinting
- Identifies the target’s operating system
Phase 5: AI Analysis
- Evaluates collected data for security implications
- Identifies outdated software versions
- Highlights potential vulnerabilities
- Provides actionable recommendations
Sample Comprehensive Output
A typical comprehensive AI-powered port scanning report includes:
The target host 192.168.0.100 is running a Linux operating system and has two main services exposed:
### I. Services Identified
| Port | Protocol | Service | Version |
|-------|----------|---------|---------------------------------------------|
| 22 | TCP | SSH | OpenSSH 10.0p2 Debian 5 (protocol 2.0) |
| 80 | TCP | HTTP | Apache httpd 2.4.63 ((Debian)) |
### II. Security Analyst Review and Items of Interest
#### A. OpenSSH Service (Port 22)
* **Version:** OpenSSH 10.0p2 Debian 5 (protocol 2.0)
* **Security Concern:** OpenSSH version 10.0p2 is a very recent or potentially
unreleased/custom version. If this is an actual, non-standard version number,
it needs to be treated with caution. Assuming the Nmap output is accurate,
this version is likely bleeding-edge, which generally reduces the likelihood
of known, patched vulnerabilities, but does not eliminate zero-day risks.
* **Action:** Verify the exact source and patch level of this OpenSSH version.
Ensure that key security practices are enforced (e.g., strong ciphers,
disabled root login, key-based authentication, rate-limiting/fail2ban).
#### B. Apache HTTP Service (Port 80)
* **Version:** Apache httpd 2.4.63 ((Debian))
* **Security Concern (Versioning):** Apache 2.4.63 is a very high version
number. Current stable versions are typically in the low 2.4.x range (e.g.,
2.4.58). As with the SSH service, this version is either custom/bleeding-edge
or the reported version is slightly unusual. It is likely a well-patched
system, but the version should be verified.
* **Configuration/Default Content:**
* **Title:** "Apache2 Debian Default Page: It works"
* **Implication:** The website is currently displaying the default
installation page. This suggests the web server is either newly set up,
is not yet configured with actual content, or is only meant to serve as
a placeholder or internal testing server.
* **Security Risk:** The presence of a default page is low-risk itself,
but it indicates that the configuration has not been fully customised,
which might leave default directories, settings, or sample files exposed.
* **HTTP Headers:**
* **Server Disclosure:** The server explicitly discloses the full version:
"Server: Apache/2.4.63 (Debian)". This is a common practice but provides
attackers with specific target information. While not a vulnerability,
it is a policy/hardening issue that should be remediated by hiding or
obfuscating the server version.
* **Vulnerability Scan:** A general Nmap vulnerability script scan (`vuln`)
did not immediately identify any easy-to-exploit issues like CSRF or XSS
on the default page.
#### C. General System Information
* **Operating System:** Linux (Debian distribution is implied by the service
banners).
* **MAC Address:** 11:22:33:44:55:66 (Unknown Vendor).
* **Summary:** The host is a Linux server running recent/well-maintained
versions of the SSH and Apache services, but is currently displaying the
default Apache welcome page.
### III. Next Steps for the Analyst
1. **Version Verification:** Confirm the exact patch level and known
vulnerabilities for OpenSSH 10.0p2 and Apache 2.4.63.
2. **SSH Hardening:** Attempt to connect via SSH and check for:
* Password vs. Key authentication.
* Allowed users (Is `root` login permitted?).
* Available ciphers and key exchange algorithms.
3. **HTTP Directory Brute-Force:** Since the default page is up, use a tool
(like Nmap's `http-enum` or dedicated tools like dirb/dirbuster) to find
hidden or unlinked directories and files that may contain sensitive
information or configuration errors.
4. **Configuration Check:** Ensure the Apache configuration restricts access
to all unnecessary default directories (e.g., `/server-status`, `/manual`).
This comprehensive AI-powered port scanning report provides actionable intelligence for security assessment.
Step 9: Advanced AI-Powered Port Scanning Techniques
Once comfortable with basic operations, explore advanced AI-powered port scanning capabilities.
Operating System Detection
Identify the target’s operating system:
sudo llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Detect the operating system of 192.168.0.100"
Note: OS detection requires root privileges (hence sudo).
Specific Port Scanning
Target particular ports or ranges:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan ports 443, 8080, and 3306 on 192.168.0.100"
Or scan a range:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan all ports between 8000 and 9000 on 192.168.0.100"
Running Specific NSE Scripts
Execute targeted vulnerability checks:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Run the http-sql-injection script against port 80 on 192.168.0.100"
Or check for specific vulnerabilities:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Check if 192.168.0.100 is vulnerable to Heartbleed"
Scanning Multiple Targets
Scan entire subnets:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Perform a quick scan on all devices in the 192.168.0.0/24 network"
Or scan multiple specific hosts:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan 192.168.0.100, 192.168.0.101, and 192.168.0.102 for web services"
Step 10: Interpreting and Acting on AI-Powered Port Scanning Results
Understanding how to interpret and act upon AI-powered port scanning results is crucial for effective security assessment.
Prioritising Findings
The AI typically categorises discoveries into:
Critical Issues:
- Unpatched services with known exploits
- Default credentials
- Services vulnerable to active exploitation
High Priority:
- Outdated software versions
- Unnecessary services exposed
- Information disclosure issues
Medium Priority:
- Minor version updates available
- Configuration improvements recommended
- Security hardening opportunities
Informational:
- Service identification
- Network topology information
- General system characteristics
Creating Action Plans
Based on AI-powered port scanning results, develop remediation strategies:
For Outdated Services:
- Document the current version
- Research available updates
- Test updates in a staging environment
- Schedule maintenance windows for deployment
- Verify fixes with follow-up scans
For Exposed Services:
- Determine if the service is necessary
- Implement firewall rules if external access isn’t required
- Configure authentication where applicable
- Enable encryption for sensitive services
- Monitor access logs
For Configuration Issues:
- Review default configurations
- Remove or secure default content
- Disable unnecessary features
- Implement principle of least privilege
- Document changes for compliance
Documenting Your AI-Powered Port Scanning Results
Maintain comprehensive records of your scans:
Essential Documentation:
- Scan date and time
- Target systems scanned
- Commands executed
- Full output from AI-powered port scanning
- Identified vulnerabilities
- Recommended actions
- Implemented fixes
- Follow-up scan results
Creating Reports:
Export scan results by redirecting output:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Comprehensive scan of 192.168.0.100" > scan_report_$(date +%Y%m%d).txt
This creates a timestamped file containing your AI-powered port scanning results.
Step 11: Troubleshooting Common AI-Powered Port Scanning Issues
Even with proper setup, you may encounter issues. Here are solutions to common problems.
Issue 1: Command Not Found Errors
Symptom: llm: command not found
Solutions:
Ensure the llm tool is in your PATH:
export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"
Add this permanently to your .bashrc:
echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.local/bin:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc source ~/.bashrc
Verify installation:
which llm pipx list
Issue 2: API Key Errors
Symptom: Error: API key not configured or authentication failures
Solutions:
Verify your API key is set:
llm keys list
Reset your API key:
llm keys set gemini
Test API connectivity:
llm "Say hello"
Issue 3: Permission Denied for Scanning
Symptom: Nmap returns permission errors
Solutions:
Run with sudo for privileged scans:
sudo llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "your command here"
Ensure Nmap has proper permissions:
sudo chmod +x /usr/bin/nmap
Issue 4: Slow or Hanging Scans
Symptom: AI-powered port scanning takes excessively long or appears stuck
Solutions:
Reduce scan scope:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Quick scan of only common ports on 192.168.0.100"
Check network connectivity:
ping <target_ip>
Verify target is accessible:
nmap -sn <target_ip>
Issue 5: Incomplete or Vague Results
Symptom: AI provides insufficient detail or misses important findings
Solutions:
Be more specific in your queries:
# Instead of: "Scan this host" # Use: "Perform comprehensive service detection and vulnerability analysis on 192.168.0.100"
Request additional analysis:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Re-analyse the previous scan results and identify any security concerns I should investigate further"
Chain multiple queries for deeper investigation:
# First scan llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Quick scan of 192.168.0.100" # Follow-up based on results llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Now detect service versions on ports 22 and 80 of 192.168.0.100" # Further investigation llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Run vulnerability scripts against the Apache service on 192.168.0.100"
Step 12: Best Practices for AI-Powered Port Scanning
Maximise the effectiveness and safety of your AI-powered port scanning operations.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Always Obtain Authorization:
- Only scan systems you own or have explicit written permission to test
- Document your authorisation
- Stay within the scope of your engagement
- Be aware of relevant laws and regulations
Practice Responsible Disclosure:
- Report discovered vulnerabilities to system owners
- Allow reasonable time for remediation
- Follow coordinated disclosure principles
Operational Best Practices
Start Small:
- Begin with known systems in controlled environments
- Gradually expand scope as you gain confidence
- Test in lab environments before production
Combine AI with Manual Verification:
- Use AI-powered port scanning for initial reconnaissance
- Validate critical findings with manual Nmap commands
- Cross-reference results with other tools
Maintain Scan Schedules:
- Conduct regular scans to identify new issues
- Document changes between scans
- Track remediation progress
Optimise Query Clarity:
- Be specific about what you want to discover
- Include relevant context in queries
- Ask follow-up questions for clarification
Example Effective Queries:
# Good: Specific and actionable llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Identify all web services on 192.168.0.0/24 and check for outdated software versions" # Better: Includes context and desired analysis llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan the 192.168.0.0/24 network for web services, identify their versions, and flag any that are more than 12 months old or have known vulnerabilities"
Security Considerations
Protect Your API Keys:
- Never share API keys publicly
- Rotate keys periodically
- Use environment variables for automation
- Monitor API usage for anomalies
Secure Your Scan Data:
- Encrypt stored scan results
- Implement access controls on reports
- Sanitise data before sharing
- Follow data retention policies
Network Impact:
- Be mindful of scan intensity on production networks
- Schedule intensive scans during maintenance windows
- Communicate with network operations teams
- Monitor for unintended disruptions
Step 13: Integrating AI-Powered Port Scanning into Your Workflow
Incorporate AI-powered port scanning into your broader security operations.
Creating Scan Scripts
Automate routine AI-powered port scanning tasks:
#!/bin/bash # save as: weekly_scan.sh NETWORK="192.168.0.0/24" REPORT_DIR="$HOME/scan_reports" DATE=$(date +%Y%m%d_%H%M%S) mkdir -p "$REPORT_DIR" echo "Starting weekly network scan..." llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Comprehensive security scan of $NETWORK with vulnerability analysis" > "$REPORT_DIR/weekly_scan_$DATE.txt" echo "Scan complete. Report saved to $REPORT_DIR/weekly_scan_$DATE.txt"
Make executable and run:
chmod +x weekly_scan.sh ./weekly_scan.sh
Scheduling Automated Scans
Use cron for scheduled AI-powered port scanning:
crontab -e
Add weekly scans (Sundays at 2 AM):
0 2 * * 0 /home/yourusername/weekly_scan.sh
Integrating with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Export AI-powered port scanning results in formats compatible with your SIEM:
# Generate JSON-formatted output llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan 192.168.0.0/24 and format results as structured data" | jq '.' > scan_results.json
Collaboration and Reporting
Share findings with your team:
Create Executive Summaries:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan our production network and create an executive summary highlighting only critical and high-priority security issues"
Generate Technical Details:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Provide detailed technical analysis of all findings from the previous scan, including specific CVEs and remediation steps"
Step 14: Expanding Your AI-Powered Port Scanning Capabilities
Take your skills further by exploring advanced configurations and integrations.
Using Local LLM Models with Ollama
For complete privacy or offline scanning, set up local models:
Install Ollama:
curl https://ollama.ai/install.sh | sh
Download a Model:
ollama pull llama2
Configure llm for Ollama:
llm install llm-ollama
Use Local Models:
llm -m ollama/llama2 --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan 192.168.0.100"
Combining Multiple Security Tools
Integrate AI-powered port scanning with other reconnaissance tools:
Nmap + Nikto for Web Application Scanning:
# First: AI-powered port scanning to identify web servers llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Find all web servers on 192.168.0.0/24" # Then: Run Nikto against discovered web servers nikto -h 192.168.0.100
Nmap + Metasploit Integration:
Use AI-powered port scanning results to inform Metasploit targeting:
# Identify services and versions llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Detailed service detection on 192.168.0.100" # Use findings in Metasploit msfconsole msf6 > search apache 2.4.63 msf6 > use exploit/...
Custom Function Development
Advanced users can extend AI-powered port scanning with custom functions. Review the LLM-Tools-Nmap source code to understand function structure and create specialised scanning functions for your environment.
Step 15: Continuous Learning and Improvement
Stay current with AI-powered port scanning developments and enhance your skills.
Recommended Resources
Official Documentation:
Community Resources:
- Nmap mailing lists and forums
- Cybersecurity subreddits and Discord servers
- AI and machine learning in security conferences
Practice Environments
Develop your AI-powered port scanning skills safely:
Vulnerable Lab Environments:
- Metasploitable
- DVWA (Damn Vulnerable Web Application)
- VulnHub virtual machines
- HackTheBox and TryHackMe platforms
Home Lab Setup:
- Create isolated virtual networks
- Deploy various operating systems and services
- Practice different scanning scenarios
- Document your findings
Keeping AI-Powered Port Scanning Tools Updated
Regularly update your tools to access new features and security patches:
# Update LLM CLI tool pipx upgrade llm # Update LLM-Tools-Nmap (if installed from GitHub) cd ~/llm-tools-nmap git pull origin main # Update Nmap sudo apt update sudo apt upgrade nmap # Update all Gemini plugins llm install --upgrade llm-gemini
Measuring Your Progress
Track your AI-powered port scanning proficiency:
Beginner Milestones:
- Successfully complete installation and configuration
- Perform basic host discovery scans
- Identify open ports on target systems
- Interpret AI-generated reports
Intermediate Milestones:
- Conduct comprehensive service detection
- Identify and validate security vulnerabilities
- Create custom scanning scripts
- Integrate with other security tools
Advanced Milestones:
- Develop automated scanning workflows
- Contribute to open-source security tools
- Train others in AI-powered port scanning techniques
- Publish security research and findings
Conclusion: Mastering AI-Powered Port Scanning
AI-powered port scanning represents a significant evolution in network reconnaissance, making sophisticated Nmap operations accessible through natural language commands. By following this comprehensive guide, you’ve learned to install, configure, and effectively use LLM-Tools-Nmap for security assessments.
Remember that AI-powered port scanning serves as a powerful tool to augment, not replace, human expertise. The technology excels at streamlining routine reconnaissance tasks and making advanced scanning techniques more accessible, but experienced security professionals remain essential for interpreting context, making strategic decisions, and adapting to complex scenarios.
As you continue developing your AI-powered port scanning skills, maintain focus on the fundamentals: understanding network protocols, recognising service vulnerabilities, and following ethical security practices. The AI assists with execution and initial analysis, but your knowledge and judgement determine the quality of your security assessments.
Practice regularly in safe, authorised environments, stay current with emerging threats and vulnerabilities, and always prioritise responsible disclosure when discovering security issues. The combination of AI efficiency and human expertise creates a powerful approach to network security that benefits both individual practitioners and the broader cybersecurity community.
Whether you’re conducting routine network inventories, performing comprehensive penetration tests, or investigating potential security incidents, AI-powered port scanning streamlines your workflow whilst maintaining the depth and accuracy required for professional security work. Embrace this technology as part of your toolkit, continue learning, and contribute to the evolving landscape of AI-assisted cybersecurity operations.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI-Powered Port Scanning
Is AI-powered port scanning legal?
AI-powered port scanning is legal when conducted on systems you own or have explicit written permission to test. Unauthorised scanning of networks and systems you don’t control is illegal in most jurisdictions and can result in criminal prosecution. Always obtain proper authorisation before conducting any security assessments.
Can AI-powered port scanning replace traditional Nmap?
No, AI-powered port scanning complements rather than replaces traditional Nmap usage. Whilst the AI interface simplifies common tasks and provides intelligent analysis, experienced professionals still need direct Nmap access for fine-grained control in complex scenarios. The technology is best viewed as an additional tool in your security arsenal.
What are the costs associated with AI-powered port scanning?
The costs depend on your chosen LLM provider. Google Gemini offers a generous free tier suitable for most individual users. OpenAI requires a paid subscription with usage-based pricing. Local models through Ollama are free but require significant hardware investment. The core tools (Nmap and LLM-Tools-Nmap) are open source and completely free.
How accurate are AI-powered port scanning results?
The accuracy of AI-powered port scanning depends on several factors: the underlying Nmap scan quality, the LLM’s ability to interpret results, and the specificity of your queries. The AI uses the same reliable Nmap engine that security professionals have trusted for decades, so scan data accuracy is excellent. However, AI interpretation can occasionally miss nuances or require follow-up queries for complete analysis.
Can AI-powered port scanning detect zero-day vulnerabilities?
AI-powered port scanning excels at identifying known vulnerabilities, outdated software versions, and configuration issues. However, it cannot reliably detect previously unknown (zero-day) vulnerabilities. The AI analyses based on existing knowledge and known vulnerability databases. Zero-day discovery still requires human expertise, creative thinking, and often manual exploitation attempts.
What hardware do I need for AI-powered port scanning?
For cloud-based LLMs (Gemini, OpenAI), modest hardware suffices—any system capable of running Kali Linux and Nmap works fine. Internet connectivity is required for API access. For local LLM models through Ollama, you’ll need significantly more resources: at least 16GB RAM (32GB recommended), modern CPU with multiple cores, and substantial storage for model files.
How can I improve the quality of AI-powered port scanning responses?
Provide specific, detailed queries rather than vague requests. Include context about what you’re investigating and what findings interest you. Ask follow-up questions to drill deeper into initial results. Review and understand the AI’s analysis rather than accepting it uncritically. Combine AI insights with your own security knowledge for optimal results.
Is my scan data private when using AI-powered port scanning?
Data privacy depends on your LLM provider. Cloud-based services (Gemini, OpenAI) transmit your queries and scan results to their servers for processing. Review each provider’s privacy policy and terms of service. For maximum privacy, use local LLM models through Ollama, which process everything on your machine without external data transmission.
Can I use AI-powered port scanning in professional penetration testing?
Yes, AI-powered port scanning can be valuable in professional penetration testing engagements, particularly for initial reconnaissance and rapid assessment. However, always validate AI-generated findings manually, document your methodology thoroughly, and ensure your reports distinguish between AI-assisted and manual testing. Many clients appreciate the efficiency gains whilst maintaining professional testing standards.
What’s the future of AI-powered port scanning?
The future looks promising as AI models become more sophisticated and specialised for cybersecurity tasks. Expect improvements in vulnerability detection accuracy, better integration with additional security tools, enhanced reporting capabilities, and potentially AI assistance throughout the entire penetration testing lifecycle. However, human expertise will remain crucial for strategic decision-making and complex security challenges.
Additional Tips for Successful AI-Powered Port Scanning
Optimising Your Queries for Better Results
The quality of your AI-powered port scanning results directly correlates with query quality. Consider these optimisation strategies:
Include Specific Objectives:
# Vague query llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan this network" # Optimised query llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan 192.168.0.0/24 to identify all SSH servers, check their versions, and flag any running OpenSSH older than version 8.0"
Request Specific Analysis Depth:
# Basic query llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Check 192.168.0.100 for vulnerabilities" # Enhanced query llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Perform comprehensive vulnerability analysis on 192.168.0.100 including service detection, version identification, common vulnerability checks, and provide specific CVE numbers for any discovered issues"
Specify Output Format Preferences:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan our web servers and present results in a table format with columns for IP address, port, service, version, and security risk level"
Building an AI-Powered Port Scanning Knowledge Base
Document your scanning experiences to build institutional knowledge:
Create a Scanning Playbook:
- Common scan types and their queries
- Typical findings for different service types
- Remediation procedures for frequent issues
- Escalation criteria for serious vulnerabilities
Maintain a Query Library:
Save effective queries for reuse:
# Create a queries directory mkdir -p ~/ai-nmap-queries # Save useful queries echo 'llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Comprehensive web server security assessment of TARGET"' > ~/ai-nmap-queries/web_server_scan.sh # Make executable chmod +x ~/ai-nmap-queries/*.sh
Collaborating with Your Team
Share AI-powered port scanning capabilities across your security team:
Standardise Query Templates:
Create organisation-wide query templates for consistent results:
# quarterly_assessment.sh NETWORK=$1 QUARTER=$2 llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Conduct quarterly security assessment of $NETWORK focusing on: 1) All internet-facing services, 2) Outdated software versions, 3) Default configurations, 4) Missing security patches. Generate executive summary for Q$QUARTER compliance reporting."
Knowledge Sharing Sessions:
Conduct regular team meetings to:
- Share effective query techniques
- Discuss interesting findings from AI-powered port scanning
- Review and improve scanning methodologies
- Train new team members
Centralised Results Repository:
Establish a shared location for scan results:
# Create team repository structure
mkdir -p /shared/security/scans/{daily,weekly,monthly,incident_response}
# Save scans with consistent naming
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Daily scan of production network" > /shared/security/scans/daily/scan_$(date +%Y%m%d).txt
Real-World AI-Powered Port Scanning Scenarios
Scenario 1: New Device Discovery
Situation: Unknown devices appear on your corporate network.
AI-Powered Port Scanning Approach:
# Step 1: Identify all active devices llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Find all live hosts on our corporate network 10.0.0.0/16 and identify any devices that weren't present in our last scan" # Step 2: Detailed investigation of new devices llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Perform comprehensive reconnaissance on [new device IP] including OS detection, all open ports, running services, and any security concerns" # Step 3: Risk assessment llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Analyse the previous scan results and determine if [new device IP] poses security risks to our network"
Scenario 2: Vulnerability Management
Situation: Your organisation needs to identify systems requiring security patches.
AI-Powered Port Scanning Approach:
# Comprehensive vulnerability assessment llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan all servers in 10.0.10.0/24 data centre subnet, identify service versions, check for known vulnerabilities, and prioritise findings by severity with specific patch recommendations" # Generate remediation report llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Based on the previous vulnerability scan, create a prioritised remediation plan listing each vulnerable system, the specific vulnerability, available patches, and recommended timeline for implementation"
Scenario 3: Incident Response
Situation: Suspicious activity detected on a specific server.
AI-Powered Port Scanning Approach:
# Rapid initial assessment llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Emergency scan of potentially compromised server 10.0.5.50 - identify all open ports, unusual services, and any indicators of compromise such as backdoor ports or suspicious processes" # Comparison with baseline llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Compare current scan of 10.0.5.50 with our baseline configuration and highlight any differences in open ports, services, or configurations"
Scenario 4: Compliance Auditing
Situation: Preparing for security compliance audit.
AI-Powered Port Scanning Approach:
# PCI DSS compliance check llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan our payment processing environment 10.0.20.0/24 and verify compliance with PCI DSS requirements including: no unnecessary services, current security patches, proper segmentation, and secure configurations" # Generate audit documentation llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Create a compliance-ready report of the previous scan formatted for audit submission, including scan methodology, findings summary, and remediation status"
Scenario 5: Cloud Infrastructure Security
Situation: Assessing security of cloud-hosted resources.
AI-Powered Port Scanning Approach:
# Cloud instance assessment llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Scan our AWS EC2 instances at [IP ranges] and identify any services exposed to the internet that should be internal-only, check for proper security group configurations, and flag any high-risk exposures" # Container security llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Analyse our Kubernetes cluster nodes for exposed management interfaces, API endpoints without proper authentication, and any services running with elevated privileges"
Maximising the Value of AI-Powered Port Scanning
Integration with Security Orchestration
Combine AI-powered port scanning with security orchestration platforms:
SOAR Platform Integration:
# Trigger scan from SOAR playbook curl -X POST https://your-soar-platform.com/api/run-scan \ -d "command=llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py 'Scan new asset and report findings'"
Continuous Security Monitoring
Implement AI-powered port scanning as part of continuous monitoring:
Daily Delta Scanning:
#!/bin/bash
# daily_delta_scan.sh
NETWORK="10.0.0.0/8"
BASELINE="/security/baselines/network_baseline.txt"
CURRENT="/security/scans/current_scan.txt"
DELTA="/security/reports/delta_$(date +%Y%m%d).txt"
# Current scan
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Quick scan of $NETWORK" > "$CURRENT"
# Compare with baseline
diff "$BASELINE" "$CURRENT" > "$DELTA"
# Analyse changes with AI
if [ -s "$DELTA" ]; then
llm "Analyse these network changes and identify any security concerns: $(cat $DELTA)"
fi
Metrics and Reporting
Track AI-powered port scanning effectiveness:
Key Metrics to Monitor:
- Number of vulnerabilities identified per scan
- Average time to vulnerability discovery
- False positive rate
- Remediation time for identified issues
- Coverage percentage of network assets
- Scan frequency and consistency
Generate Trend Reports:
llm --functions llm-tools-nmap.py "Analyse the last 30 days of scan reports in /security/scans/monthly/ and generate a trend analysis showing: vulnerability discovery rates, most common security issues, remediation effectiveness, and recommendations for improving our security posture"
Summary: Your Journey with AI-Powered Port Scanning
You’ve now completed a comprehensive journey through AI-powered port scanning, from initial installation through advanced operational techniques. This guide has equipped you with the knowledge to leverage artificial intelligence for more efficient and effective network security assessments.
The key advantages of AI-powered port scanning include simplified access to complex Nmap functionality, intelligent interpretation of scan results, natural language interaction that reduces the learning curve, and automated analysis that identifies security implications. These benefits make advanced reconnaissance techniques accessible to a broader range of security professionals whilst enhancing productivity for experienced practitioners.
Remember that successful AI-powered port scanning requires balancing automation with expertise. Use the AI to handle routine tasks and initial analysis, but apply your critical thinking and security knowledge to validate findings, understand context, and make strategic decisions. This combination of AI efficiency and human insight creates a powerful approach to modern cybersecurity.
As you implement AI-powered port scanning in your environment, start conservatively with known systems, gradually expand your usage as confidence grows, document your processes and findings, share knowledge with your team, and continuously refine your techniques based on results. Regular practice in authorised environments will develop your proficiency and help you discover new applications for this innovative technology.
The cybersecurity landscape continues evolving rapidly, with AI playing an increasingly important role in both offensive and defensive operations. By mastering AI-powered port scanning now, you’re positioning yourself at the forefront of this transformation, ready to leverage emerging technologies whilst maintaining the rigorous standards essential for professional security work.
Image Courtesy: https://www.sigmasolve.com/blog/the-future-of-ai-in-cybersecurity-emerging-technologies-and-trends/
Stay curious, keep learning, and always prioritise ethical, authorised security practices. The tools and techniques covered in this guide represent just the beginning of what’s possible when combining artificial intelligence with traditional cybersecurity methodologies. Your continued exploration and innovation will help shape the future of AI-powered security operations.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh