
日益复杂的网络威胁尤其是"living-off-the-land"(LotL)攻击正利用身份漏洞入侵关键基础设施。这些攻击利用现有工具而非恶意软件以规避检测,在OT环境中尤其危险因 legacy系统缺乏监控且常与IT共享资源。强化身份安全与统一暴露管理可帮助检测、优先处理及缓解跨IT与OT环境的风险。 2025-2-26 14:0:0 Author: www.tenable.com(查看原文) 阅读量:25 收藏
Sophisticated OT threats, like living-off-the-land (LotL) attacks, exploit identity vulnerabilities to infiltrate critical infrastructure. Find out how robust identity security and unified exposure management can help you detect, prioritize and mitigate risks across IT and OT environments.
The attack surface that today’s security leaders have to defend is growing at an unprecedented rate, and the situation is particularly challenging for organizations managing critical infrastructure: almost 70% of cyber attacks in 2023 targeted critical infrastructure, according to IBM’s “X-Force Threat Intelligence Index 2024” report. What was once a manageable task of protecting a defined network perimeter has transformed into a complex challenge of securing a vast, interconnected web of cyber-physical systems – IT, operational technology (OT), internet-of-things (IoT) devices, and more. These devices and their associated networks are under increasing pressure from sophisticated threat actors, who are leveraging advanced techniques such as living-off-the-land (LotL) attacks to infiltrate critical infrastructure networks.
LotL techniques are especially dangerous in OT networks because they usually house “insecure by design” legacy and unmanaged systems that may not support the latest patches or cannot be easily upgraded without affecting operations. Additionally, these OT networks may share resources or trusted zones with IT environments. These two elements create an ideal landscape for attackers to move laterally and undetected between IT and OT networks.
Advanced attack techniques blur the boundaries between historically separate security domains
Operational technology (OT) refers to the hardware and software systems that monitor and control physical devices, processes and events in environments such as industrial operations, building facilities, energy and water infrastructure, data centers and transportation systems. Unlike IT, which focuses on data and information, OT systems interact directly with the physical world.
LotL attacks and similar modern attack strategies exploit legitimate, trusted applications pre-installed on many devices that control OT devices, as well as credentials within a system to avoid traditional detection methods. Rather than deploying new malware, these attacks rely on exploiting tools that are already present in the breached network.
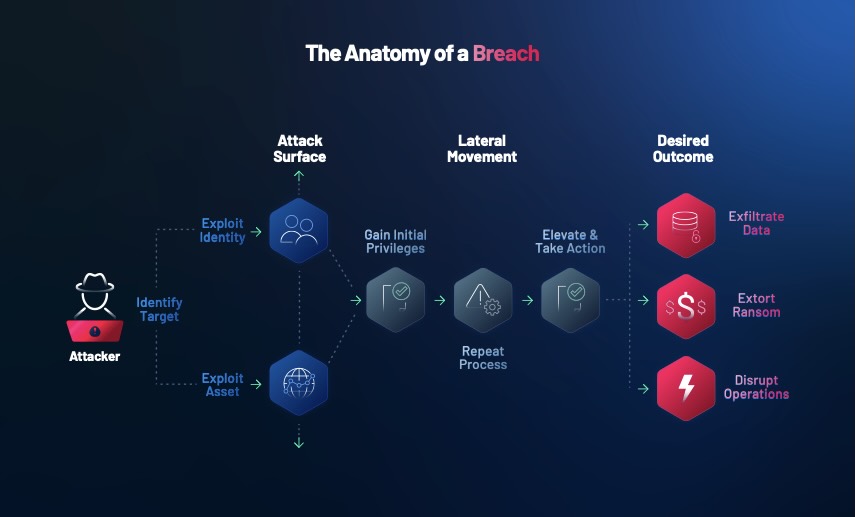
With legacy OT systems often lacking detailed logging or monitoring of user activities, attackers target over-privileged accounts to perform critical actions like modifying system configurations, disabling security controls or accessing sensitive data using legitimate permissions. This allows them to evade traditional IT-based security tools that rely on identifying malicious software and that are separate from the OT environment.
Common LotL tactics include:
- Misusing legitimate tools: Attackers leverage tools pre-loaded onto operating systems such as Certutil, Ntdsutil and XCOPY to achieve their goals while masking as regular system activity.
- Hands-on-keyboard attacks: Human attackers directly manipulate compromised systems instead of relying on automated or programmed tools to evade detection by common security tools, such as endpoint detection and response (EDR).
These techniques are particularly dangerous in OT environments, where:
- Legacy systems may lack robust logging and monitoring capabilities, and may share resources or trusted zones with IT.
- Shared or default accounts make it difficult to track user activity and identify unauthorized access.
These conditions result in an ideal landscape for attackers to move laterally across IT and OT undetected.
Case in point: The Volt Typhoon group
The state-sponsored Chinese hacking group Volt Typhoon (first identified in May 2023), exemplifies the threat posed by LotL attacks. The group targeted critical infrastructure organizations in the U.S., including in the energy, communications and maritime sectors, using legitimate tools and native Windows commands to avoid detection. By exploiting existing system tools like PowerShell and WMI and not using malware, Volt Typhoon seeks to evade traditional defenses. Its focus on credential harvesting and maintaining persistent access highlights the importance of securing identities as a cornerstone of OT security, alongside robust OT network monitoring and configuration change tracking.
Identity security: the missing ingredient for securing cyber-physical systems
Understanding what assets you have and the vulnerabilities associated with them helps ensure you are closing your exposure to stop attackers from getting a foothold in the first place. Attackers typically exploit identity and access systems—especially Microsoft’s Active Directory, a common entry point and target—to escalate privileges, maintain access and execute their strategies. Other common identity exploits that can impact OT systems include shared credentials, default passwords and lack of multi-factor authentication.
Effective OT security requires a holistic approach that prioritizes identity security. Such an approach helps you:
- Understand your assets: By identifying and assessing vulnerabilities across your OT environment, you can prevent attackers from gaining a foothold.
- Monitor for anomalies: This allows you to monitor credential usage for unusual activity, such as logins from unexpected locations or outside of normal work hours.
- Limit privilege escalation: Proactively identifying privileged accounts and enforcing least privilege policies helps you restrict access to sensitive resources, even if an account is compromised.
- Harden AD: Given attackers’ focus on AD, it’s key for you to regularly audit AD for misconfigurations and enforce strong access controls. Consider dedicated AD domains for OT environments for enhanced security.
- Identify attack paths: Using exposure management tools can help you identify potential attack paths involving compromised identities and OT assets, allowing for proactive intervention.
Closing the gap with exposure management
The role of the CISO continues to evolve in parallel with today’s expanding threat landscape. No longer limited to safeguarding traditional IT environments, security leaders find themselves increasingly responsible for securing OT environments, along with cloud infrastructures, mobile devices, IoT and smart devices, advanced AI systems and shadow IT assets. Each component introduces vulnerabilities, making comprehensive security more difficult.
Securing an organization today requires a far-reaching approach – it’s no longer sufficient to rely on basic defenses. Instead, security leaders must address a continuously shifting environment where attackers use sophisticated techniques and exploit diverse entry points.
However, siloed security tools fail to provide a comprehensive view of the entire attack surface. Such fragmented solutions for security make it difficult for security teams to collaborate across IT and OT to identify risky connections that enable attackers to gain initial access, move laterally across the network and escalate privileges.
The Tenable One Exposure Management Platform offers a unified solution to address this challenge by providing security teams with a set of critical capabilities:
- Complete attack surface visibility, which gives you insights across the modern attack surface, including OT, IoT, and IT assets
- Prioritized risk management, which lets you identify and prioritize the exposures most likely to have a significant impact on critical infrastructure
- Bridging of security silos, which brings together data across Tenable products – including Tenable OT Security and Tenable Identity Exposure – and combines it with third-party data to generate a holistic and real-time view of identities, risks, and configurations
- Attack path visualization, which identifies and closes potential attack paths that allow threat actors to traverse across converged IT and OT environments
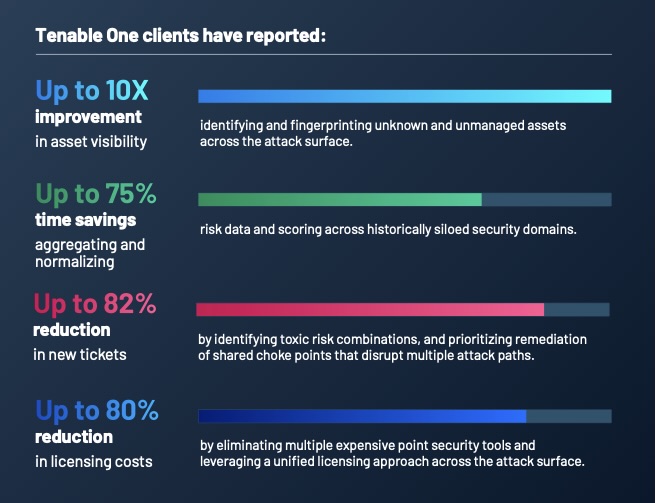
(Source: Internal Tenable survey, July 2024)
Incorporating identity security and OT security monitoring as part of any security strategy is critical—through real-time monitoring, anomaly detection, privilege controls, and AD hardening to proactively close risk exposures. By adopting a comprehensive exposure management approach, organizations can gain the visibility and context needed to effectively protect critical infrastructure from evolving threats.
To see how Tenable One helps organizations bridge the gap between securing OT and identities, check out this video, where we demonstrate how Tenable’s AI-powered capabilities help you identify likely attack paths and close risky exposures before attackers can exploit them.

For a deeper dive into how exposure management helps bolster your security posture, download the whitepaper "Hackers Don't Honor Security Silos: 5 Steps To Prioritize True Business Exposure" and read the blog post "CISA Finding: 90% of Initial Access to Critical Infrastructure Is Gained Via Identity Compromise. What Can You Do About It?"

Chris Baker
Chris Baker joined Tenable in 2021 as part of the EMEA OT security specialist team supporting customers on their OT security journey. Prior to joining Tenable, Chris worked for global cybersecurity vendor Trend Micro focusing on managing some of its largest customers in the industrial and manufacturing verticals.
如有侵权请联系:admin#unsafe.sh